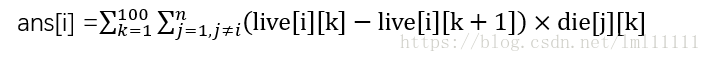http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5985
Lucky Coins
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1110 Accepted Submission(s): 416
Problem Description
Bob has collected a lot of coins in different kinds. He wants to know which kind of coins is lucky. He finds out a lucky kind of coins by the following way. He tosses all the coins simultaneously, and then removes the coins that come up tails. He then tosses all the remaining coins and removes the coins that come up tails. He repeats the previous step until there is one kind of coins remaining or there are no coins remaining. If there is one kind of coins remaining, then this kind of coins is lucky. Given the number of coins and the probability that the coins come up heads after tossing for each kind, your task is to calculate the probability for each kind of coins that will be lucky.
Input
The first line is the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains an integer k representing the number of kinds. Each of the following k lines describes a kind of coins, which contains an integer and a real number representing the number of coins and the probability that the coins come up heads after tossing. It is guaranteed that the number of kinds is no more than 10, the total number of coins is no more than 1000000, and the probabilities that the coins come up heads after tossing are between 0.4 and 0.6.
Output
For each test case, output a line containing k real numbers with the precision of 6 digits, which are the probabilities of each kind of coins that will be lucky.
Sample Input
3
1
1000000 0.5
2
1 0.4
1 0.6
3
2 0.4
2 0.5
2 0.6
Sample Output
1.000000 0.210526 0.473684 0.124867 0.234823 0.420066
Source
2016ACM/ICPC亚洲区青岛站-重现赛(感谢中国石油大学)
题意:
给你n(n<=10)种硬币,每种硬币有a[i]个。对一枚硬币,每操作一次,硬币留下的概率为p[i]。
求进行若干次操作后只留下这一种硬币概率,输出每种的结果。保留六位小数。
分析:
100次以后每一种留下的概率就近似为0了。。
die[j][k]表示第j种硬币在k次操作后没有剩余的概率,而留下的概率是1-die[j][k],即live[j][k]
所以结果就是:
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=20;
int a[maxn],n;
double p[maxn];
double die[maxn][110],live[maxn][110];
int main()
{
int T,cas=1;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%lf",&a[i],&p[i]);
}
if(n==1) {puts("1.000000");continue;}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int k=0;k<=100;k++)
{
die[i][k]=pow(1.0-pow(p[i],k),a[i]);
live[i][k]=1.0-die[i][k];
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
double ans=0;
for(int k=1;k<=100;k++)
{
double tmp=1;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(j!=i)tmp*=die[j][k];
ans+=(live[i][k]-live[i][k+1])*tmp;
}
printf("%.6lf%c",ans,i==n?'\n':' ');
}
}
return 0;
}