版权声明:转载本博客原创文章,请标明出处并附上链接。 https://blog.csdn.net/fourierFeng/article/details/46753651
【此系列文章基于熔融沉积( fused depostion modeling, FDM )成形工艺】
这一篇文章我讲一下多边打印的问题,多边打印是切片引擎的一项关键的技术。
图1 双边打印
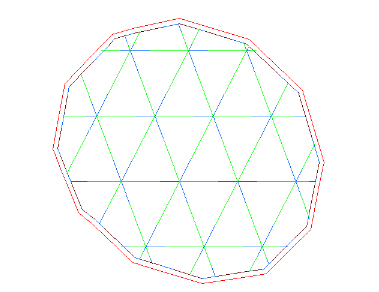
首先,它可以保证打印实体表面免受内部填充的冲击,保证外观的真实度;其次,在上层在相对于下层倾斜较大时,多边打印可以很好的起到支撑的作用,避免上层塌陷。
但是,目前来说,我的多边打印还不够普适,对一些不规范的模型,以及模型中非常尖锐的特征效果并不好,对绝大部分的较为平滑的模型是完全没有问题的。
下面就简单说一下它的原理:假设边界中的任意相邻的向量AB和BC,这里要找的是点d(角ABC中心线上的一点),看下图:
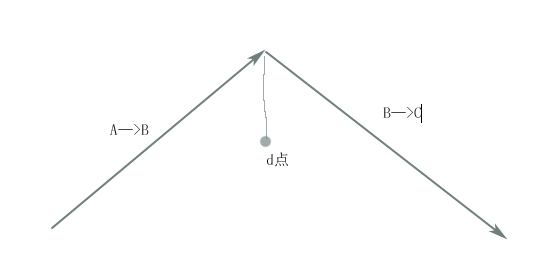
找出边界环中每一个相邻向量的d点,工作就基本完成了。所以原理非常简单,只不过是很多琐碎的细节需要处理好,比如说向量Bd的方向问题,B点和d点的欧氏距离等等,不能再说了,再说就有误导人之嫌,其实这段时间细想,我的切片引擎的这些想法并无优秀可言,可是还是想把那段时间的工作记录下来,仅此而已,闲话说几句,这段时间在做与测绘相关的算法,本来认为可以写成博文与大家分享的东西,结果硬是变成了核心期刊上的论文了,哎,只是觉得那个东西离论文水平的创新还有不小的距离啊,看来,国内的论文质量……,呵呵。下面呈上代码,其中getInnerBoundary函数有些不够规范,用了goto跳转,而且一些细节也不是最科学,当初主要是赶进度,为了适应公司的建模能力不足。
void getAngularBisector(float3 &bisector,float3 point,float3 leftPoint,float3 rightPoint)
{
float3 v1,v2;
float norm1,norm2,angle;
get_vector_diff(v1,leftPoint,point);
get_vector_diff(v2,rightPoint,point);
if(v1[0]*v2[1]==v1[1]*v2[0])
{
if(v1[1]==v2[1])
{
bisector[0]=0;
bisector[1]=1;
bisector[2]=0;
}
else if(v1[0]==v2[0])
{
bisector[0]=1;
bisector[1]=0;
bisector[2]=0;
}
else
{
bisector[0]=point[0]-1;
bisector[1]=((v1[0]-v2[0])+(v1[1]-v2[1])*point[1])/(v1[1]-v2[1]);
bisector[2]=0;
}
}
else
{
getNormalizeVector(v1);
getNormalizeVector(v2);
if(v1[0]*v2[1]==v1[1]*v2[0])
{
if(v1[1]==v2[1])
{
bisector[0]=0;
bisector[1]=1;
bisector[2]=0;
}
else if(v1[0]==v2[0])
{
bisector[0]=1;
bisector[1]=0;
bisector[2]=0;
}
else
{
bisector[0]=point[0]-1;
bisector[1]=((v1[0]-v2[0])+(v1[1]-v2[1])*point[1])/(v1[1]-v2[1]);
bisector[2]=0;
}
}
else
{
get_vector_sum(bisector,v1,v2);
}
}
}
void getInnerPoint(float3 &innerPoint,float3 point,float3 leftPoint,float3 rightPoint,float margin)
{
float3 bisector;
float distance,rate;
distance=margin;
getAngularBisector(bisector,point,leftPoint,rightPoint);
rate=distance/sqrt(pow(bisector[0],2)+pow(bisector[1],2)+pow(bisector[2],2));
innerPoint[0]=point[0]+bisector[0]*rate;
innerPoint[1]=point[1]+bisector[1]*rate;
innerPoint[2]=point[2]+bisector[2]*rate;
if(get_vector3_det(point,rightPoint,innerPoint)<0)
{
innerPoint[0]=point[0]-bisector[0]*rate;
innerPoint[1]=point[1]-bisector[1]*rate;
innerPoint[2]=point[2]-bisector[2]*rate;
}
}
void getInnerPoint(Phasor *innerPhasor,Phasor *phasor,Phasor*leftPhasor,Phasor *rightPhasor,float margin,int fillMaterial)
{
getInnerPoint(innerPhasor->beginPoint,phasor->beginPoint,leftPhasor->beginPoint,phasor->endPoint,margin);
getInnerPoint(innerPhasor->endPoint,phasor->endPoint,phasor->beginPoint,rightPhasor->endPoint,margin);
innerPhasor->material=fillMaterial;
}
void getInnerBoundary(Phasor *&innerPhasors,Phasor *phasors,int phasor_num,vector<vector<int> > &closedSet
,float lineHeight,int fillMaterial,bool *innerBoundaryStatus)
{
innerPhasors=new Phasor[phasor_num];
int index,indexMain,phasorIndex,phasorIndexLeft,phasorIndexRight;
float margin=lineHeight;
againScan:
if(margin<0.1)
{
*innerBoundaryStatus=false;
innerPhasors=NULL;
return;
}
for(indexMain=0;indexMain!=closedSet.size();++indexMain)
{
int count=0;
for(index=0;index!=closedSet[indexMain].size();++index)
{
phasorIndex=closedSet[indexMain][index];
if(index>0)
{
phasorIndexLeft=closedSet[indexMain][index-1];
}
else
{
phasorIndexLeft=closedSet[indexMain][closedSet[indexMain].size()-1];
}
phasorIndexRight=closedSet[indexMain][(index+1)%closedSet[indexMain].size()];
getInnerPoint(innerPhasors+phasorIndex
,phasors+phasorIndex
,phasors+phasorIndexLeft
,phasors+phasorIndexRight
,margin,fillMaterial);
for(int i=0;i!=phasor_num;++i)
{
if(i==phasorIndex)
{
continue;
}
if(get_vector_distance2(innerPhasors[phasorIndex].beginPoint,phasors[phasorIndex].beginPoint)>
get_vector_distance2(innerPhasors[phasorIndex].beginPoint,phasors[i].beginPoint))
{
count++;
break;
}
}
if(count>closedSet[indexMain].size()/5+1)
{
margin-=0.05;
goto againScan;
}
}
}
}