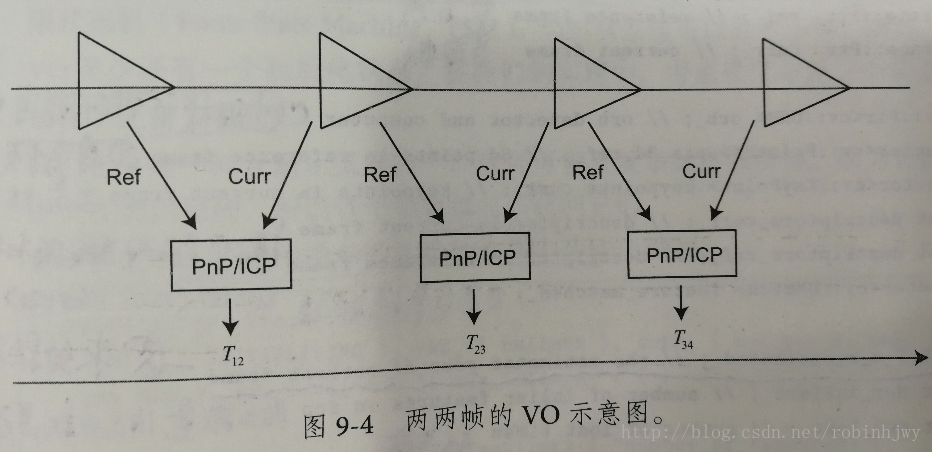
0.2版本实现一个基本的VO,也就是两两帧间的无结构VO,它的任务是根据输入的图像,计算相机运动和特征点位置。在这里我们只关心运动,不关心结构,也就是说只要通过特征点成功的求出了运动,我们就不再需要这一帧的特征点了。
整体逻辑如下图:
这种VO工作方式非常简单。在匹配特征点的方式中,最重要的是参考帧与当前帧之间的特征匹配关系。流程如下:
visual_odometry.h类为算法实现。对比发现,0.1版本的此类是空的。所以在0.2版本要写入两两帧VO功能。
#ifndef VISUALODOMETRY_H
#define VISUALODOMETRY_H
#include "myslam/common_include.h"
#include "myslam/map.h"
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
namespace myslam
{
class VisualOdometry
{
public:
//定义指向自身的智能指针,在后面传递参数是使用VisualOdometry::Ptr即可
typedef shared_ptr<VisualOdometry> Ptr;
//定义枚举来表征VO状态,分别为:初始化、正常、丢失
enum VOState
{
INITIALIZING=-1,
OK=0,
LOST
};
//这里为两两帧VO所用到的参考帧和当前帧。还有VO状态和整个地图。
VOState state_; // current VO status
Map::Ptr map_; // map with all frames and map points
Frame::Ptr ref_; // reference frame
Frame::Ptr curr_; // current frame
//这里是两帧匹配需要的:keypoints,descriptors,matches
cv::Ptr<cv::ORB> orb_; // orb detector and computer
vector<cv::Point3f> pts_3d_ref_; // 3d points in reference frame
vector<cv::KeyPoint> keypoints_curr_; // keypoints in current frame
Mat descriptors_curr_; // descriptor in current frame
Mat descriptors_ref_; // descriptor in reference frame
vector<cv::DMatch> feature_matches_;
//这里为匹配结果T,还有表征结果好坏的内点数和丢失数
SE3 T_c_r_estimated_; // the estimated pose of current frame
int num_inliers_; // number of inlier features in icp
int num_lost_; // number of lost times
// parameters
int num_of_features_; // number of features
double scale_factor_; // scale in image pyramid
int level_pyramid_; // number of pyramid levels
float match_ratio_; // ratio for selecting good matches
int max_num_lost_; // max number of continuous lost times
int min_inliers_; // minimum inliers
//用于判定是否为关键帧的标准,说白了就是规定一定幅度的旋转和平移,大于这个幅度就归为关键帧
double key_frame_min_rot; // minimal rotation of two key-frames
double key_frame_min_trans; // minimal translation of two key-frames
public: // functions
VisualOdometry();
~VisualOdometry();
//这个函数为核心处理函数,将帧添加进来,然后处理。
bool addFrame( Frame::Ptr frame ); // add a new frame
protected:
// inner operation
//一些内部处理函数,这块主要是特征匹配的
void extractKeyPoints();
void computeDescriptors();
void featureMatching();
void poseEstimationPnP();
void setRef3DPoints();
//这里是关键帧的一些功能函数
void addKeyFrame();
bool checkEstimatedPose();
bool checkKeyFrame();
};
}
#endif // VISUALODOMETRY_H- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
类实现,visual_odometry.cpp
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <algorithm>
#include <boost/timer.hpp>
#include "myslam/config.h"
#include "myslam/visual_odometry.h"
namespace myslam
{
//默认构造函数,提供默认值、读取配置参数
VisualOdometry::VisualOdometry():
state_ ( INITIALIZING ), ref_ ( nullptr ), curr_ ( nullptr ), map_ ( new Map ), num_lost_ ( 0 ), num_inliers_ ( 0 )
{
num_of_features_ = Config::get<int> ( "number_of_features" );
scale_factor_ = Config::get<double> ( "scale_factor" );
level_pyramid_ = Config::get<int> ( "level_pyramid" );
match_ratio_ = Config::get<float> ( "match_ratio" );
max_num_lost_ = Config::get<float> ( "max_num_lost" );
min_inliers_ = Config::get<int> ( "min_inliers" );
key_frame_min_rot = Config::get<double> ( "keyframe_rotation" );
key_frame_min_trans = Config::get<double> ( "keyframe_translation" );
//这个create(),之前用的时候,都是用的默认值,所以没有任何参数,这里传入了一些参数,可参见函数定义
orb_ = cv::ORB::create ( num_of_features_, scale_factor_, level_pyramid_ );
}
VisualOdometry::~VisualOdometry()
{
}
//最核心的添加帧,参数即为新的一帧,根据VO当前状态选择是进行初始化还是计算T
bool VisualOdometry::addFrame ( Frame::Ptr frame )
{
//根据VO状态来进行不同处理。
switch ( state_ )
{
//第一帧,则进行初始化处理
case INITIALIZING:
{
//更改状态为OK
state_ = OK;
//因为是初始化,所以当前帧和参考帧都为此第一帧
curr_ = ref_ = frame;
//并将此帧插入到地图中
map_->insertKeyFrame ( frame );
// extract features from first frame
//匹配的操作,提取keypoint和计算描述子
extractKeyPoints();
computeDescriptors();
// compute the 3d position of features in ref frame
//这里提取出的keypoint要形成3d坐标,所以调用setRef3DPoints()去补齐keypoint的depth数据。
setRef3DPoints();
break;
}
//如果为正常,则匹配并调用poseEstimationPnP()函数计算T。
case OK:
{
curr_ = frame;
extractKeyPoints();
computeDescriptors();
featureMatching();
//进行位姿估计
poseEstimationPnP();
//根据位姿估计的结果进行分别处理
if ( checkEstimatedPose() == true ) // a good estimation
{
//好的估计,计算当前位姿
curr_->T_c_w_ = T_c_r_estimated_ * ref_->T_c_w_; // T_c_w = T_c_r*T_r_w
//把当前帧赋值为参考帧
ref_ = curr_;
//补全参考帧的depth数据
setRef3DPoints();
num_lost_ = 0;
//检验一下是否为关键帧,是的话加入关键帧
if ( checkKeyFrame() == true ) // is a key-frame
{
addKeyFrame();
}
}
else // bad estimation due to various reasons
{
//坏的估计将丢失计数+1,并判断是否大于最大丢失数,如果是,将VO状态切换为lost。
num_lost_++;
if ( num_lost_ > max_num_lost_ )
{
state_ = LOST;
}
return false;
}
break;
}
case LOST:
{
cout<<"vo has lost."<<endl;
break;
}
}
return true;
}
//提取keypoint
void VisualOdometry::extractKeyPoints()
{
orb_->detect ( curr_->color_, keypoints_curr_ );
}
//计算描述子
void VisualOdometry::computeDescriptors()
{
orb_->compute ( curr_->color_, keypoints_curr_, descriptors_curr_ );
}
//特征匹配
void VisualOdometry::featureMatching()
{
// match desp_ref and desp_curr, use OpenCV's brute force match
vector<cv::DMatch> matches;
cv::BFMatcher matcher ( cv::NORM_HAMMING );
matcher.match ( descriptors_ref_, descriptors_curr_, matches );
// select the best matches
//寻找最小距离,这里用到了STL中的std::min_element和lambda表达式,单开博客总结
//总之这的作用就是找到matches数组中最小的距离,然后赋值给min_dis
float min_dis = std::min_element (matches.begin(), matches.end(),[] ( const cv::DMatch& m1, const cv::DMatch& m2 )
{
return m1.distance < m2.distance;
} )->distance;
//根据最小距离,对matches数组进行刷选,只有小于最小距离一定倍率或者小于30的才能push_back进数组。
//最终得到筛选过的,距离控制在一定范围内的可靠匹配
feature_matches_.clear();
for ( cv::DMatch& m : matches )
{
if ( m.distance < max<float>( min_dis*match_ratio_, 30.0 ) )
{
feature_matches_.push_back(m);
}
}
cout<<"good matches: "<<feature_matches_.size()<<endl;
}
//说一下这个函数,新的帧来的时候,是一个2D数据,因为PNP需要的是参考帧的3D,当前帧的2D。
//所以在当前帧迭代为参考帧时,有个工作就是加上depth数据。也就是设置参考帧的3D点。
void VisualOdometry::setRef3DPoints()
{
// select the features with depth measurements
//3D点数组先清空,后面重新装入
pts_3d_ref_.clear();
//参考帧的描述子也是构建个空Mat。
descriptors_ref_ = Mat();
//对当前keypoints数组进行遍历
for ( size_t i=0; i<keypoints_curr_.size(); i++ )
{
//找到对应的depth数据赋值给d
double d = ref_->findDepth(keypoints_curr_[i]);
//如果>0说明depth数据正确,进行构造
if ( d > 0)
{
//由像素坐标求得相机下3D坐标
Vector3d p_cam = ref_->camera_->pixel2camera(Vector2d(keypoints_curr_[i].pt.x, keypoints_curr_[i].pt.y), d);
//由于列向量,所以按行构造Point3f,push_back进参考帧的3D点。
pts_3d_ref_.push_back( cv::Point3f( p_cam(0,0), p_cam(1,0), p_cam(2,0) ));
//参考帧描述子这里就按照当前帧描述子按行push_back。这里也可以发现,算出来的Mat类型的描述子,是按行存储为一列,读取时需要遍历行。
descriptors_ref_.push_back(descriptors_curr_.row(i));
}
}
}
//核心功能函数,用PnP估计位姿
void VisualOdometry::poseEstimationPnP()
{
// construct the 3d 2d observations
vector<cv::Point3f> pts3d;
vector<cv::Point2f> pts2d;
//从这里就可以看出,参考帧用的是3D,当前帧用的2D。
for ( cv::DMatch m:feature_matches_ )
{
//这里不一样的,pts_3d_ref_本来就是3dpoint数组,所以直接定位索引就是3d点了
pts3d.push_back( pts_3d_ref_[m.queryIdx] );
//而这里keypoints_curr_是keypoint数组,所以定位索引后类型是keypoint,还需一步.pt获取关键点像素坐标。
pts2d.push_back( keypoints_curr_[m.trainIdx].pt );
}
//构造相机内参矩阵K
Mat K = ( cv::Mat_<double>(3,3)<<
ref_->camera_->fx_, 0, ref_->camera_->cx_,
0, ref_->camera_->fy_, ref_->camera_->cy_,
0,0,1
);
//旋转向量,平移向量,内点数组
Mat rvec, tvec, inliers;
//整个核心就是用这个cv::solvePnPRansac()去求解两帧之间的位姿变化
cv::solvePnPRansac( pts3d, pts2d, K, Mat(), rvec, tvec, false, 100, 4.0, 0.99, inliers );
//内点数量为内点行数,所以为列存储。
num_inliers_ = inliers.rows;
cout<<"pnp inliers: "<<num_inliers_<<endl;
//根据旋转和平移构造出当前帧相对于参考帧的T,这样一个T计算完成了。循环计算就能得到轨迹。
T_c_r_estimated_ = SE3(
SO3(rvec.at<double>(0,0), rvec.at<double>(1,0), rvec.at<double>(2,0)),
Vector3d( tvec.at<double>(0,0), tvec.at<double>(1,0), tvec.at<double>(2,0))
);
}
//简单的位姿检验函数,整体思路就是匹配点不能过少,运动不能过大。
bool VisualOdometry::checkEstimatedPose()
{
// check if the estimated pose is good
//这里简单的做一下位姿估计判断,主要有两个,一就是匹配点太少的话,直接false,或者变换向量模长太大的话,也直接false
if ( num_inliers_ < min_inliers_ )
{
cout<<"reject because inlier is too small: "<<num_inliers_<<endl;
return false;
}
// if the motion is too large, it is probably wrong
//将变换矩阵取log操作得到变换向量。
Sophus::Vector6d d = T_c_r_estimated_.log();
//根据变换向量的模长来判断运动的大小。过大的话返回false
if ( d.norm() > 5.0 )
{
cout<<"reject because motion is too large: "<<d.norm()<<endl;
return false;
}
//如果让面两项都没return,说明内点量不少,运动也没过大,return true
return true;
}
bool VisualOdometry::checkKeyFrame()
{
//说一下这个是否为关键帧的判断,也很简单,
//关键帧并不是之前理解的轨迹比较长了,隔一段选取一个,而还是每一帧的T都判断一下,比较大就说明为关键帧,说明在这一帧中,要么平移比较大,要么拐弯导致旋转比较大,所以添加,如果在运动上一直就是小运动,运动多久都不会添加为关键帧。
//另外上方的判断T计算错误也是运动过大,但是量级不一样,判断计算错误是要大于5,而关键帧,在配置文件中看只需要0.1就定义为关键帧了,所以0.1到5的差距,导致这两个函数并不冲突
Sophus::Vector6d d = T_c_r_estimated_.log();
Vector3d trans = d.head<3>();
Vector3d rot = d.tail<3>();
if ( rot.norm() >key_frame_min_rot || trans.norm() >key_frame_min_trans )
return true;
return false;
}
//关键帧添加,直接调用insertKeyFrame()将当前帧插入就好了。
void VisualOdometry::addKeyFrame()
{
cout<<"adding a key-frame"<<endl;
map_->insertKeyFrame ( curr_ );
}
}