预备知识
前置声明头文件:https://blog.csdn.net/hanzheng6602/article/details/80031130
动态顺序表:https://blog.csdn.net/hanzheng6602/article/details/79917391
拓展:带环迷宫求最短路
https://blog.csdn.net/hanzheng6602/article/details/80054038
栈应用——括号匹配和逆波兰表达式
https://blog.csdn.net/hanzheng6602/article/details/80077502
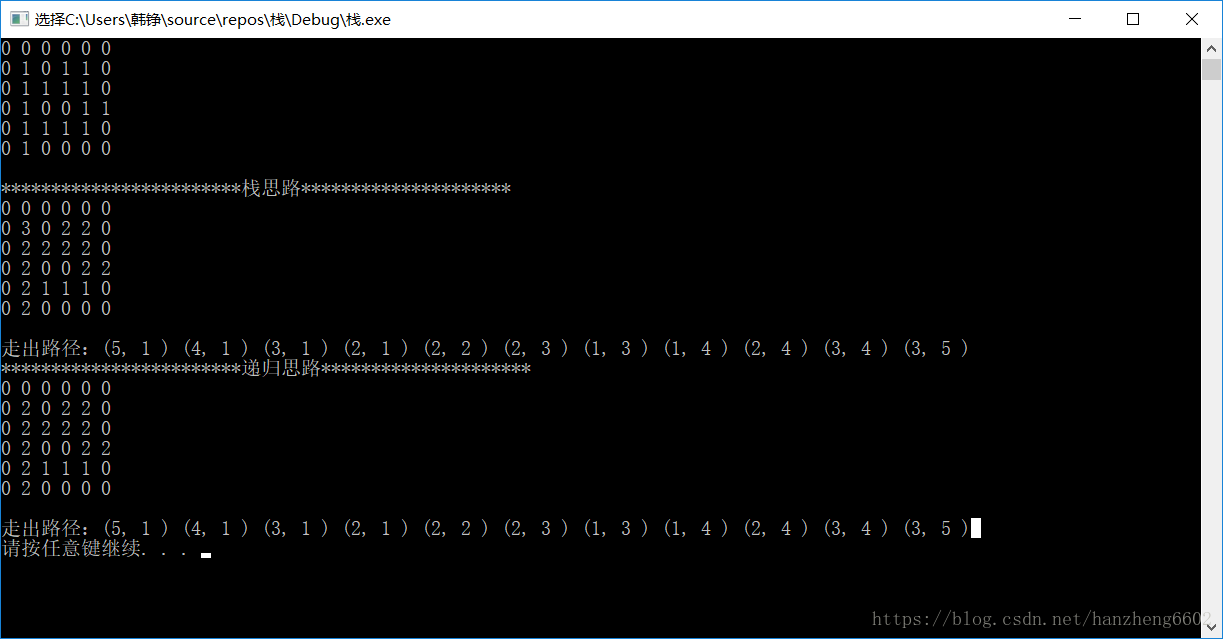
结果:
利用栈走迷宫的思路:从入口点开始,先标记入口结点为2,表示已经走过。然后向四个方向进行试探,如果是合法的点就标记,入栈,检测是否是出口,不是的话取栈顶点开始向四周试探,若四周均不合法,则出栈该点。
判合法点函数:是地图边界内,且不是入口结点,没走过
判出口函数:是边界上的点,并且是可以走的点
递归思路:先标记进来的点2,入栈,形成子问题——如何走剩下的迷宫?从入口点向四周试探,如果任意一个方向走成功了,就return 1,也就是整个迷宫就有解了,如果这个方向走失败了,说明这个方向以后不论怎么走都失败,要出栈这个结点。当四个方向全失败了,出栈入口点,并返回0.
stack.h
动态栈根据动态顺序表演变而来,涉及对其指针进行动态内存开辟,array当作数组使用,数组中存放的是封装的Position坐标。
#pragma once
extern struct position;
typedef struct position Position;
#define Datatype Position
//动态栈
typedef struct stack {
Datatype *array;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
void init(Stack *s);//初始化
void pushBack(Stack *s, Datatype data);//入栈
void pop(Stack *s);//出栈
Datatype top(Stack *s);//获取栈顶元素
int checkCapacity(Stack *s);//检查容量,扩容
void destory(Stack* s);//销毁栈
int isEmpty(Stack* s);//判空
int stackSize(Stack * s);//获取栈元素个数
void printStack(Stack * min);//从底到顶打印栈
maze.h
#pragma once
#define ROW 6
#define COL 6
extern struct stack;
typedef struct stack Stack;
//对坐标进行封装
typedef struct position {
int x;
int y;
}Position;
int map[ROW][COL];//迷宫
void initMap(int maze[ROW][COL]); //初始化map
int isValidEntry(int maze[ROW][COL], Position entry);//检测合法入口
//检查是否可以走
int isValidPath(int maze[ROW][COL], Position next);
//检查是不是出口
int isExit(int maze[ROW][COL], Position next, Position entry);
//栈实现走迷宫
int passMaze(int maze[ROW][COL], Position entry, Stack* path);
//递归走迷宫
int passMazeR(int maze[ROW][COL], Position cur, Position entry, Stack* path);
void printMap(); //打印迷宫stack.c
#include "stack.h"
#include "maze.h"
#include <assert.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void init(Stack *s)
{
assert(s);
s->capacity = 10;
s->array = (Datatype*)malloc(sizeof(Datatype)*(s->capacity));
if (NULL == s->array) {
printf("分配失败");
}
s->top = 0;
}
void pushBack(Stack *s, Datatype data)
{
assert(s);
if (checkCapacity(s)) {
s->array[s->top] = data;
s->top++;
}
}
int checkCapacity(Stack *s)
{
assert(s);
//需要扩容了
if (s->top == s->capacity) {
Datatype * new = NULL;
new = (Datatype*)realloc(s->array, sizeof(Datatype) * 2 * (s->capacity)); //扩容两倍
if (NULL == new) {
return 0;
}
s->array = new;
s->capacity *= 2;
}
return 1;
}
void pop(Stack *s)
{
assert(s);
if (0 == s->top) {
return;
}
s->top--;
}
Datatype top(Stack *s)
{
if (0 == s->top) {
printf("没有元素可取了");
return s->array[0];
}
return s->array[(s->top) - 1];
}
void destory(Stack* s)
{
free(s->array);
s->array = NULL;
s->capacity = 0;
s->top = 0;
}
//判空
int isEmpty(Stack* s)
{
return s->top ? 0 : 1;
}
//获取栈元素个数
int stackSize(Stack * s)
{
return s->top;
}
//从底到顶打印栈
void printStack(Stack * min)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < min->top; i++) {
printf("(%d, %d ) ", min->array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
maze.c
#include "maze.h"
#include "stack.h"
#include <malloc.h>
void initMap(int maze[ROW][COL])
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < COL; j++) {
map[i][j] = maze[i][j];
}
}
}
/*******************************栈实现走迷宫*******************************/
int passMaze(int maze[ROW][COL], Position entry, Stack* path)
{
//检测合法入口
if (!isValidEntry(maze, entry)) {
return 0;
}
maze[entry.x][entry.y] = 2; //标记已走的为2
pushBack(path, entry); //走一步入口节点
Position cur; //记录当前走的位置
//上右下左走
while (!isEmpty(path)) {
cur = top(path);
if (isExit(maze, cur, entry)) {
maze[cur.x][cur.y] = 2;
return 1;
}
Position next;
next = cur;
next.x -= 1;
if (isValidPath(maze, next)) {
maze[next.x][next.y] = 2;
pushBack(path, next);
continue;
}
next = cur;
next.y += 1;
if (isValidPath(maze, next)) {
maze[next.x][next.y] = 2;
pushBack(path, next);
continue;
}
next = cur;
next.x += 1;
if (isValidPath(maze, next)) {
maze[next.x][next.y] = 2;
pushBack(path, next);
continue;
}
next = cur;
next.y -= 1;
if (isValidPath(maze, next)) {
maze[next.x][next.y] = 2;
pushBack(path, next);
continue;
}
//四个方向均无法走,回退一步
maze[cur.x][cur.y] = 3; //标记为3可以看出哪些点是回退的
pop(path);
}
return 0;
}
/*******************************递归实现走迷宫*******************************/
int passMazeR(int maze[ROW][COL], Position cur, Position entry, Stack* path)
{
if (!isValidEntry(maze, entry)) {
return 0;
}
//先标记入口点
maze[entry.x][entry.y] = 2;
//求解子迷宫问题
return _passMazeR(maze, entry, entry, path);
}
int _passMazeR(int maze[ROW][COL], Position cur, Position entry, Stack* path)
{
//入栈当前点
pushBack(path, cur);
if (isExit(maze, cur, entry)) {
return 1;
}
//上右下左走
Position tmp = cur; //下一个要试探的位置
tmp.x -= 1;
if (isValidPath(maze, tmp)) {
maze[tmp.x][tmp.y] = 2;
if (_passMazeR(maze, tmp, entry, path))
return 1;
}
tmp = cur;
tmp.y += 1;
if (isValidPath(maze, tmp)) {
maze[tmp.x][tmp.y] = 2;
if (_passMazeR(maze, tmp, entry, path))
return 1;
}
tmp = cur;
tmp.x += 1;
if (isValidPath(maze, tmp)) {
maze[tmp.x][tmp.y] = 2;
if (_passMazeR(maze, tmp, entry, path))
return 1;
}
tmp = cur;
tmp.y -= 1;
if (isValidPath(maze, tmp)) {
maze[tmp.x][tmp.y] = 2;
if (_passMazeR(maze, tmp, entry, path))
return 1;
}
//四个方向均尝试,出栈
pop(path);
return 0;
}
/*******************************辅助函数*******************************/
int isValidEntry(int maze[ROW][COL], Position entry)//检测合法入口
{
if (entry.x < 0 || entry.y < 0 || entry.x >= ROW || entry.y >= COL) {
return 0;
}
return maze[entry.x][entry.y];
}
int isValidPath(int maze[ROW][COL], Position next)//检查是否可以走
{
if (next.x < 0 || next.y < 0 || next.x >= ROW || next.y >= COL) {
return 0;
}
else if (1 == maze[next.x][next.y]) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int isExit(int maze[ROW][COL], Position next, Position entry)//检查是不是出口
{
//不能是入口
if (next.x == entry.x && (next.y == entry.y)) {
return 0;
}
//因为进来的都是有效点,所以只用判断是不是边界
else if ((0 == next.x || 0 == next.y || (ROW - 1) == next.x || (COL - 1) == next.y)) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void printMap()
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < COL; j++) {
printf("%d ", map[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}test.c
#include "stack.h"
#include "maze.h"
#include <Windows.h>
int main()
{
Stack path;
init(&path);
int tmp[ROW][COL] = {
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,1,0,1,1,0 },
{ 0,1,1,1,1,0 },
{ 0,1,0,0,1,1 },
{ 0,1,1,1,1,0 },
{ 0,1,0,0,0,0 },
};
initMap(tmp);
printMap();
Position entry = { 5,1 };
printf("************************栈思路*********************\n");
passMaze(map, entry, &path);
printMap();
printf("走出路径:");
printStack(&path);
printf("************************递归思路*********************\n");
init(&path);
initMap(tmp);
int ret = passMazeR(map, entry, entry, &path);
printMap();
printf("走出路径:");
printStack(&path);
}