参加的第一个线上比赛,经历了下比赛过程, 记录下。
这个比赛比较简单, 主要是要调参费时间,只提交了两次结果,下次比赛认真对待。
核心思路:文本矢量化后进行逻辑回归训练。
print("start....")
## 导入需要的库
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
df_train = pd.read_csv('./train_set.csv')
df_test = pd.read_csv('./test_set.csv')
df_train.drop(columns=['article','id'],inplace=True)
#pandas的drop函数:删除表中的某一行或者某一列,当inplace手动设为True时(默认false)
# 改变原有的df中的数据,原数据直接就被替换。
df_test.drop(columns=['article'],inplace=True)
## 进行训练数据的文本矢量化
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(ngram_range=(1,2),min_df=3,max_df=0.9,max_features=100000)
#文本特征提取方法:CountVectorizer,将文本转换为文字计数向量,它只考虑每种词汇在该训练文本中出现的频。
# CountVectorizer算法是将文本向量转换成稀疏表示数值向量(字符频率向量)。该数值向量可以传递给其他算法,譬如LDA 。
# 在fitting过程中,CountVectorizer将会把频率高的单词排在前面。可选参数minDF表示文本中必须出现的次数
vectorizer.fit(df_train['word_seg'])
# 拟合训练集'word_seg'列的数据,调用 fit() 函数以从一个或多个文档中建立索引
x_train = vectorizer.transform(df_train['word_seg'])
# 再标准化训练集'word_seg'列数据,tranform()将文档编码为一个向量,返回的向量是稀疏向量,
# 这里可以通过调用 toarray() 函数将它们转换回 numpy 数组以便查看并更好地理解这个过程。
x_test = vectorizer.transform(df_test['word_seg'])
y_train = df_train['class']-1
## 模型训练
lg = LogisticRegression(C=4,dual=True) # 导入模型。调用逻辑回归LogisticRegression()函数。
lg.fit(x_train,y_train) # 调用fit(x,y)的方法来训练模型,其中x为数据的属性,y为所属类型。
y_test = lg.predict(x_test) # predict()预测。利用训练得到的模型对数据集进行预测,返回预测结果。
## 生成结果数据
df_test['class'] = y_test.tolist()
df_test['class'] = df_test['class'] + 1
df_result = df_test.loc[:,['id','class']]
df_result.to_csv('./result.csv',index=False)
print('done over.')几个关键函数的参数说明:
参考 http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/feature_extraction.html#text-feature-extraction
(1)CountVectorizer
class sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer(input='content', encoding='utf-8', decode_error='strict', strip_accents=None, lowercase=True, preprocessor=None, tokenizer=None, stop_words=None, token_pattern='(?u)\b\w\w+\b', ngram_range=(1, 1), analyzer='word', max_df=1.0, min_df=1, max_features=None, vocabulary=None, binary=False, dtype=<class 'numpy.int64'>)
(分为三个处理步骤:preprocessing、tokenizing、n-grams generation)
参数:(一般要设置的参数是decode_error,stop_words='english',token_pattern='...'(重要参数),max_df,min_df,max_features)
input:一般使用默认即可,可以设置为"filename'或'file',尚不知道其用法
encodeing:使用默认的utf-8即可,分析器将会以utf-8解码raw document
decode_error:默认为strict,遇到不能解码的字符将报UnicodeDecodeError错误,设为ignore将会忽略解码错误,还可以设为replace,作用尚不明确
strip_accents:默认为None,可设为ascii或unicode,将使用ascii或unicode编码在预处理步骤去除raw document中的重音符号
analyzer:一般使用默认,可设置为string类型,如'word', 'char', 'char_wb',还可设置为callable类型,比如函数是一个callable类型
preprocessor:设为None或callable类型
tokenizer:设为None或callable类型
ngram_range:词组切分的长度范围,ngram_range(1,2)为了保存一些本地排序信息,除了1-g(单个单词)外,我们还可以提取2-g单词
stop_words:设置停用词,设为english将使用内置的英语停用词,设为一个list可自定义停用词,设为None不使用停用词,设为None且max_df∈[0.7, 1.0)将自动根据当前的语料库建立停用词表
lowercase:将所有字符变成小写
token_pattern:表示token的正则表达式,需要设置analyzer == 'word',默认的正则表达式选择2个及以上的字母或数字作为token,标点符号默认当作token分隔符,而不会被当作token
max_df:可以设置为范围在[0.0 1.0]的float,也可以设置为没有范围限制的int,默认为1.0。这个参数的作用是作为一个阈值,当构造语料库的关键词集的时候,如果某个词的document frequence大于max_df,这个词不会被当作关键词。如果这个参数是float,则表示词出现的次数与语料库文档数的百分比,如果是int,则表示词出现的次数。如果参数中已经给定了vocabulary,则这个参数无效
min_df:类似于max_df,不同之处在于如果某个词的document frequence小于min_df,则这个词不会被当作关键词
max_features:默认为None,可设为int,对所有关键词的term frequency进行降序排序,只取前max_features个作为关键词集
vocabulary:默认为None,自动从输入文档中构建关键词集,也可以是一个字典或可迭代对象?
binary:默认为False,一个关键词在一篇文档中可能出现n次,如果binary=True,非零的n将全部置为1,这对需要布尔值输入的离散概率模型的有用的
dtype:使用CountVectorizer类的fit_transform()或transform()将得到一个文档词频矩阵,dtype可以设置这个矩阵的数值类型
属性:
vocabulary_:字典类型,key为关键词,value是特征索引,样例如下:
com.furiousapps.haunt2: 57048
bale.yaowoo: 5025
asia.share.superayiconsumer: 4660
com.cooee.flakes: 38555
com.huahan.autopart: 67364
关键词集被存储为一个数组向量的形式,vocabulary_中的key是关键词,value就是该关键词在数组向量中的索引,使用get_feature_names()方法可以返回该数组向量。使用数组向量可验证上述关键词,如下:
ipdb> count_vec.get_feature_names()[57048]
u'com.furiousapps.haunt2'
ipdb> count_vec.get_feature_names()[5025]
u'bale.yaowoo'
stop_words_:集合类型,官网的解释十分到位,如下:
Terms that were ignored because they either:
occurred in too many documents (max_df)
occurred in too few documents (min_df)
were cut off by feature selection (max_features).
This is only available if no vocabulary was given.
这个属性一般用来程序员自我检查停用词是否正确,在pickling的时候可以设置stop_words_为None是安全的
(2)TfidfVectorizer --- 这个后来没用
class sklearn.feature_extraction.text.TfidfVectorizer(input='content', encoding='utf-8', decode_error='strict', strip_accents=None, lowercase=True, preprocessor=None, tokenizer=None, analyzer='word', stop_words=None, token_pattern='(?u)\b\w\w+\b', ngram_range=(1, 1), max_df=1.0, min_df=1, max_features=None, vocabulary=None, binary=False, dtype=<class 'numpy.int64'>, norm='l2', use_idf=True, smooth_idf=True, sublinear_tf=False)
TfidfVectorizer与CountVectorizer有很多相同的参数,下面只解释不同的参数
binary:默认为False,tf-idf中每个词的权值是tf*idf,如果binary设为True,所有出现的词的tf将置为1,TfidfVectorizer计算得到的tf与CountVectorizer得到的tf是一样的,就是词频,不是词频/该词所在文档的总词数。
norm:默认为'l2',可设为'l1'或None,计算得到tf-idf值后,如果norm='l2',则整行权值将归一化,即整行权值向量为单位向量,如果norm=None,则不会进行归一化。大多数情况下,使用归一化是有必要的。
use_idf:默认为True,权值是tf*idf,如果设为False,将不使用idf,就是只使用tf,相当于CountVectorizer了。
smooth_idf:idf平滑参数,默认为True,idf=ln((文档总数+1)/(包含该词的文档数+1))+1,如果设为False,idf=ln(文档总数/包含该词的文档数)+1
sublinear_tf:默认为False,如果设为True,则替换tf为1 + log(tf)。
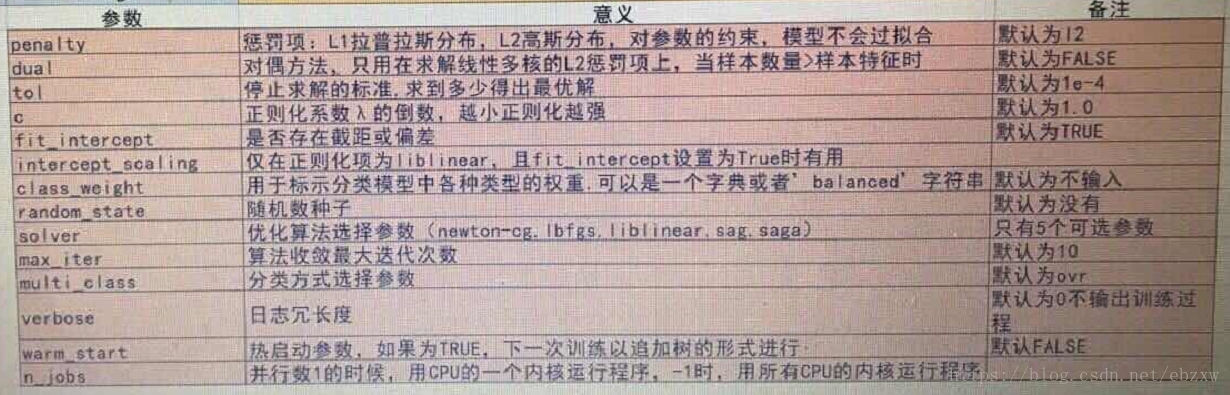
(3)LogisticRegression 函数参数: