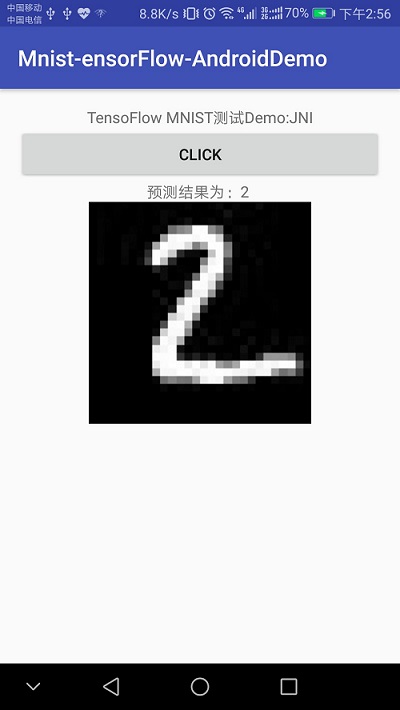
将tensorflow训练好的模型移植到Android (MNIST手写数字识别)
【尊重原创,转载请注明出处】https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/79672257
本博客将以最简单的方式,利用TensorFlow实现了MNIST手写数字识别,并将Python TensoFlow训练好的模型移植到Android手机上运行。网上也有很多移植教程,大部分是在Ubuntu(Linux)系统,一般先利用Bazel工具把TensoFlow编译成.so库文件和jar包,再进行Android配置,实现模型移植。不会使用Bazel也没关系,实质上TensoFlow已经为开发者提供了最新的.so库文件和对应的jar包了(如libtensorflow_inference.so和libandroid_tensorflow_inference_java.jar),我们只需要下载文件,并在本地Android Studio导入jar包和.so库文件,即可以在Android加载TensoFlow的模型了。
当然了,本博客的项目代码都上传到Github:https://github.com/PanJinquan/Mnist-tensorFlow-AndroidDemo
先说一下,本人的开发环境:
Windows 7
Python3.5
TensoFlow 1.6.0(2018年3月23日—当前最新版)
Android Studio 3.0.1(2018年3月23日—当前最新版)
一、利用Python训练模型
以MNIST手写数字识别为例,这里首先使用Python版的TensorFlow实现单隐含层的SoftMax Regression分类器,并将训练好的模型的网络拓扑结构和参数保存为pb文件。首先,需要定义模型的输入层和输出层节点的名字(通过形参 'name'指定,名字可以随意,后面加载模型时,都是通过该name来传递数据的):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x_input')#输入节点:x_input . . . pre_num=tf.argmax(y,1,output_type='int32',name="output")#输出节点:output
PS:说一下鄙人遇到坑:起初,我参照网上相关教程训练了一个模型,在Windows下测试没错,但把模型移植到Android后就出错了,但用别人的模型又正常运行;后来折腾了半天才发现,是类型转换出错啦!!!! TensorFlow默认类型是float32,但我们希望返回的是一个int型,因此需要指定output_type='int32';但注意了,在Windows下测试使用int64和float64都是可以的,但在Android平台上只能使用int32和float32,并且对应Java的int和float类型。
将训练好的模型保存为.pb文件,这就需要用到tf.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants函数了。
# 保存训练好的模型
#形参output_node_names用于指定输出的节点名称,output_node_names=['output']对应pre_num=tf.argmax(y,1,name="output"),
output_graph_def = graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, sess.graph_def,output_node_names=['output'])
with tf.gfile.FastGFile('model/mnist.pb', mode='wb') as f:#’wb’中w代表写文件,b代表将数据以二进制方式写入文件。
f.write(output_graph_def.SerializeToString())
关于tensorflow保存模型和加载模型的方法,请参考本人另一篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/79693741
这里给出Python训练模型完整的代码如下:
#coding=utf-8
# 单隐层SoftMax Regression分类器:训练和保存模型模块
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.framework import graph_util
print('tensortflow:{0}'.format(tf.__version__))
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("Mnist_data/", one_hot=True)
#create model
with tf.name_scope('input'):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x_input')#输入节点名:x_input
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y_input')
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
with tf.name_scope('W'):
#tf.zeros([3, 4], tf.int32) ==> [[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]]
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]),name='Weights')
with tf.name_scope('b'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]),name='biases')
with tf.name_scope('W_p_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(x, W), b, name='Wx_plus_b')
y = tf.nn.softmax(Wx_plus_b, name='final_result')
# 定义损失函数和优化方法
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y))
with tf.name_scope('train_step'):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(loss)
print(train_step)
# 初始化
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# 训练
for step in range(100):
batch_xs,batch_ys =mnist.train.next_batch(100)
train_step.run({x:batch_xs,y_:batch_ys})
# variables = tf.all_variables()
# print(len(variables))
# print(sess.run(b))
# 测试模型准确率
pre_num=tf.argmax(y,1,output_type='int32',name="output")#输出节点名:output
correct_prediction = tf.equal(pre_num,tf.argmax(y_,1,output_type='int32'))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
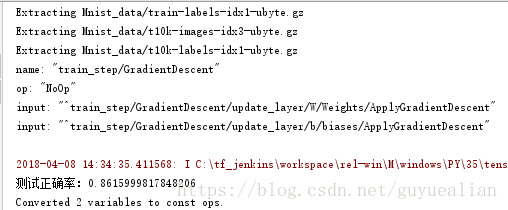
a = accuracy.eval({x:mnist.test.images,y_:mnist.test.labels})
print('测试正确率:{0}'.format(a))
# 保存训练好的模型
#形参output_node_names用于指定输出的节点名称,output_node_names=['output']对应pre_num=tf.argmax(y,1,name="output"),
output_graph_def = graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, sess.graph_def,output_node_names=['output'])
with tf.gfile.FastGFile('model/mnist.pb', mode='wb') as f:#’wb’中w代表写文件,b代表将数据以二进制方式写入文件。
f.write(output_graph_def.SerializeToString())
sess.close()
上面的代码已经将训练模型保存在model/mnist.pb,当然我们可以先在Python中使用该模型进行简单的预测,测试方法如下:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#模型路径
model_path = 'model/mnist.pb'
#测试图片
testImage = Image.open("data/test_image.jpg");
with tf.Graph().as_default():
output_graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
with open(model_path, "rb") as f:
output_graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
tf.import_graph_def(output_graph_def, name="")
with tf.Session() as sess:
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
# x_test = x_test.reshape(1, 28 * 28)
input_x = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name("input/x_input:0")
output = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name("output:0")
#对图片进行测试
testImage=testImage.convert('L')
testImage = testImage.resize((28, 28))
test_input=np.array(testImage)
test_input = test_input.reshape(1, 28 * 28)
pre_num = sess.run(output, feed_dict={input_x: test_input})#利用训练好的模型预测结果
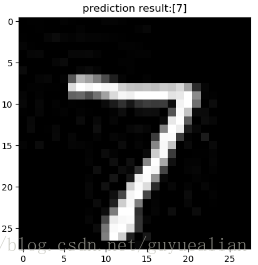
print('模型预测结果为:',pre_num)
#显示测试的图片
# testImage = test_x.reshape(28, 28)
fig = plt.figure(), plt.imshow(testImage,cmap='binary') # 显示图片
plt.title("prediction result:"+str(pre_num))
plt.show()
二、移植到Android
相信大家看到很多大神的博客,都是要自己编译TensoFlow的so库和jar包,说实在的,这个过程真TM麻烦,反正我弄了半天都没成功过,然后放弃了……。本博客的移植方法不需要安装Bazel,也不需要构建TensoFlow的so库和jar包,因为Google在TensoFlow github中给我们提供了,为什么不用了!!!
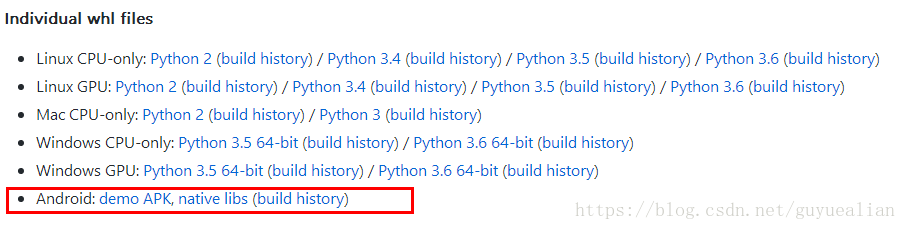
1、下载TensoFlow的jar包和so库
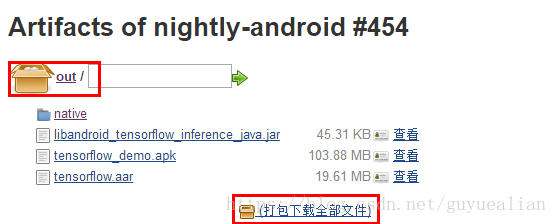
TensoFlow在Github已经存放了很多开发文件:https://github.com/PanJinquan/tensorflow
我们需要做的是,下载Android: native libs ,打包下载全部文件,其中有我们需要的libtensorflow_inference.so和libandroid_tensorflow_inference_java.jar,有了这两个文件,剩下的就是在Android Studio配置的问题了
2、Android Studio配置
(1)新建一个Android项目
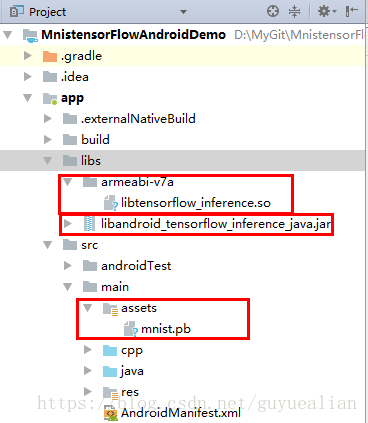
(2)把训练好的pb文件(mnist.pb)放入Android项目中app/src/main/assets下,若不存在assets目录,右键main->new->Directory,输入assets。
(3)将下载的libtensorflow_inference.so和libandroid_tensorflow_inference_java.jar如下结构放在libs文件夹下
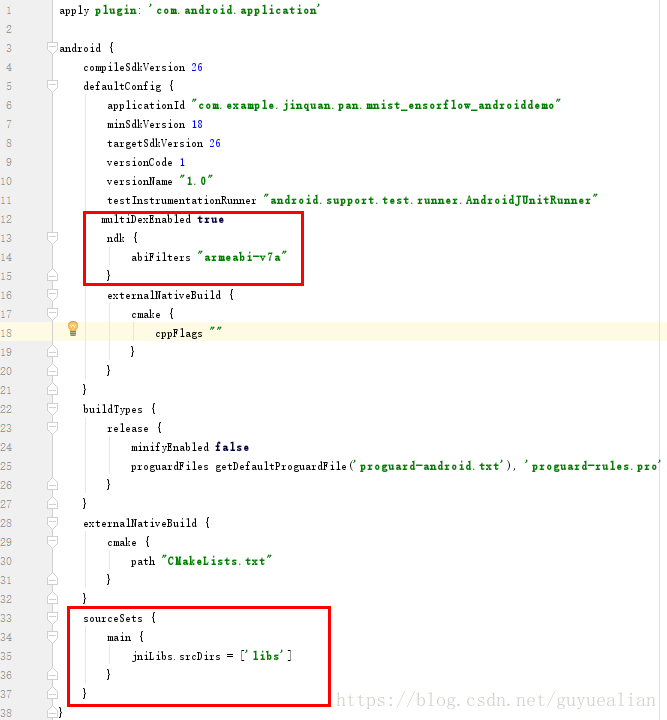
(4)app\build.gradle配置
在defaultConfig中添加
multiDexEnabled true
ndk {
abiFilters "armeabi-v7a"
}
增加sourceSets
sourceSets {
main {
jniLibs.srcDirs = ['libs']
}
}
在dependencies中增加TensoFlow编译的jar文件libandroid_tensorflow_inference_java.jar:
compile files('libs/libandroid_tensorflow_inference_java.jar')
OK了,build.gradle配置完成了,剩下的就是java编程的问题了。
3、模型调用
在需要调用TensoFlow的地方,加载so库“System.loadLibrary("tensorflow_inference");并”import org.tensorflow.contrib.android.TensorFlowInferenceInterface;就可以使用了
注意,旧版的TensoFlow,是如下方式进行,该方法可参考大神的博客:https://www.jianshu.com/p/1168384edc1e
TensorFlowInferenceInterface.fillNodeFloat(); //送入输入数据 TensorFlowInferenceInterface.runInference(); //进行模型的推理 TensorFlowInferenceInterface.readNodeFloat(); //获取输出数据
但在最新的libandroid_tensorflow_inference_java.jar中,已经没有这些方法了,换为
TensorFlowInferenceInterface.feed() TensorFlowInferenceInterface.run() TensorFlowInferenceInterface.fetch()
下面是以MNIST手写数字识别为例,其实现方法如下:
package com.example.jinquan.pan.mnist_ensorflow_androiddemo;
import android.content.res.AssetManager;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.util.Log;
import org.tensorflow.contrib.android.TensorFlowInferenceInterface;
public class PredictionTF {
private static final String TAG = "PredictionTF";
//设置模型输入/输出节点的数据维度
private static final int IN_COL = 1;
private static final int IN_ROW = 28*28;
private static final int OUT_COL = 1;
private static final int OUT_ROW = 1;
//模型中输入变量的名称
private static final String inputName = "input/x_input";
//模型中输出变量的名称
private static final String outputName = "output";
TensorFlowInferenceInterface inferenceInterface;
static {
//加载libtensorflow_inference.so库文件
System.loadLibrary("tensorflow_inference");
Log.e(TAG,"libtensorflow_inference.so库加载成功");
}
PredictionTF(AssetManager assetManager, String modePath) {
//初始化TensorFlowInferenceInterface对象
inferenceInterface = new TensorFlowInferenceInterface(assetManager,modePath);
Log.e(TAG,"TensoFlow模型文件加载成功");
}
/**
* 利用训练好的TensoFlow模型预测结果
* @param bitmap 输入被测试的bitmap图
* @return 返回预测结果,int数组
*/
public int[] getPredict(Bitmap bitmap) {
float[] inputdata = bitmapToFloatArray(bitmap,28, 28);//需要将图片缩放带28*28
//将数据feed给tensorflow的输入节点
inferenceInterface.feed(inputName, inputdata, IN_COL, IN_ROW);
//运行tensorflow
String[] outputNames = new String[] {outputName};
inferenceInterface.run(outputNames);
///获取输出节点的输出信息
int[] outputs = new int[OUT_COL*OUT_ROW]; //用于存储模型的输出数据
inferenceInterface.fetch(outputName, outputs);
return outputs;
}
/**
* 将bitmap转为(按行优先)一个float数组,并且每个像素点都归一化到0~1之间。
* @param bitmap 输入被测试的bitmap图片
* @param rx 将图片缩放到指定的大小(列)->28
* @param ry 将图片缩放到指定的大小(行)->28
* @return 返回归一化后的一维float数组 ->28*28
*/
public static float[] bitmapToFloatArray(Bitmap bitmap, int rx, int ry){
int height = bitmap.getHeight();
int width = bitmap.getWidth();
// 计算缩放比例
float scaleWidth = ((float) rx) / width;
float scaleHeight = ((float) ry) / height;
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.postScale(scaleWidth, scaleHeight);
bitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(bitmap, 0, 0, width, height, matrix, true);
Log.i(TAG,"bitmap width:"+bitmap.getWidth()+",height:"+bitmap.getHeight());
Log.i(TAG,"bitmap.getConfig():"+bitmap.getConfig());
height = bitmap.getHeight();
width = bitmap.getWidth();
float[] result = new float[height*width];
int k = 0;
//行优先
for(int j = 0;j < height;j++){
for (int i = 0;i < width;i++){
int argb = bitmap.getPixel(i,j);
int r = Color.red(argb);
int g = Color.green(argb);
int b = Color.blue(argb);
int a = Color.alpha(argb);
//由于是灰度图,所以r,g,b分量是相等的。
assert(r==g && g==b);
// Log.i(TAG,i+","+j+" : argb = "+argb+", a="+a+", r="+r+", g="+g+", b="+b);
result[k++] = r / 255.0f;
}
}
return result;
}
}
简单说明一下:项目新建了一个PredictionTF类,该类会先加载libtensorflow_inference.so库文件;PredictionTF(AssetManager assetManager, String modePath) 构造方法需要传入AssetManager对象和pb文件的路径;
从资源文件中获取BitMap图片,并传入 getPredict(Bitmap bitmap)方法,该方法首先将BitMap图像缩放到28*28的大小,由于原图是灰度图,我们需要获取灰度图的像素值,并将28*28的像素转存为行向量的一个float数组,并且每个像素点都归一化到0~1之间,这个就是bitmapToFloatArray(Bitmap bitmap, int rx, int ry)方法的作用;
然后将数据feed给tensorflow的输入节点,并运行(run)tensorflow,最后获取(fetch)输出节点的输出信息。
MainActivity很简单,一个单击事件获取预测结果:
package com.example.jinquan.pan.mnist_ensorflow_androiddemo;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
// Used to load the 'native-lib' library on application startup.
static {
System.loadLibrary("native-lib");//可以去掉
}
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
private static final String MODEL_FILE = "file:///android_asset/mnist.pb"; //模型存放路径
TextView txt;
TextView tv;
ImageView imageView;
Bitmap bitmap;
PredictionTF preTF;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// Example of a call to a native method
tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text);
txt=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_id);
imageView =(ImageView)findViewById(R.id.imageView1);
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.test_image);
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
preTF =new PredictionTF(getAssets(),MODEL_FILE);//输入模型存放路径,并加载TensoFlow模型
}
public void click01(View v){
String res="预测结果为:";
int[] result= preTF.getPredict(bitmap);
for (int i=0;i<result.length;i++){
Log.i(TAG, res+result[i] );
res=res+String.valueOf(result[i])+" ";
}
txt.setText(res);
tv.setText(stringFromJNI());
}
/**
* A native method that is implemented by the 'native-lib' native library,
* which is packaged with this application.
*/
public native String stringFromJNI();//可以去掉
}
activity_main布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingBottom="16dp"
android:paddingLeft="16dp"
android:paddingRight="16dp"
android:paddingTop="16dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/sample_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian"
android:layout_gravity="center"/>
<Button
android:onClick="click01"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="click" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="结果为:"/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"/>
</LinearLayout>