效果示例
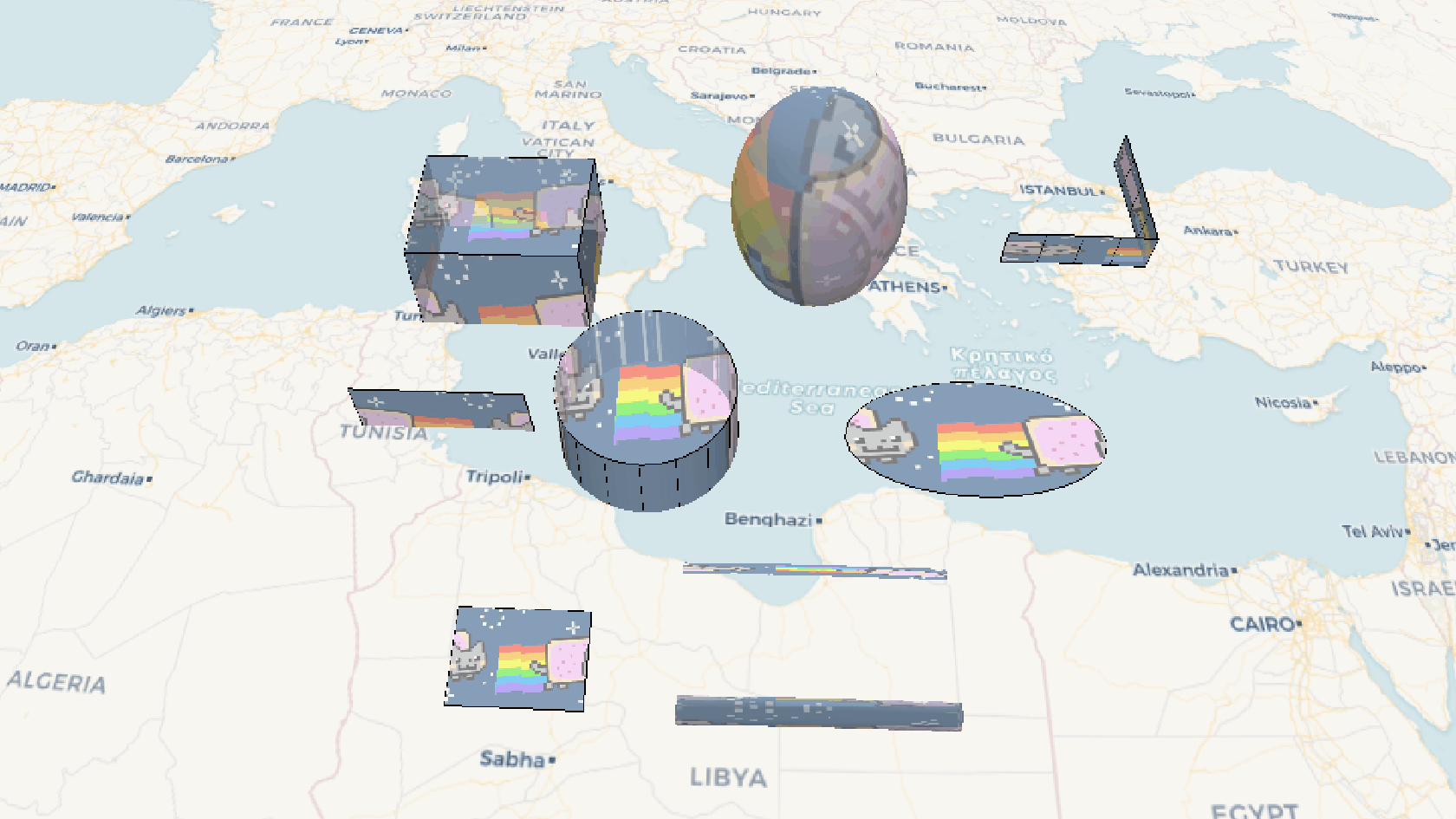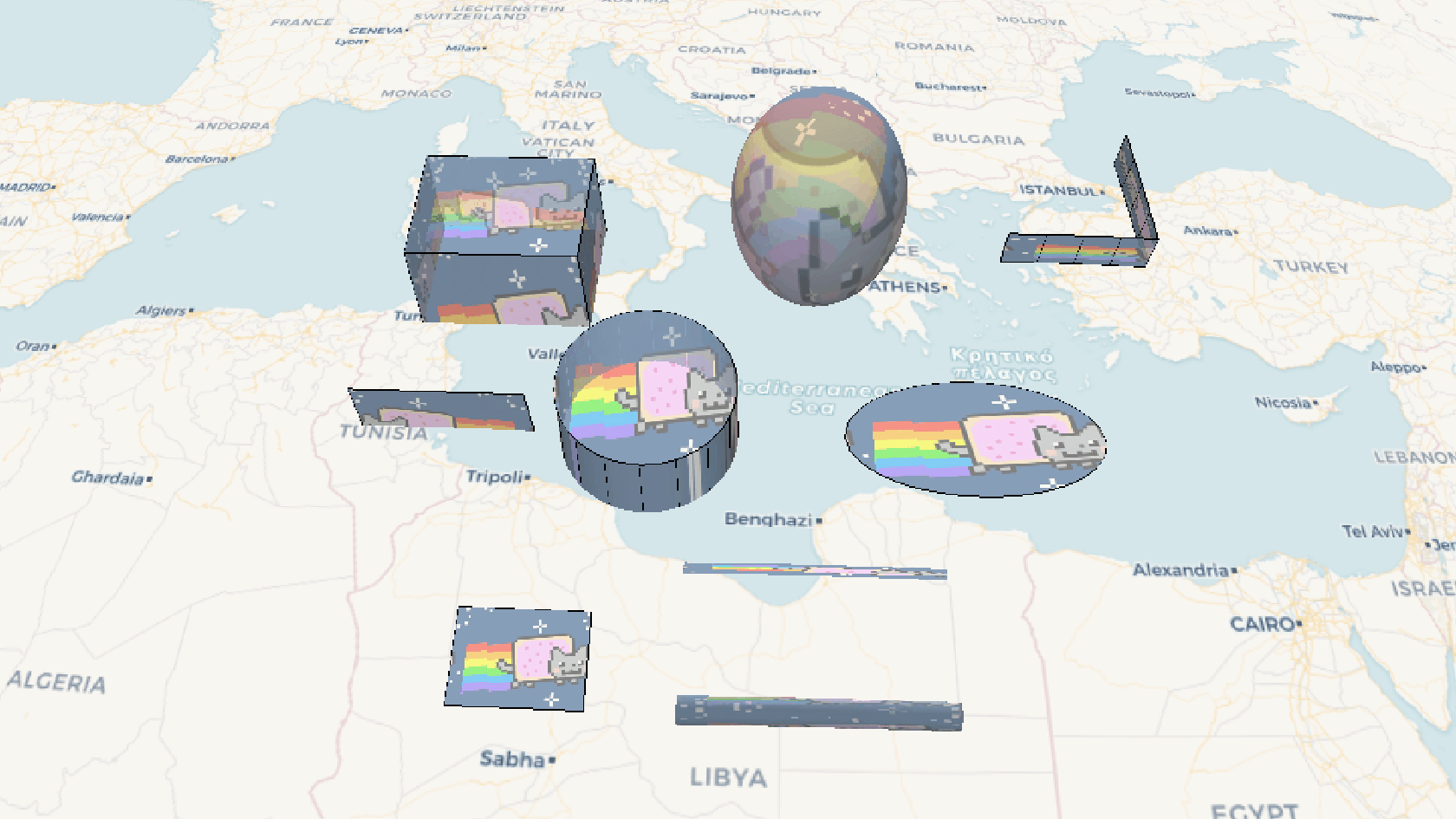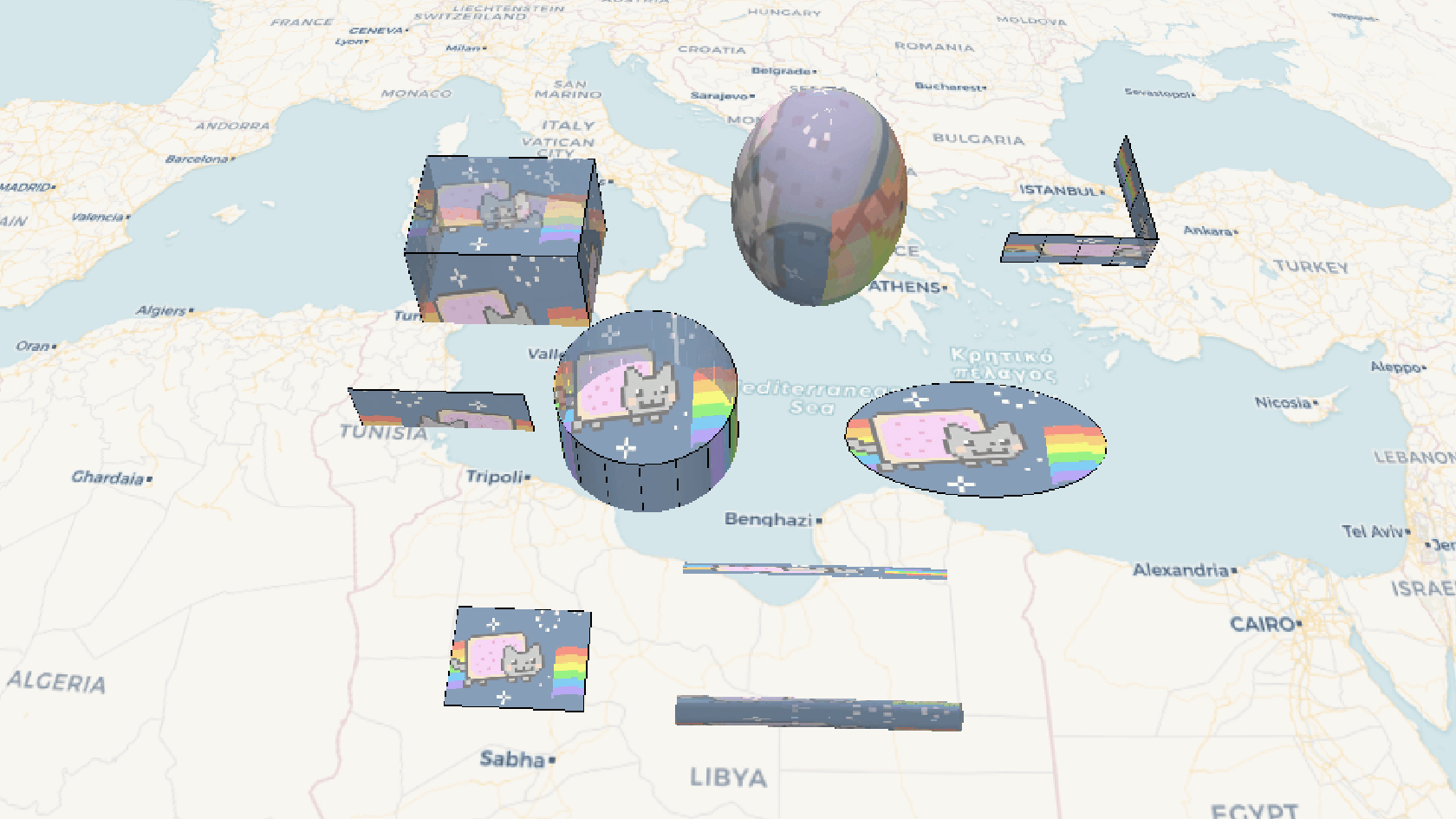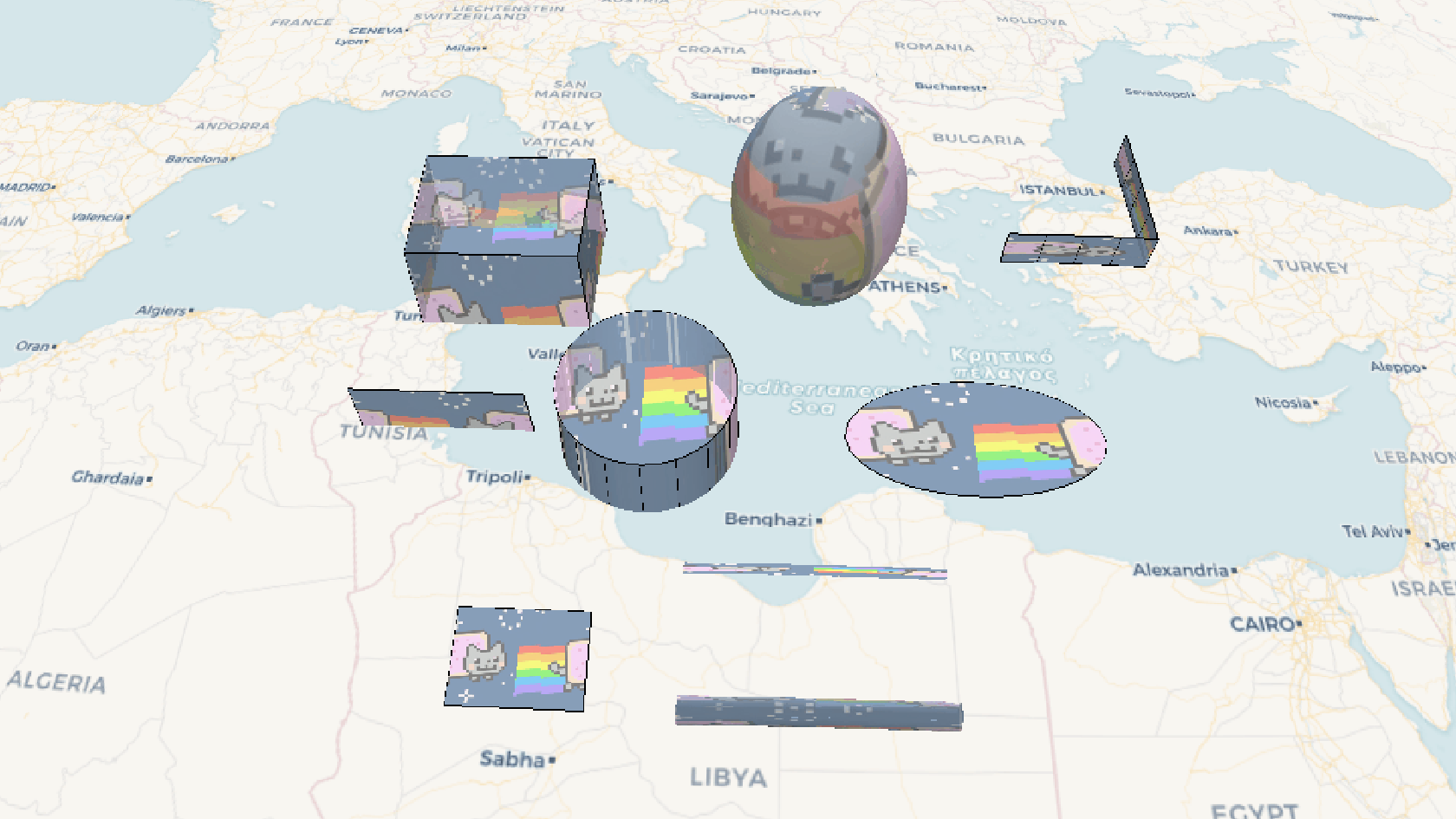
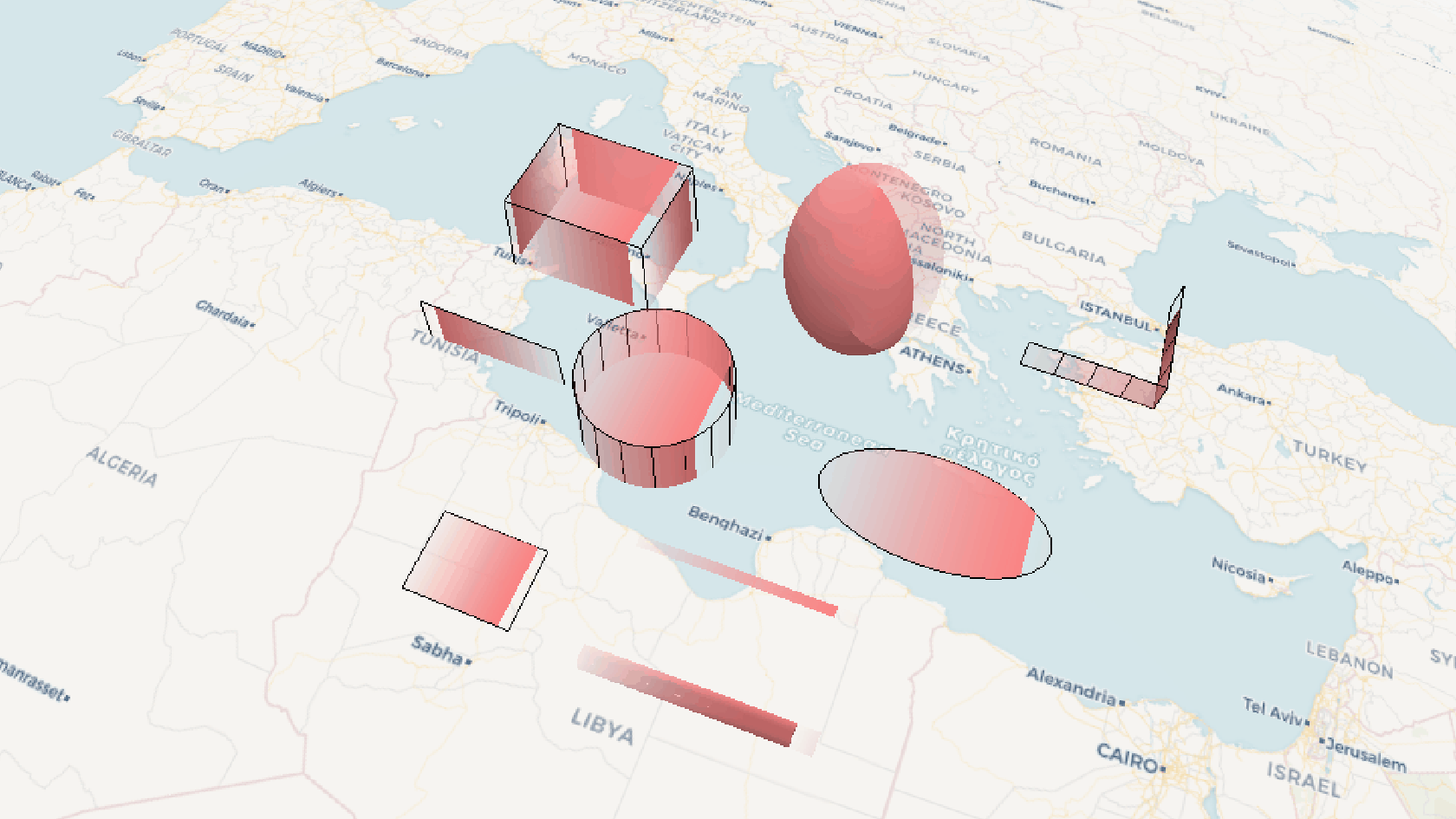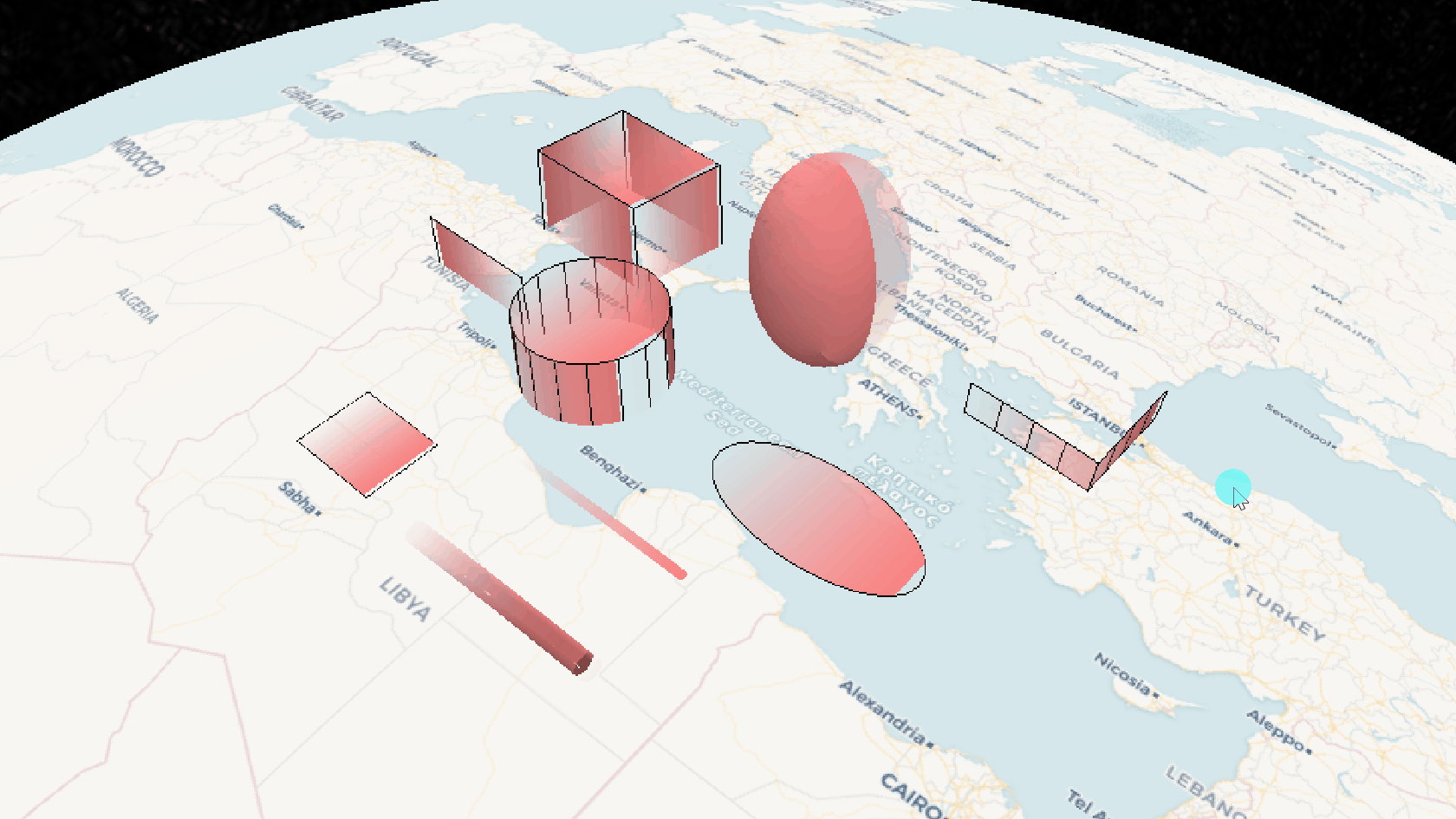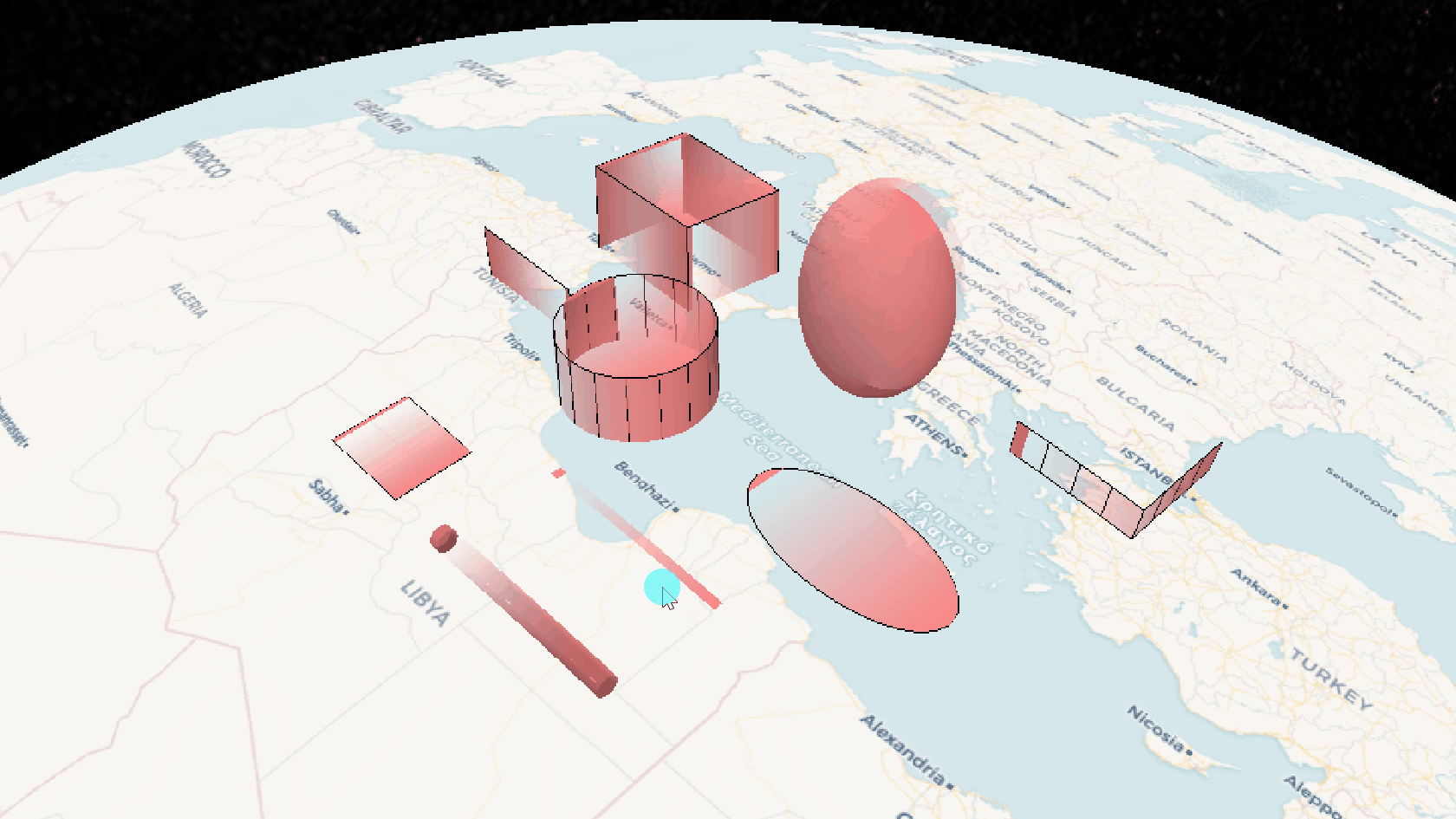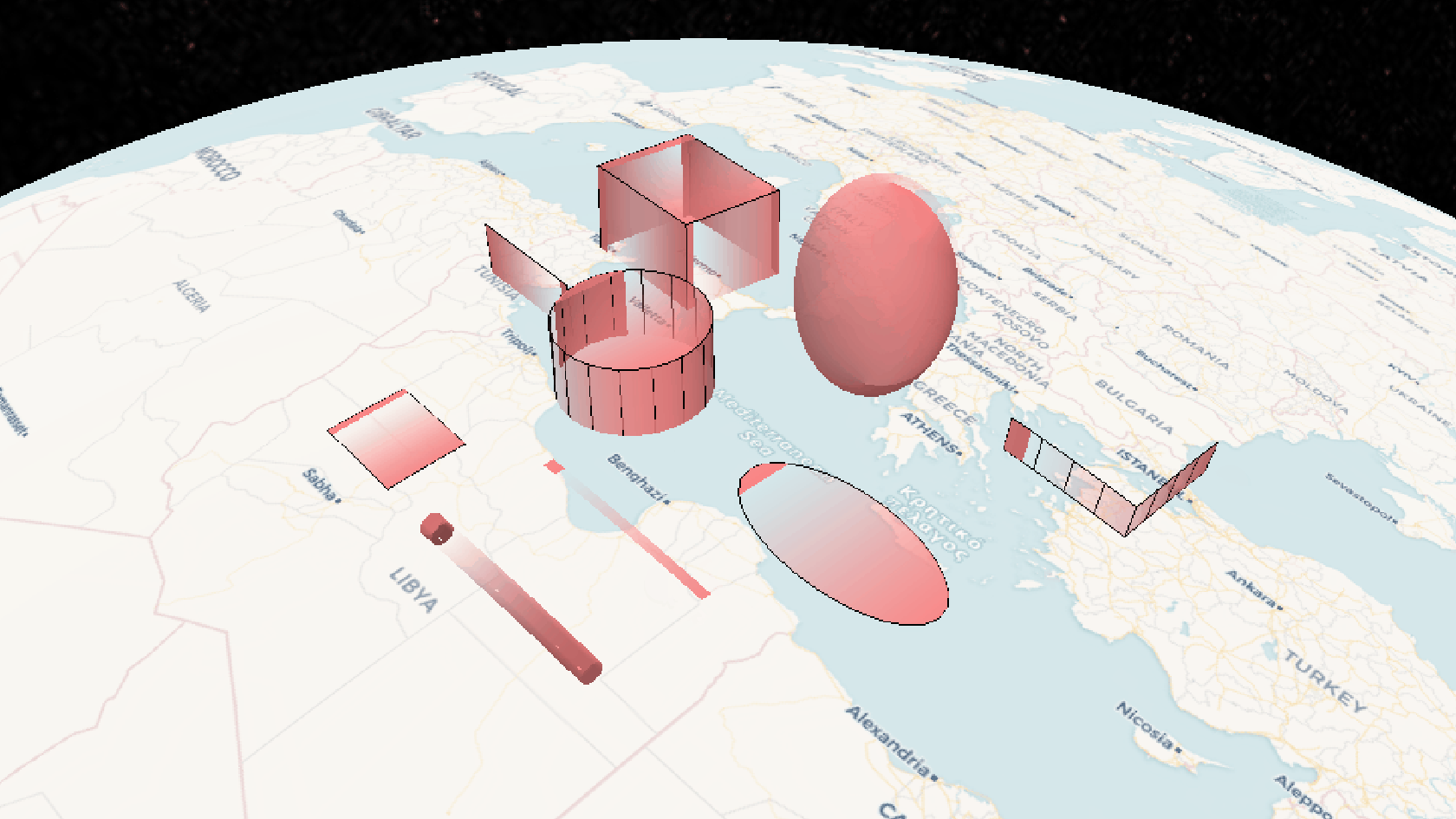
要素说明:
代码
/*
* @Date: 2023-07-19 11:15:22
* @LastEditors: ReBeX [email protected]
* @LastEditTime: 2023-07-28 12:08:58
* @FilePath: \cesium-tyro-blog\src\utils\Material\FlowPictureMaterialProperty.js
* @Description: 流动纹理/图片材质
*/
import * as Cesium from 'cesium'
export default class FlowPictureMaterialProperty {
constructor(options) {
this._definitionChanged = new Cesium.Event();
this._color = undefined;
this._colorSubscription = undefined;
this.image = options.image;
this.color = options.color;
this.duration = options.duration;
this._time = (new Date()).getTime();
};
get isConstant() {
return false;
}
get definitionChanged() {
return this._definitionChanged;
}
getType(time) {
return Cesium.Material.FlowPictureMaterialType;
}
getValue(time, result) {
if (!Cesium.defined(result)) {
result = {
};
}
result.time = (((new Date()).getTime() - this._time) % this.duration) / this.duration;
result.color = Cesium.Property.getValueOrDefault(this._color, time, Cesium.Color.RED, result.color);
// result.color = Cesium.Property.getValueOrClonedDefault(this._color, time, Cesium.Color.WHITE, result.color);
result.image = this.image;
return result
}
equals(other) {
return (this === other ||
(other instanceof FlowPictureMaterialProperty &&
Property.equals(this._color, other._color))
)
}
}
Object.defineProperties(FlowPictureMaterialProperty.prototype, {
color: Cesium.createPropertyDescriptor('color'),
})
// Cesium.FlowPictureMaterialProperty = FlowPictureMaterialProperty;
Cesium.Material.FlowPictureMaterialProperty = 'FlowPictureMaterialProperty';
Cesium.Material.FlowPictureMaterialType = 'FlowPictureMaterialType';
Cesium.Material.FlowPictureMaterialSource =
`
czm_material czm_getMaterial(czm_materialInput materialInput)
{
czm_material material = czm_getDefaultMaterial(materialInput);
vec2 st = materialInput.st;
vec4 colorImage = texture(image, vec2(fract(st.s - time), st.t));
material.alpha = colorImage.a * color.a;
material.diffuse = (colorImage.rgb+color.rgb)/2.0;
return material;
}
`
Cesium.Material._materialCache.addMaterial(Cesium.Material.FlowPictureMaterialType, {
fabric: {
type: Cesium.Material.FlowPictureMaterialType,
uniforms: {
color: new Cesium.Color(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0),
time: 0,
image: ''
},
source: Cesium.Material.FlowPictureMaterialSource
},
translucent: function (material) {
return true;
}
})
console.log('成功加载流动纹理/图片材质');
// ? 如何使用
// import FlowPictureMaterialProperty from '@/utils/Material/FlowPictureMaterialProperty.js'
// material: new FlowPictureMaterialProperty({
// color: new Cesium.Color(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0),
// image: '/src/assets/images/cat.png',
// duration: 3000,
// })
用例
import FlowPictureMaterialProperty from '@/utils/Material/FlowPictureMaterialProperty.js'
import {
viewer } from '@/utils/createCesium.js' // 引入地图对象
import * as Cesium from 'cesium'
const ellipse = viewer.entities.add({
position: Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(50, 50),
ellipse: {
semiMajorAxis: 150000.0, // 长半轴距离
semiMinorAxis: 150000.0, // 短半轴距离
material: new FlowPictureMaterialProperty({
color: Cesium.Color.WHITE, // new Cesium.Color(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0),
image: '/src/assets/images/redBar.png',
duration: 1500,
})
}
});
viewer.zoomTo(ellipse);
着色器
实现一个自定义材质的核心,是fabric对象的source属性,下面是本材质的基于GLSL语法的着色器代码:
czm_material czm_getMaterial(czm_materialInput materialInput)
{
czm_material material = czm_getDefaultMaterial(materialInput);
vec2 st = materialInput.st;
vec4 colorImage = texture(image, vec2(fract(st.s - time), st.t));
material.alpha = colorImage.a * color.a;
material.diffuse = (colorImage.rgb+color.rgb)/2.0;
return material;
}
代码的主要功能是根据输入的 materialInput 创建一个材质对象 material,然后通过对纹理图像和颜色进行处理来修改该材质,并最终返回修改后的材质。以下是代码的解释:
- 创建默认材质:通过调用函数
czm_getDefaultMaterial(materialInput)创建一个默认的材质对象,并将其赋值给变量material。 - 获取纹理坐标和颜色:通过
materialInput.st获取纹理的坐标,并将其赋值给变量st。然后,使用全局变量time对st.s进行计算,得到一个新的纹理坐标vec2(fract(st.s - time), st.t)。接着,使用该纹理坐标从image纹理中读取颜色值,并将其赋值给变量colorImage。 - 修改透明度和漫反射颜色:将
material.alpha设置为colorImage.a乘以color.a,表示材质的透明度是原始颜色和纹理图像的透明度乘积。然后,将material.diffuse设置为colorImage.rgb和color.rgb相加后除以 2.0,表示材质的漫反射颜色是原始颜色和纹理图像的颜色均值。 - 返回修改后的材质:将修改后的材质
material返回作为函数的结果。
其他

