一、定制URL匹配规则的方法
问题由来:编写一个/hello访问路径,但是吧,不管是输入/hello还是/hello.html,还是/hello.xxx都能进行访问。这是Spring Boot路由规则。
构建web应用程序时,并不是所有的URL请求都遵循默认的规则。有时,我们希望RESTful URL匹配的时候包含定界符“.”,这种情况在Spring中可以称之为“定界符定义的格式”;有时,我们希望识别斜杠的存在。Spring提供了接口供开发人员按照需求定制。
核心的开发步骤就是两步:
(1)启动类 extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport
(2)重写configurePathMatch方法;
启动类代码:
package com.dlb;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.PathMatchConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport;
/**
*
* @ClassName: AppletApplication
* @Description: springboot入口
* @author cheng
* @date 2017年9月19日 上午8:48:45
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class AppletApplication extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
/**
* 1、 extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport
* 2、重写下面方法;
* setUseSuffixPatternMatch: 设置是否是后缀模式匹配,如“/user”是否匹配/user.*,默认真即匹配;
* setUseTrailingSlashMatch: 设置是否自动后缀路径模式匹配,如“/user”是否匹配“/user/”,默认真即匹配;
*/
@Override
protected void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
configurer
.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(false)
.setUseTrailingSlashMatch(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AppletApplication.class);
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
以上代码有两句核心的代码:
setUseSuffixPatternMatch(boolean useSuffixPatternMatch):
设置是否是后缀模式匹配,如“/user”是否匹配/user.*,默认匹配即true;
当此参数设置为true的时候,那么/user.html,/user.aa,/user.*都能是正常访问的。
当此参数设置为false的时候,那么只能访问/user或者/user/( 这个前提是setUseTrailingSlashMatch 设置为true了)。
setUseTrailingSlashMatch (boolean useSuffixPatternMatch):
设置是否自动后缀路径模式匹配,如“/user”是否匹配“/user/”,默认匹配即true;
当此参数设置为true的会后,那么地址/user,/user/或者/user? 都能正常访问。
当此参数设置为false的时候,那么就只能访问/user了。
当以上两个参数都设置为true的时候,那么路径/user或者/user.aa,/user.*,/user/都是能正常访问的,但是类似/user.html/ 是无法访问的。
当都设置为false的时候,那么就只能访问/user路径了。
二、web基础配置
1、访问静态资源
1)进入规则为 / 时
默认规则就为”/”,及访问路径后面不跟任何后缀
如果进入SpringMVC的规则为/时,Spring Boot的默认静态资源的路径为:
application.yml
spring:
resources:
static-locations: classpath:/META-INF/resources/,classpath:/resources/,classpath:/static/,classpath:/public/- 1
- 2
- 3
其中的classpath表示src/main/resources
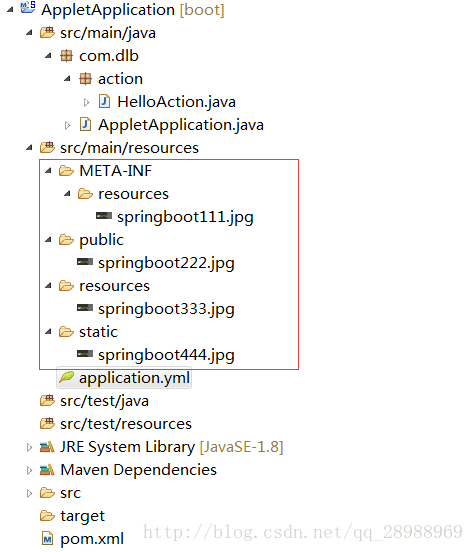
也就是说,在默认的Spring MVC进入规则下,classpath下的META-INF/resources目录、resources目录、static目录和public目录中的静态资料是可以直接通过 ” http://xxx.com/ 静态资源” 的方式访问到的。
注意:访问静态资源时不用带上静态资源所在的目录名称!!!
模拟静态资源:
浏览器访问:
直接是项目域名+静态资源名称 即可访问,不用带上静态资源所在的目录名称
访问地址:
META-INF/resources目录下:
http://localhost:8080/springboot111.jpg
public目录下:
http://localhost:8080/springboot222.jpg
resources目录下:
http://localhost:8080/springboot333.jpg
static目录下:
http://localhost:8080/springboot444.jpg
2)进入规则为/xxx 或者 不指定静态文件路径时
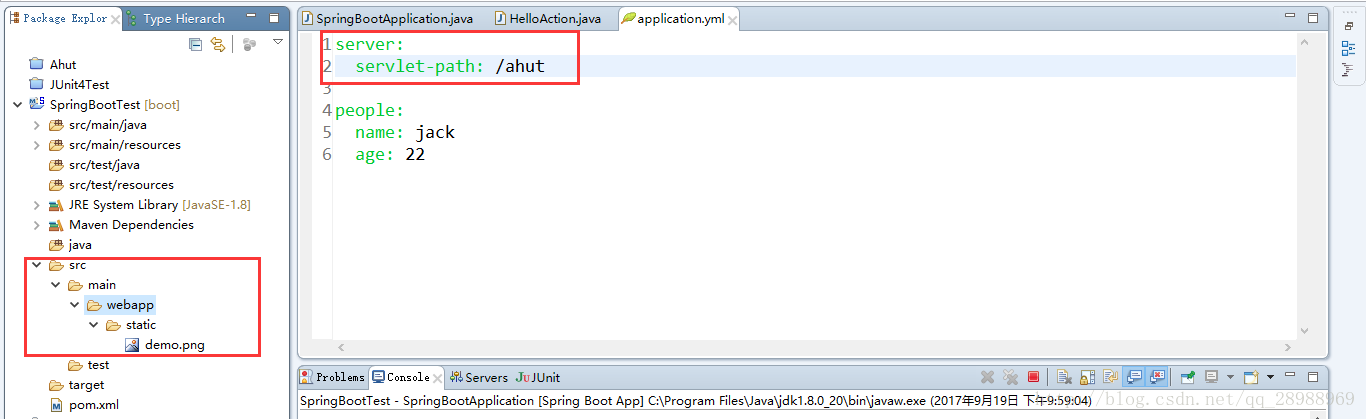
如果进入SpringMVC的规则为*/xxx时(如:/ahut),则上述目录下的静态资源将无法直接访问,需要将静态资源放置到webapp下的static目录中即可通过 ” http://xxx.com/static/ 静态资源” 访问。此外,默认不配置SpringMVC的规则下也可以如此访问,也就是说这种访问静态资源的方式是通用的。
webapp目录 : src > main > webapp > static > 静态资源
如图所示:
访问静态资源:http://localhost:8080/static/demo.png
访问控制层:http://localhost:8080/ahut/hello
2、自定义拦截器
主要分两步完成:
- 书写自定义的拦截器 - - - 实现HandlerInterceptor接口
- 配置自定义的拦截器 - - - 继承WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类
项目目录结构如下图:
书写自定义拦截器:
package com.ahut.interceptor;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
/**
*
* @ClassName: MyInterceptor
* @Description: 自定义拦截器
* @author cheng
* @date 2017年9月19日 下午10:56:13
*/
@Component//将该组件加入spring ioc容器
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 在请求处理的方法之前执行,true让行,false不让行
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("方法执行之前===============");
return true;
}
/**
* 在请求处理方法之后执行
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2, ModelAndView arg3)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("方法执行之后===============");
}
/**
* 在DispatcherServlet处理后执行--清理工作(因为是单利)
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2, Exception arg3)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行清理工作===============");
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
配置自定义拦截器:
package com.ahut.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
import com.ahut.interceptor.MyInterceptor;
/**
*
* @ClassName: MyInterceptor
* @Description:springboot拦截器配置
* @author cheng
* @date 2017年9月19日 下午10:14:48
*/
@Configuration//表示这是一个配置类
public class MyInterceptorConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyInterceptor myInterceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
// 添加拦截器并设置拦截规则
// /*表示路径
// /**表示路径及其自路径 registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
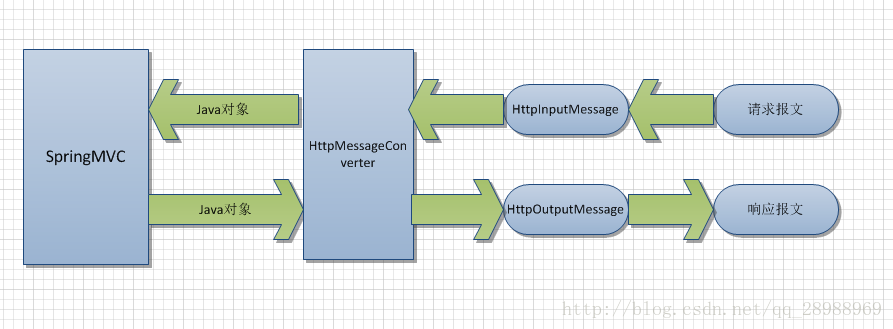
3、自定义消息转化器
消息转换器示意图:
@RequestBody : 请求报文 => java对象
@ResponseBody : java对象 => 响应报文
自定义消息转化器有两种实现方式,一种是@Bean方式,另一种是自定义拦截器。
1)@Bean方式
只需要在@Configuration的类中添加消息转化器的@bean加入到Spring容器,就会被Spring Boot自动加入到容器中。
// spring boot默认就有消息转化器,其编码格式为utf-8
@Bean
public StringHttpMessageConverter stringHttpMessageConverter() {
StringHttpMessageConverter stringHttpMessageConverter = new StringHttpMessageConverter(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
return stringHttpMessageConverter;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
2)自定义拦截器方式
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter的功能很强大,除了可以配置拦截器外,还可以配置消息转换器。
@Configuration
public class MySpringMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
StringHttpMessageConverter stringHttpMessageConverter = new StringHttpMessageConverter(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
converters.add(stringHttpMessageConverter);
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
4、读取外部的配置文件
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = { "classpath:jdbc.properties", "classpath:base.properties" }, ignoreResourceNotFound = true)
public class 任意类 {
}