一、Maze.h
#ifndef __Maze_h__
#define __Maze_h__
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#define N 6
#define Initsize 5 //初始存储空间
#define Increment 2 //每次增量
typedef struct Pos
{
int row;
int col;
}Pos;
typedef Pos DataType;
typedef struct Maze
{
int maze[N][N];
Pos entry;
}Maze;
typedef struct Stack
{
DataType* _array;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack *s);
void CheckCapacity(Stack* s);
void StackPush(Stack* s, DataType x);
void StackPop(Stack* s);
DataType StackTop(Stack* s);
size_t StackSize(Stack* s);
void StackDestroy(Stack* s);
void MazeInit(Maze* m);
void MazePrint(Maze* m);
int MazeCheckIsAccess(Pos pos);
void MazeGetPath(Maze* m, Pos entry, Stack *path);
void MazeGetShortPath(Maze* m, Pos entry, Stack *path, Stack *shortpath, int flag);
#endif __Maze_h__
二、Maze.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Maze.h"
void StackInit(Stack* s)
{
assert(s);
s->_size = 0;
s->_capacity = Initsize;
s->_array = (DataType*)malloc(Initsize*sizeof(DataType));
assert(s->_array);
memset(s->_array, 0, s->_capacity * sizeof(DataType));
}
void CheckCapacity(Stack* s)
{
assert(s);
if (s->_size >= s->_capacity)
{
DataType* ptr = (DataType*)realloc(s->_array, (s->_capacity + Increment)*sizeof(DataType));
assert(ptr);
s->_array = ptr;
s->_capacity += Increment;
}
}
void StackPush(Stack* s, DataType x)
{
assert(s);
CheckCapacity(s);
s->_array[s->_size] = x;
s->_size++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* s)
{
assert(s);
if (s->_size == 0)
{
return;
}
else
{
s->_size--;
}
}
DataType StackTop(Stack* s)
{
assert(s&&s->_size > 0);
return s->_array[(s->_size) - 1];
}
size_t StackSize(Stack* s)
{
assert(s);
return s->_size;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* s)
{
free(s->_array);
s->_size = 0;
s->_capacity = 0;
}
void MazeInit(Maze* m)
{
assert(m);
int a[N][N] =
{
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
};
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
m->maze[i][j] = a[i][j];
}
}
m->entry.row = 5;
m->entry.col = 2;
}
void MazePrint(Maze* m)
{
assert(m);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
printf("%d ", m->maze[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
int MazeCheckIsAccess(Pos pos)
{
if (pos.col == N - 1)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void MarkPath(Maze** pm, Pos entry)
{
(*pm)->maze[entry.row][entry.col] = 2;
}
void MazeGetPath(Maze* m, Pos entry, Stack *path)
{
assert(m);
if (entry.row < 0 || entry.row >= N || entry.col < 0 || entry.col >= N)
{
return;
}
if (m->maze[entry.row][entry.col] == 1)
{
StackPush(path, entry);
MarkPath(&m, entry);
}
else
{
return;
}
if (MazeCheckIsAccess(entry))
{
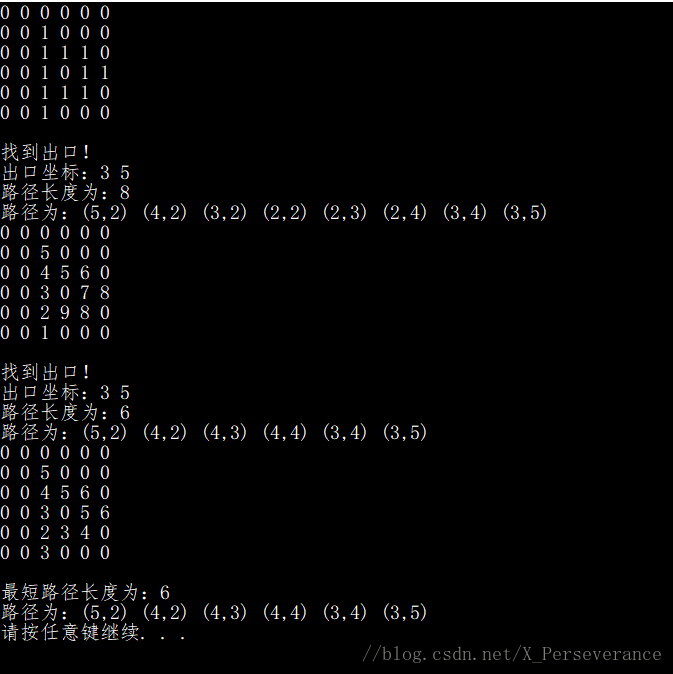
printf("找到出口!\n");
printf("出口坐标:%d %d\n", StackTop(path).row, StackTop(path).col);
printf("路径长度为:%d\n", StackSize(path));
printf("路径为:");
for (int i = 0; i < (int)path->_size; i++)
{
printf("(%d,%d) ", path->_array[i].row, path->_array[i].col);
}
printf("\n");
StackPop(path);
MazePrint(m);
return;
}
Pos up_pos = entry;
up_pos.row--;
MazeGetPath(m, up_pos, path);
Pos down_pos = entry;
down_pos.row++;
MazeGetPath(m, down_pos, path);
Pos left_pos = entry;
left_pos.col--;
MazeGetPath(m, left_pos, path);
Pos right_pos = entry;
right_pos.col++;
MazeGetPath(m, right_pos, path);
StackPop(path);
return;
}
void StackCopy(Stack *src, Stack *dst)
{
assert(src&&dst);
if (src->_size == 0)
{
dst->_size = 0;
}
else
{
if (dst->_capacity < src->_size)
{
DataType *ptr = (DataType *)realloc(dst->_array, src->_size*sizeof(DataType));
assert(ptr);
dst->_array = ptr;
dst->_capacity = src->_size;
}
dst->_size = src->_size;
memcpy(dst->_array, src->_array, sizeof(DataType)*src->_size);
}
}
void MarkPath1(Maze** pm, Pos entry, int flag)
{
(*pm)->maze[entry.row][entry.col] = flag;
}
void MazeGetShortPath(Maze* m, Pos entry, Stack *path, Stack *shortpath, int flag)
{
assert(m);
if (entry.row < 0 || entry.row >= N || entry.col < 0 || entry.col >= N)
{
return;
}
if (m->maze[entry.row][entry.col] == 1 || m->maze[entry.row][entry.col]>flag)
{
StackPush(path, entry);
MarkPath1(&m, entry, flag++);
}
else
{
return;
}
if (MazeCheckIsAccess(entry))
{
printf("找到出口!\n");
printf("出口坐标:%d %d\n", StackTop(path).row, StackTop(path).col);
printf("路径长度为:%d\n", StackSize(path));
printf("路径为:");
for (int i = 0; i < (int)path->_size; i++)
{
printf("(%d,%d) ", path->_array[i].row, path->_array[i].col);
}
printf("\n");
if (StackSize(shortpath) == 0 || StackSize(path) < StackSize(shortpath))
{
StackCopy(path, shortpath);
}
StackPop(path);
MazePrint(m);
return;
}
Pos up_pos = entry;
up_pos.row--;
MazeGetShortPath(m, up_pos, path, shortpath, flag);
Pos down_pos = entry;
down_pos.row++;
MazeGetShortPath(m, down_pos, path, shortpath, flag);
Pos left_pos = entry;
left_pos.col--;
MazeGetShortPath(m, left_pos, path, shortpath, flag);
Pos right_pos = entry;
right_pos.col++;
MazeGetShortPath(m, right_pos, path, shortpath, flag);
StackPop(path);
return;
}
三、Test.c
int main()
{
Maze m;
MazeInit(&m);
MazePrint(&m);
Stack path;
Stack shortpath;
StackInit(&path);
StackInit(&shortpath);
MazeGetShortPath(&m, m.entry, &path, &shortpath, 1);
printf("最短路径长度为:%d\n", StackSize(&shortpath));
printf("路径为:");
for (int i = 0; i < (int)shortpath._size; i++)
{
printf("(%d,%d) ", shortpath._array[i].row, shortpath._array[i].col);
}
printf("\n");
StackDestroy(&path);
StackDestroy(&shortpath);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
执行结果: