import tensorflow as tf
hello = tf.constant("hello,tensorflow!") #创建一个常量
sess = tf.Session() #启动Tensorflow的Session
print(sess.run(hello)) #调用sess的run方法来启动整个graph
# b'hello,tensorflow!'
a = tf.constant(2)
b = tf.constant(3)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print("a = 2, b = 3")
print("Addition with constants:%i"%sess.run(a + b))
print("Multiplication with constants:%i"%sess.run(a * b))
# a = 2, b = 3
# Addition with constants:5
# Multiplication with constants:6
# 用tensorflow的placeholder来定义变量做类似计算
a = tf.placeholder(tf.int16)
b = tf.placeholder(tf.int16)
add = tf.add(a,b)
mul = tf.multiply(a,b)
with tf.Session() as sess:
#run every operation with variable input
print("Addition with variables:%i"% sess.run(add,feed_dict={a:2,b:3}))
print("Multiplication with variables:%i"%sess.run(mul,feed_dict={a:2,b:3}))
# Addition with variables:5
# Multiplication with variables:6
#线性回归
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = numpy.random
# Parameters
learning_rate = 0.01
training_epochs = 2000
display_step = 50
# Training Data
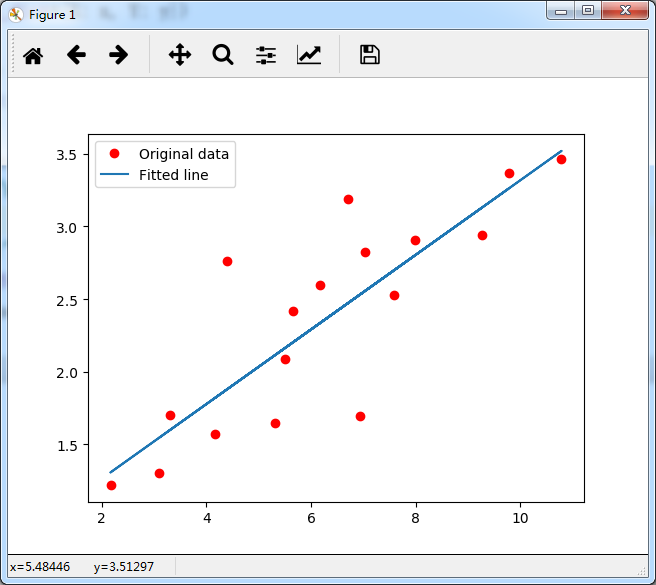
train_X = numpy.asarray([3.3,4.4,5.5,6.71,6.93,4.168,9.779,6.182,7.59,2.167,7.042,10.791,5.313,7.997,5.654,9.27,3.1])
train_Y = numpy.asarray([1.7,2.76,2.09,3.19,1.694,1.573,3.366,2.596,2.53,1.221,2.827,3.465,1.65,2.904,2.42,2.94,1.3])
n_samples = train_X.shape[0]
# tf Graph Input
X = tf.placeholder("float")
Y = tf.placeholder("float")
# Create Model
# Set model weights
W = tf.Variable(rng.randn(), name="weight")
b = tf.Variable(rng.randn(), name="bias")
# Construct a linear model
activation = tf.add(tf.multiply(X, W), b)
# Minimize the squared errors
cost = tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(activation-Y, 2))/(2*n_samples) #L2 loss
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) #Gradient descent
# Initializing the variables
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
# Launch the graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
# Fit all training data
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for (x, y) in zip(train_X, train_Y):
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
#Display logs per epoch step
if epoch % display_step == 0:
print ("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch+1), "cost=", \
"{:.9f}".format(sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: train_X, Y:train_Y})), \
"W=", sess.run(W), "b=", sess.run(b))
print ("Optimization Finished!")
print ("cost=", sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: train_X, Y: train_Y}), \
"W=", sess.run(W), "b=", sess.run(b))
#Graphic display
plt.plot(train_X, train_Y, 'ro', label='Original data')
plt.plot(train_X, sess.run(W) * train_X + sess.run(b), label='Fitted line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()