JDK 1.8中的HashTable是底层实现由“数组+链表”实现,相对于hashMap来说简单很多,而且他们两个最大的区别是
hashTable是线程安全的,hashMap不是
本文就HashTable中的几个常用的重要方法展开学习讨论。hashtable的数据结构是table数组,数组里面是链表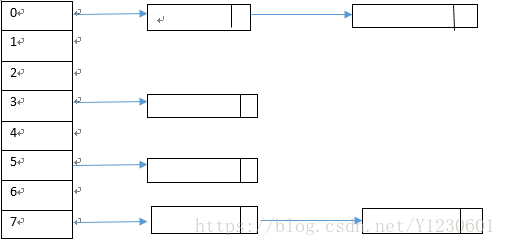
/**
* The hash table data.
*
* 数据保存数组 和hashMap中的tab同理
*/
private transient Entry<?,?>[] table;
/**
* The total number of entries in the hash table.
*
* 总条数 和hashMap中的size同理
*/
private transient int count;
/**
* The table is rehashed when its size exceeds this threshold. (The
* value of this field is (int)(capacity * loadFactor).)
*
* @serial
*
* 就是table扩容的门槛 当count 大于等于threshold时 table数组进行扩容操作
* threshold = 当前table.length * loadFactor (loadFactor默认为0.75)
*/
private int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hashtable.
*
* 扩容门槛相对于 数组的比例计算公式 table.length * loadFactor = threshold
* @serial
*/
private float loadFactor;构造方法
hashtable没有size规定默认为11,在hashMap中默认为16,并且hashMap必须是大于16的2的次方(特殊指定除外,但是hashMap自动会计算得出大于指定值得2的次方)
/**
* Constructs a new, empty hashtable with the specified initial
* capacity and the specified load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hashtable.
* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hashtable.
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less
* than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive.
*/
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);
if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity];
threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty hashtable with the specified initial capacity
* and default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hashtable.
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less
* than zero.
*/
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0.75f);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty hashtable with a default initial capacity (11)
* and load factor (0.75).
*
*
*
* 这里默认 table的大小为11 但是hashMap默认16 loadFactor默认0.75
*
*/
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);
}扩容 rehash()方法
他也是和hashmap差不多 就是直接扩容两倍,但是hashTable中会在加1,并且扩容后要重新计算每个元素对应的数组位子,相对于hashMap来说性能会有点差距,hashMap少一步取余的计算,他们在插入数据时都是放在链表的头位子上。
/**
* Increases the capacity of and internally reorganizes this
* hashtable, in order to accommodate and access its entries more
* efficiently. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in the hashtable exceeds this hashtable's capacity
* and load factor.
*
* 扩容操作
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table;
// todo hashMap中的length 都市2的次方倍数并且扩容都是 * 2的 但是hashTable 实在原来的基础上* 2 还要加1
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity];
modCount++;
// 这里计算 下次扩容的门槛数量
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap;
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i]; old != null ; ) {
Entry<K,V> e = old;
old = old.next;
// 这里是重新计算hash 但是hashMap中优化的比较好,不需要重新计算, 根据二进制来 判断hash和老长度 与运算 是否大于0 大于则在 老长度加上再老数组中的下标 就是新下标 小于则下标不变
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
// 这里相同hashMap和 hashTable都是放在第一个
e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
}实际新增addEntry() 方法
这里面就是实际的插入过程,但是这里面判断了是否需要扩容,没有判断是否已经包含,是否包含都是在调用这个方法前判断的。
/**
* 这里没有判断 原来的table中是否已经包含这个key 在外面判断的 这里直接加上去
*
* @param hash
* @param key
* @param value
* @param index
*/
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
// 判断是不是要扩容
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
//蒋元素插入到对应的链表第一个位子上 直接加 不需要判断是否存在 调用的地方判断
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}put 方法
方法前加了synchronized。所有对外提供的方法上基本独有这个关键字。hashTable中value不能为空,HashMap中是可以的。而且如果key已经存在就直接覆盖老的value
/**
* Maps the specified <code>key</code> to the specified
* <code>value</code> in this hashtable. Neither the key nor the
* value can be <code>null</code>. <p>
*
* The value can be retrieved by calling the <code>get</code> method
* with a key that is equal to the original key.
*
* @param key the hashtable key
* @param value the value
* @return the previous value of the specified key in this hashtable,
* or <code>null</code> if it did not have one
* @exception NullPointerException if the key or value is
* <code>null</code>
* @see Object#equals(Object)
* @see #get(Object)
*/
// todo 这类加锁保证线程安全 这里就是实例锁,性能相对于concurrentHashMap的分段锁来说 比较慢
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
// todo 这里说明hashTable中的value不能为空
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// 查找key对应的数组下标 以便获取所在的链表
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
//这里判断是否存在当前key
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
// 这里也不太一样 hashMap中可以设置判断value是否相等类判断是否覆盖老value
// hashMap中相当于 就有一个cas的原理可供选择
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}5.
get() 方法
这个方法没什么说的 比较简单,就是根据key计算数组下标,在遍历链表查找是否相同的key
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key.equals(k))},
* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* @param key the key whose associated value is to be returned
* @return the value to which the specified key is mapped, or
* {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*
*
* 这里也没什么好说的
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index]; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
}remove() 方法
根据key计算数组下标,在遍历链表并记录当前元素的上一个元素,查找是否相同的key,将上一个元素的next节点=当前元素的下一个节点(将当前元素的next节点赋值给上一个节点的next节点)
/**
* Removes the key (and its corresponding value) from this
* hashtable. This method does nothing if the key is not in the hashtable.
*
* @param key the key that needs to be removed
* @return the value to which the key had been mapped in this hashtable,
* or <code>null</code> if the key did not have a mapping
* @throws NullPointerException if the key is <code>null</code>
*
*
* 删除 置顶key的元素 源码相对hashMap简单很多
*/
public synchronized V remove(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(Entry<K,V> prev = null; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count--;
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = null;
return oldValue;
}
}
return null;
}HashMap允许key和value为null,Hashtable不允许。
HashMap的默认初始容量为16,Hashtable为11。
HashMap的扩容为原来的2倍,Hashtable的扩容为原来的2倍加1。
HashMap是非线程安全的,Hashtable是线程安全的。
参考
HashTable源码(JDK 1.8)