版权声明:尊重原创,码字不易,转载需博主同意。 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34626097/article/details/89289444
文章目录
通道数据传输 、 内存映射文件
-
将 Buffer 中数据写入Channel
如: inChannel.write(buf); -
从Channel读取数据到Buffer
如:inChannel.read(buf); -
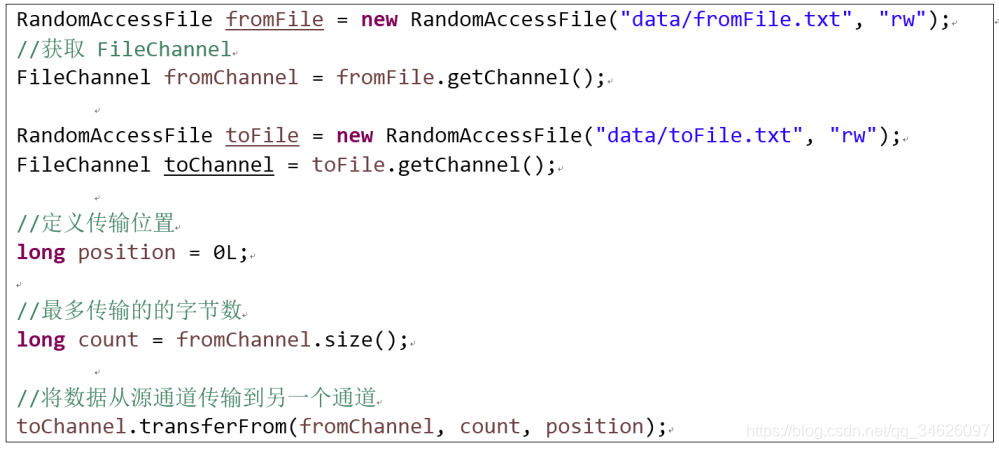
transferFrom() : 将数据从源通道传输到其他Channel中:
-
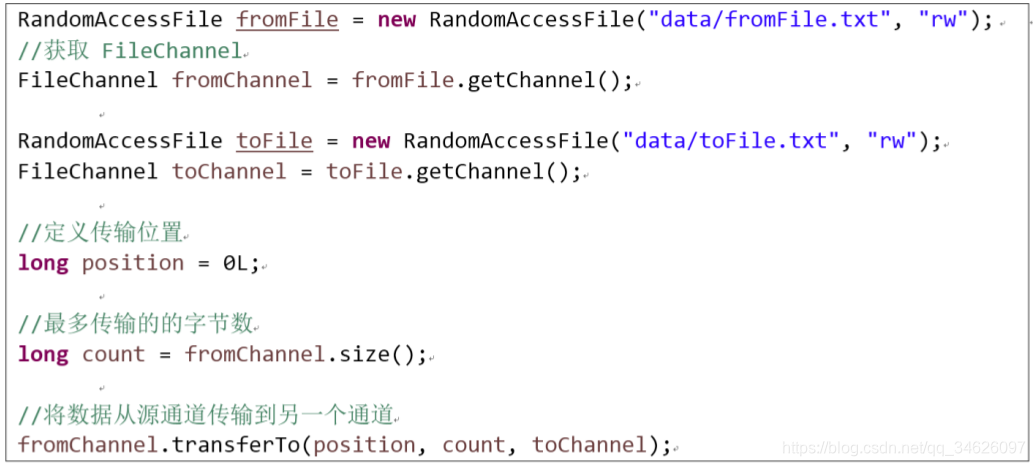
transferTo() : 将数据从源通道传输到其他Channel中:
/*
* 一、通道(Channel):用于资源节点与目标节点的连接。
* 在Java NIO 中负责缓冲中数据的传去。
* Channel本身不存储数据,需要配合缓冲区进行传输。
*
* 二、通道的主要实现类
* java.nio.channels.Channel 接口:
* |--FileChannel :
* |--SokectChannel
* |--SeverSocketChannel
* |--DatagramChannel
*
*三、获取通道
*1. Java 针对支持通道的类提供了getChannel()方法
* 本地IO操作
* FileInputStream/FileOutStream
* RandomAccessFile
*
* 网络IO:
* Socket
* ServerSocket
* DatagramSocket
*
*2.在 JDK 1.7 中的NIO.2针对各个通道提供了一个静态方法open()
*3.在 JDK 1.7 中的NIO.2的Files 工具类的newByteChannel()
*
*四、通道之间的数据传输
*transferFrom()
*transferTo()
*/
public class TestChannel {
//通道之间的数据传输(直接缓冲区的方式)
@Test
public void test3() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileChannel readChannel = null;
FileChannel writeChannel = null;
try {
readChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
writeChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("5.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE_NEW);
// readChannel.transferTo(0, readChannel.size(), writeChannel);
writeChannel.transferFrom(readChannel, 0, readChannel.size());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(readChannel != null) {
try {
readChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(writeChannel != null) {
try {
writeChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
}
//2.使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件):直接缓冲区只有ByteBuffer支持
@Test
public void test2(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileChannel readChannel = null;
FileChannel writeChannel = null;
try {
readChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
writeChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("3.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE_NEW);
//内存映射文件
MappedByteBuffer inMappedBuf = readChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, readChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outMappedBuf =writeChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, readChannel.size());
//直接对缓冲区进行数据的读写操作
byte [] dst = new byte [inMappedBuf.limit()];
inMappedBuf.get(dst);
outMappedBuf.put(dst);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(readChannel != null) {
try {
readChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(writeChannel != null) {
try {
writeChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
}
//1. 利用通道完成文件的复制(非直接缓冲区)
@Test
public void test1() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
FileChannel inChannel = null;
FileChannel outChannel= null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("1.jpg");
fos = new FileOutputStream("2.jpg");
//①获取通道
inChannel = fis.getChannel();
outChannel = fos.getChannel();
// ②分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//③将通道中数据存入缓冲区
while(inChannel.read(buf) != -1) {
buf.flip();//切换成读取数据的模式
//④将换缓冲区中的数据写入通道中
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();//清空缓冲区
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(outChannel != null) {
try {
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(inChannel != null) {
try {
inChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
}
}