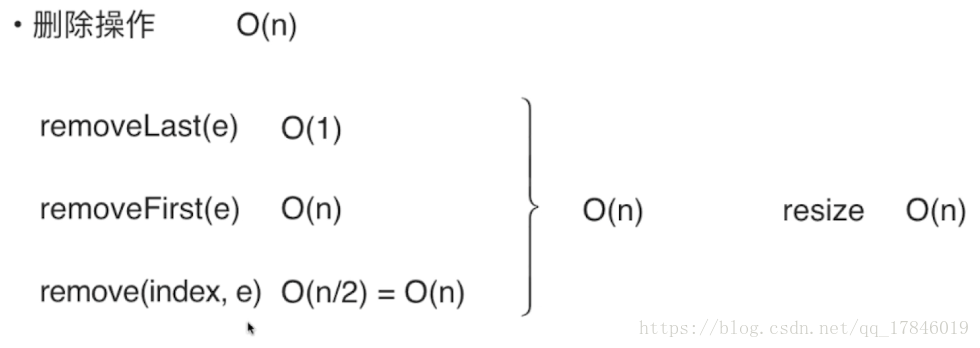内容大纲:
- 使用Java中的数组
- 二次封装属于我们自己的数组
- 向数组中添加元素
- 数组中查询元素和修改元素
- 包含,搜索,删除功能
- 使用泛型
- 动态数组
- 简单的时间复杂度分析
- 均摊复杂度和防止复杂度振荡
一、java中的数组
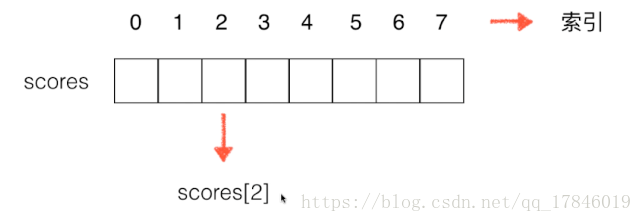
- 把数据码成一排进行存放
java中一个简单的数组使用
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[10];
for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i ++)
arr[i] = i;
int[] scores = new int[]{100, 99, 66};
for(int i = 0 ; i < scores.length ; i ++)
System.out.println(scores[i]);
for(int score: scores)
System.out.println(score);
scores[0] = 96;
for(int i = 0 ; i < scores.length ; i ++)
System.out.println(scores[i]);
}
}二、二次封装属于我们自己的数组
- 数组的最大优点:快搜查询,score[2];
- 数组最好应用于"索引有语意"的情况
- 但并非所有有语意的索引都适合用于数组 例如身份证号码
1、制作属于我们自己的数组类
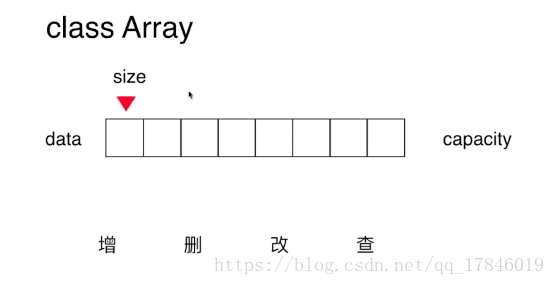
public class Array {
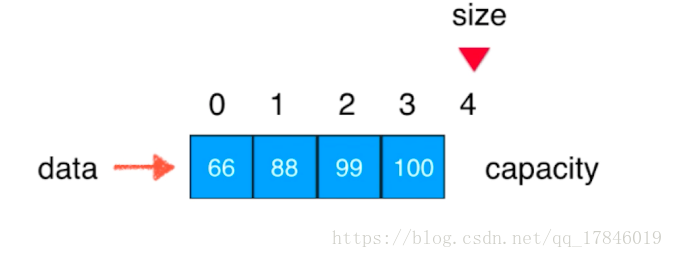
private int[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = new int[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
}
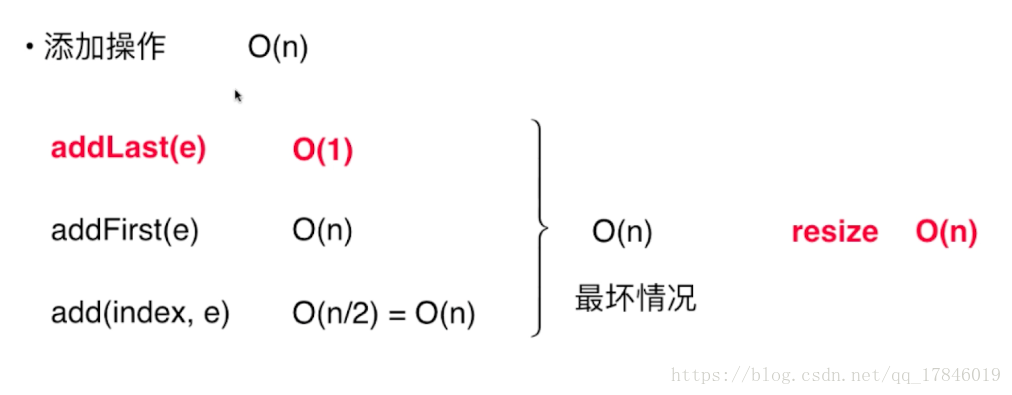
三、向数组中添加元素
在数组末尾添加元素
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(int e){
if(size == data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("AddLast failed. Array is full.");
data[size] = e;
size ++;
add(size, e);
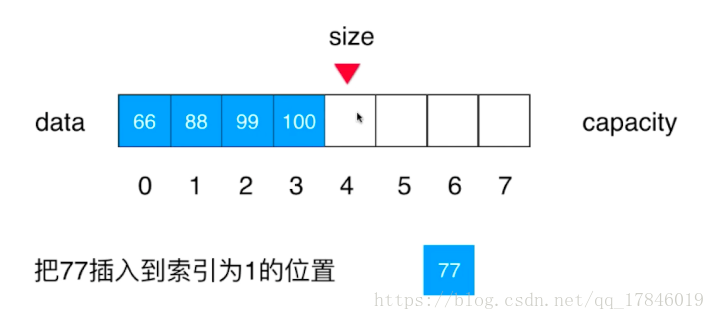
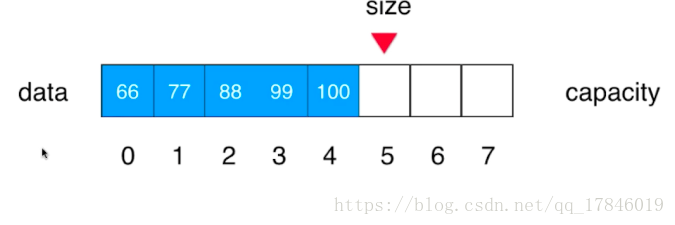
}在指定位置添加元素
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, int e){
if(size == data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Array is full.");
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}在数组头部添加一个元素和在数组末尾添加一个元素都可以改为
// 在所有元素末尾添加一个新元素
public void addLast(int e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(int e){
add(0, e);
}四、数组中查询元素和修改元素
重写父类toString()方法:返回此时数组的元素个数size和容量capacity
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res=new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size=%d, capacity=%d\n",size,data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i!=size-1)//如果没到末尾
res.append(",");//拼接一个","
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}查询数组中某个位置的元素
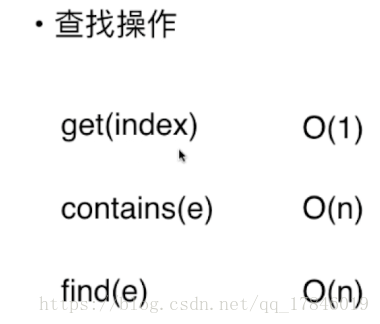
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public int get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}修改数组某个位置的元素
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, int e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
五、包含,搜索,删除功能
数组中是否包含有此元素
//查找是否有元素e
public boolean contain(int e){
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
if(data[i]==e)
return true;
}
return false;
}搜索数组中此元素 并返回此元素所在的位置
//找到某一个元素并得到他的位置index
public int find(int e){
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
if(data[i]==e)
return i;
}
return -1;
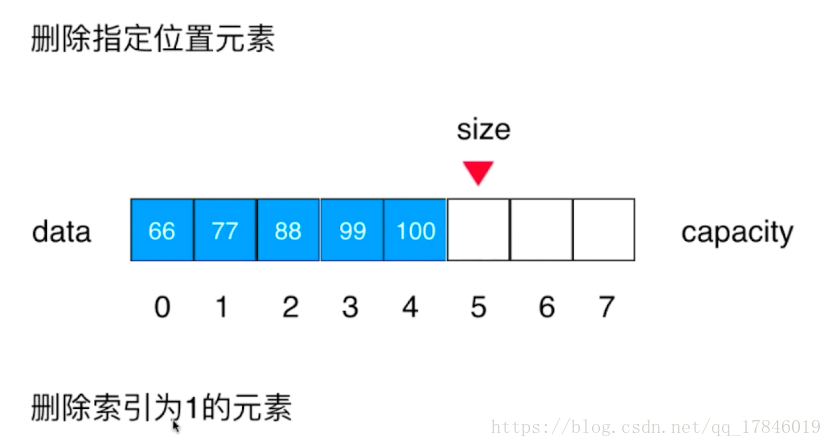
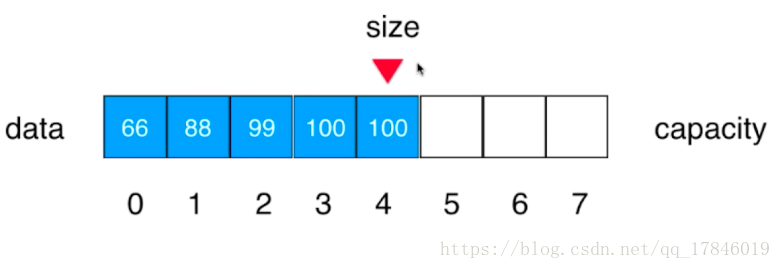
}删除指定位置的元素
数组向左移后,size也相对向左移一位到100,100不影响之后的操作
//从数组删除index位置的元素,并返回该元素
public int remove(int index){
if(index<0||index>size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove is Fail,Index Is Illegal");
for(int i=index+1;i<size;i++)
data[i-1]=data[i];
size--;//向左移
return data[index];
}删除第一个元素和最后一个元素
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public int removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public int removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
从数组删除某个元素
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(int e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}在Main中对自定义数组进行操作
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array arr = new Array(20);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){//给数组添加数据
arr.addLast(i);
}
System.out.println(arr);
//在位置1里添加数据100
arr.add(1,100);
System.out.println(arr);
//在数组第一个位置里添加数据100
arr.addFirst(99);
System.out.println(arr);
//数组是否有某一个元素
System.out.println(arr.contain(2));
//查找某个元素,返回它的index
System.out.println(arr.find(2));
//删除某一个元素,返回该元素
System.out.println(arr.remove(2));
}
}
Array: size=10, capacity=20
[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
Array: size=11, capacity=20
[0,100,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
Array: size=12, capacity=20
[99,0,100,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
true
4
1六、使用泛型
- 让我们的数据类型可以放置"任何"数据类型
- 不可是8种基本数据类型,只能是类对象
- 每个基本数据类型都有相应的包装类
public class Array {
private int[] data;
private int size;
//构建一个带参构造,给data数组开辟空间为Capacity
public Array(int Capacity) {
data = new int[Capacity];
size = 0;
}
修改相应代码 ,将int换成E,不指定它是哪种数据类型
//Array存放的数据类型是E
public class Array<E>{
private E[] data;
....
public Array(int capacity){
data=(E)new Object[capacity];
...
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
...}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
...
} Array<Integer> arr = new Array<>(20);将之前的代码转成泛型的例子
Array.java
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(size == data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Array is full.");
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
}
Student类来做数组的数据对象
public class Student {
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(String studentName, int studentScore){
name = studentName;
score = studentScore;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return String.format("Student(name: %s, score: %d)", name, score);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array<Student> arr = new Array<>();
arr.addLast(new Student("Alice", 100));
arr.addLast(new Student("Bob", 66));
arr.addLast(new Student("Charlie", 88));
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
结果:
Array: size=3, capacity=10
[Student(name:Alice, score:100),Student(name:Bob score:66),Student(name:Charlie, score:88)]七、动态数组
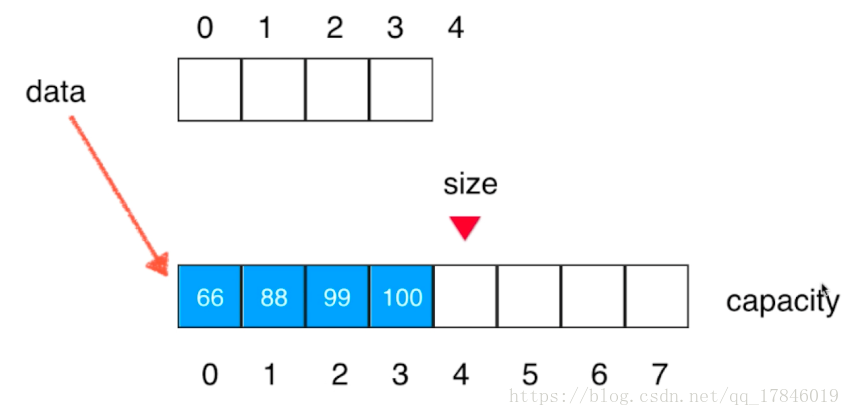
原来的数组达到最大的长度,要再末尾添加元素
新开辟一个newData是原来数组length的两倍
将原来的数组转移到新数组(循环遍历一遍)
data指向新的数组
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
//如果size达到数组的长度
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}remove也有进行缩容
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
//当数组个数是数组长度的一半时进行缩容
if(size == data.length / 2)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}resize方法动态开辟新数组
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}八、简单的复杂度分析
- O(1),O(n),O(lgN),O(nLogn),O(n)
- 大O描述的是算法的运行时间和输入数据之间的关系
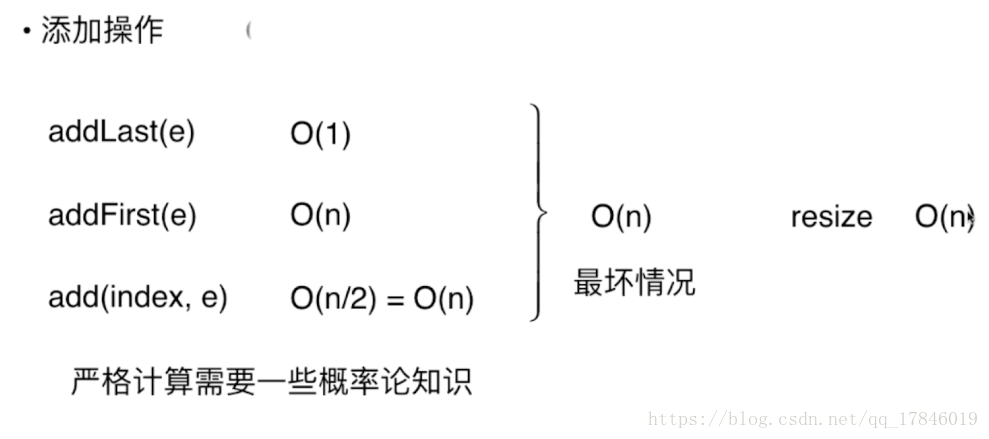
九、均摊复杂度和防止复杂度振荡
resize的复杂度分析
不可能每次添加元素都会触发resize();
9次添加操作+8次转移操作=17次操作

addLast的均摊复杂度是O(1);
同理,我们看removeLast操作,均摊复杂度也是O(1);
复杂度振荡
当我们同时看到addLast和removeLast操作,每次都调用resize();
就是在元素满在添加一个,就要扩容,然后再减少一个就要减容(resize)
以此看来原本O(1)的复杂度,却猛的变成O(n)
出现问题的原因:removeLast时resize过于着急(Eager)
解决方案:Lazy
原本size==capacity/2时就要缩容,现在改成
新的策略:原本size==capacity/4才进行缩容一半,确定他之后不会增太多数量
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
//实现lazy处理,到1/4才缩容,并且数组的长度为1时不能再减半
if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}(转自发条鱼)