- 通道(Channel):
由java.nio.channels包定义的,Channel表示IO源与目标打开的连接,Channel类似于传统的“流”,只不过Channel本身不能直接访问数据,Channel只能与Buffer进行交互。通道主要用于传输数据,从缓冲区的一侧传到另一侧的实体(如文件、套接字...),反之亦然;通道是访问IO服务的导管,通过通道,我们可以以最小的开销来访问操作系统的I/O服务;顺便说下,缓冲区是通道内部发送数据和接收数据的端点。
在标准的IO当中,都是基于字节流/字符流进行操作的,而在NIO中则是是基于Channel和Buffer进行操作,其中的Channel的虽然模拟了流的概念,实则大不相同。
| 区别 | Stream | Channel |
|---|---|---|
| 支持异步 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 是否可双向传输数据 | 不能,只能单向 | 可以,既可以从通道读取数据,也可以向通道写入数据 |
| 是否结合Buffer使用 | 不 | 必须结合Buffer使用 |
| 性能 | 较低 | 较高 |
- 传统与革新:
传统的数据流:
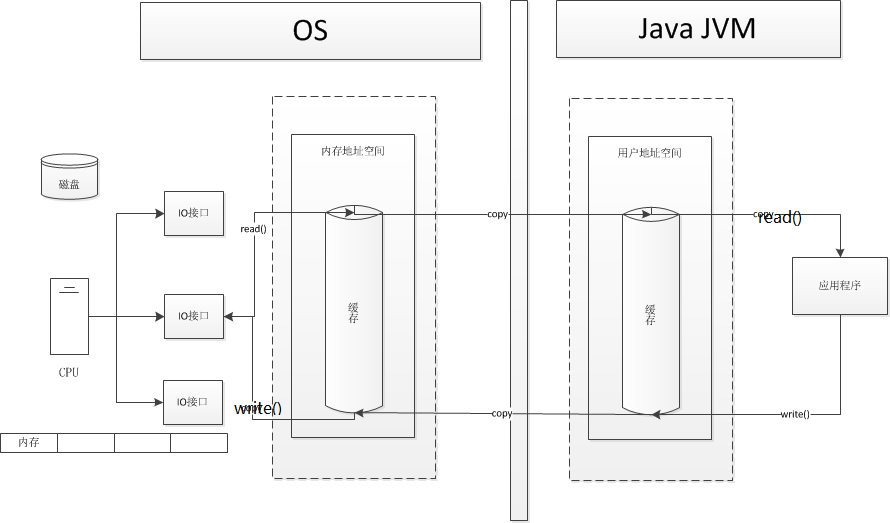
CPU处理IO,性能损耗太大
改为:
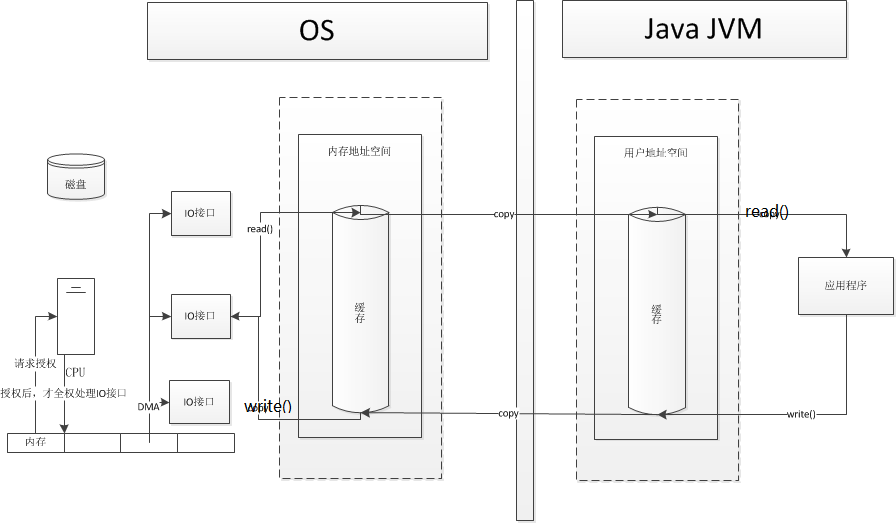
内存和IO接口之间加了 DMA(直接存储器),DMA向CPU申请权限,IO的操作全部由DMA管理。CPU不要干预。
若有大量的IO请求,会造成DMA的走线过多,则也会影响性能。
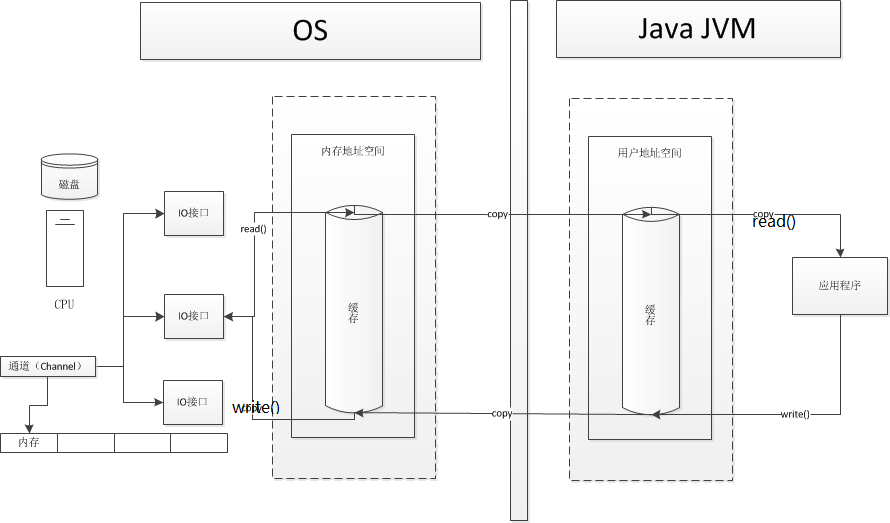
则改DMA为Channel,Channel为完全独立的单元,不需要向CPU申请权限,专门用于IO。
早一代IO操作是由CPU负责IO接口:
新一代DMA授权处理IO接口:
通道(Channel)模式:
- 代码示例:
1 package com.expgiga.NIO; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 7 import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer; 8 import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; 9 import java.nio.file.Paths; 10 import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; 11 12 /** 13 * 一、Channel:用于源节点与目标节点之间的连接。在Java NIO中,负责缓冲区中数据传输,Channel本身不存储数据,因此需要配合缓冲区进行传输。 14 * 15 * 二、Channel的实现类: 16 * java.nio.channels.Channel 接口: 17 * |-- FileChannel 18 * |-- SocketChannel 19 * |-- ServerSocketChannel 20 * |-- DatagramChannel 21 * 22 * 三、获取通道Channel 23 * 1.Java针对支持通道的类提供了getChannel()方法 24 * 本地IO 25 * FileInputStream/FileOutputStream 26 * RandomAccessFile 27 * 28 * 网络IO: 29 * Socket 30 * ServerSocket 31 * DatagramSocket 32 * 33 * 2.在jdk1.7中的NIO.2针对各个通道提供了静态方法open() 34 * 35 * 3.在jdk1.7中的NIO.2的Files工具类的newByteChannel() 36 * 37 * 四、通道之间的数据传输 38 * transferFrom() 39 * transferTo() 40 * 41 */ 42 public class TestChannel { 43 44 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 45 46 /* 47 * 1.利用通道完成文件的复制(非直接缓冲区) 48 */ 49 FileInputStream fis = null; 50 FileOutputStream fos = null; 51 52 FileChannel inChannel = null; 53 FileChannel outChannel = null; 54 55 try { 56 fis = new FileInputStream("1.jpg"); 57 fos = new FileOutputStream("2.jpg"); 58 //1.获取通道 59 inChannel = fis.getChannel(); 60 outChannel = fos.getChannel(); 61 62 //2.分配指定大小的缓冲区 63 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); 64 65 //3.将通道中的数据缓冲区中 66 while (inChannel.read(buffer) != -1) { 67 68 buffer.flip();//切换成都数据模式 69 70 //4.将缓冲区中的数据写入通道中 71 outChannel.write(buffer); 72 buffer.clear();//清空缓冲区 73 } 74 } catch (Exception e) { 75 e.printStackTrace(); 76 } finally { 77 if (outChannel != null) { 78 try { 79 outChannel.close(); 80 } catch (IOException e) { 81 e.printStackTrace(); 82 } 83 } 84 85 if (inChannel != null) { 86 try { 87 inChannel.close(); 88 } catch (IOException e) { 89 e.printStackTrace(); 90 } 91 } 92 93 if (fis != null) { 94 try { 95 fis.close(); 96 } catch (IOException e) { 97 e.printStackTrace(); 98 } 99 } 100 101 if (fos != null) { 102 try { 103 fos.close(); 104 } catch (IOException e) { 105 e.printStackTrace(); 106 } 107 } 108 } 109 110 111 /* 112 * 2.利用(直接缓冲区)通道完成文件的复制(内存映射文件的方式) 113 */ 114 115 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 116 FileChannel inChannel2 = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ); 117 FileChannel outChannel2 = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("3.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); 118 119 //内存映射文件 120 MappedByteBuffer inMappedBuf = inChannel2.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size()); 121 MappedByteBuffer outMappedBuf = outChannel2.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size()); 122 123 //直接对缓冲区进行数据读写操作 124 byte[] dst = new byte[inMappedBuf.limit()]; 125 inMappedBuf.get(dst); 126 outMappedBuf.put(dst); 127 128 inChannel2.close(); 129 outChannel2.close(); 130 131 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 132 System.out.println("耗费的时间为:" + (end - start)); 133 134 /* 135 * 通道之间的数据传输(直接缓冲区) 136 */ 137 FileChannel inChannel3 = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ); 138 FileChannel outChannel3 = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("3.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); 139 140 inChannel3.transferTo(0, inChannel3.size(), outChannel3); 141 //等价于 142 // outChannel3.transferFrom(inChannel3, 0, inChannel3.size()); 143 144 inChannel3.close(); 145 outChannel3.close(); 146 } 147 }