springboot内置Tomcat依赖图

如上图所示Tomcat在spring-boot-starter-web中自动引入
如何修改内置Tomcat属性
如果是正常的Tomcat容器可以通过在conf/web.xml、conf/server.xml文件来修改配置,但内置Tomcat并没有这两个文件,那么如何修改呢?
通过看官方文档知道可以通过server.port属性更改Tomcat端口,由我上篇文章提到的SpringBoot加载规则可以知道必然存在一个ServerProperties来设置默认的Tomcat相关属性,咱们来看下这个类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true)
public class ServerProperties {
/**
* Server HTTP port.
*/
private Integer port;
/**
* Network address to which the server should bind.
*/
private InetAddress address;
/**
中间省略
*/
}
看下哪里调用了getPort()
public class ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer implements
WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory>, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
public ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) {
PropertyMapper map = PropertyMapper.get().alwaysApplyingWhenNonNull();
map.from(this.serverProperties::getPort).to(factory::setPort);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getAddress).to(factory::setAddress);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getContextPath)
.to(factory::setContextPath);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getApplicationDisplayName)
.to(factory::setDisplayName);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getSession).to(factory::setSession);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getSsl).to(factory::setSsl);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getJsp).to(factory::setJsp);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getCompression).to(factory::setCompression);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getHttp2).to(factory::setHttp2);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getServerHeader).to(factory::setServerHeader);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getContextParameters)
.to(factory::setInitParameters);
}
}
可以看到在这里把ServerProperties中的属性都设置到到ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory,所以从这里可以知道在SpringBoot中实际对web容器做定制实际上是修改ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory类的相关属性.再来看下这个customize方法的WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor类
private void postProcessBeforeInitialization(WebServerFactory webServerFactory) {
LambdaSafe
.callbacks(WebServerFactoryCustomizer.class, getCustomizers(),
webServerFactory)
.withLogger(WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor.class)
.invoke((customizer) -> customizer.customize(webServerFactory));
}
通过上面的代码可以看到这里整个过程实际上是获取容器中所有的customizer,往customizer中传入WebServerFactory参数,然后调用customize()方法把ServerProperteis中的属性设置到WebServerFactory中,那我们是不是可以实现这种方式来达到配置服务器属性的目的呢?实际上是可以的,代码如下
@Bean
public WebServerFactoryCustomizer configWebServer(){
WebServerFactoryCustomizer webServerFactoryCustomizer = new WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory>() {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) {
factory.setPort(9000);
}
};
return webServerFactoryCustomizer;
}
再看SpringBoot官方也是通过这种方式来更改web服务器配置的;https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.0.0.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-embedded-container-application-context
总结一下就是修改web服务器配置有两种方式
1、在application.properties中通过server.XXX配置
server.port=8082
server.servlet.context-path=/test
2、通过实现WebServerFactoryCustomizer接口并用其提供的接口来通过ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory的方法来修改
@Bean
public WebServerFactoryCustomizer configWebServer(){
WebServerFactoryCustomizer webServerFactoryCustomizer = new WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory>() {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) {
factory.setPort(9000);
factory.setContextPath("/test");
}
};
return webServerFactoryCustomizer;
}
Servlet容器自动配置原理
我们首先看下ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration这个类
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
@Import({
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class })
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
//中间省略
}
这里引入的几个类比较关键,首先咱们看下BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar
public static class BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar
implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, BeanFactoryAware {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.beanFactory == null) {
return;
}
registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(registry,
"webServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor",
WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor.class);
registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(registry,
"errorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor",
ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor.class);
}
}
这个类实现了spring中的ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar、BeanFactoryAware接口,并在上面的方法中注册了WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor;而这个类就很眼熟了,我们上面刚刚分析过,这里我把代码再贴一下
public class WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor
implements BeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
//在初始化之前执行
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
//如果当前类是一个WebSerFactory
if (bean instanceof WebServerFactory) {
postProcessBeforeInitialization((WebServerFactory) bean);
}
return bean;
}
//调用WebServerFactoryCustomizer的customize对当前的WebServerFactory进行设置
private void postProcessBeforeInitialization(WebServerFactory webServerFactory) {
LambdaSafe
.callbacks(WebServerFactoryCustomizer.class, getCustomizers(),
webServerFactory)
.withLogger(WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor.class)
.invoke((customizer) -> customizer.customize(webServerFactory));
}
}
这个过程就很清晰了,++当spring启动时ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration会添加WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor类,WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor会在bean初始化之前判是否存在WebServerFactory,如果存在的话使用WebServerFactoryCustomizer来对WebServerFactory进行定制,定制的属性是从ServerProperties中读取的++
那么现在还剩下一个问题,WebServerFactory是在哪里定义的?
再看ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration引入的另外一个类ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration
class ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration {
@Configuration
//当系统中有tomcat的关键类,即有tomcat容器时,则注入TomcatServletWebServerFactory
@ConditionalOnClass({
Servlet.class, Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public static class EmbeddedTomcat {
@Bean
public TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory() {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({
Servlet.class, Server.class, Loader.class,
WebAppContext.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public static class EmbeddedJetty {
@Bean
public JettyServletWebServerFactory JettyServletWebServerFactory() {
return new JettyServletWebServerFactory();
}
}
/**
* Nested configuration if Undertow is being used.
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({
Servlet.class, Undertow.class, SslClientAuthMode.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public static class EmbeddedUndertow {
@Bean
public UndertowServletWebServerFactory undertowServletWebServerFactory() {
return new UndertowServletWebServerFactory();
}
}
}
这里可以看到当系统中有Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow容器时,会分别往系统中添加对应的WebServerFactory
那这里我们又可以发现一个事情,也就是说我们想启用jetty或者undertow的话直接引入相关的组件就行了(如果在一个项目中同时引用多个servlet容器默认使用tomcat启动的,感兴趣的可以去了解下为什么)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</dependency>
//或者
<dependency>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</dependency>
我们再来总结一下SpringBoot管理servlet容器的整个过程
- SpringBoot根据导入的依赖情况给容器添加响应的WebServerFactory
- 当有组件要创建对象时会惊动WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor,如果是WebServerFactory则会进行后续处理
- 后续处理,从容器中获取所有的WebServerFactoryCustomizer对WebServerFactory进行定制
- 定制属性从ServerProperties中获取
Servlet容器启动原理
现在我们来分析一下内嵌的servlet容器时在什么时候启动的
这里大家可以再对应的WebServerFactory的getWebServer()方法上打个断点,这样通过栈帧能清楚的看到webServer启动的逻辑,我这里以TomcatServletWebServerFactory为例说一下几个比较关键的点
public class ServletWebServerApplicationContext extends GenericWebApplicationContext
implements ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext {
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context",
ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
}
可以看到这个类重写了spring的ConfigurableApplicationContext类的onRefresh()方法,在onRefresh()方法中调用的createWebServer()方法在createWebServer()中通过调用ServletWebServerFactory的getWebServer()方法来获取webServer.咱们来看下TomcatServletWebServerFactory的getWebServer()做了那些事
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
//new一个tomcat组件
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat"));
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
//设置必要的连接器组件
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
//设置引擎
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
在getTomcatWebServer()方法中有个很重要的地方
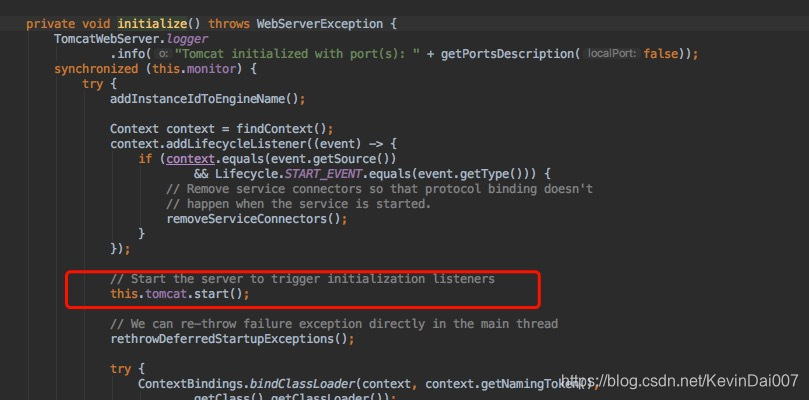
这样tomcat启动的流程咱们也清楚了
- ServletWebServerApplicationContext重写容器的onRefresh(),并在onRefresh()中调用createWebServer()
- createWebServer()获取容器中的ServletWebServerFactory,并调用getWebServer()
- getWebServer()对servlet容器进行初始化并启动
SpringBoot外部servelt容器启动原理
上面我们讲了SpringBoot通过内嵌servlet启动的相关的东西,下面我们分析下SpringBoot在外部servlet容器中是如何启动的
大家都知道要把SpringBoot放到外置servlet容器中运行需要以下几个步骤
- 设置SpringBoot打包的方式为war包
- 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
- 在应用中继承SpringBootServletInitializer类
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(SpringbootApplicationStarter.class);
}
}
这里咱们对比以下内嵌、外部两种方式的启动区别:
内嵌servlet容器:jar包,执行SpringBoot主程序的main(),启动ioc容器,启动servlet容器
外部servlet容器:war包,启动servlet容器,启动SpringBoot,启动ioc容器
想明白这种区别的原理要从servlet3.0的规范说起(见servlet规范 8.2.4 共享库 / 运行时可插拔性)
- 对于每一个应用,应用启动时,由容器创建一个ServletContainerInitializer实例
- ServletContainerInitializer实现必须绑定在jar包的META-INF/services目录中的一个叫做javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 的文件
- 在ServletContainerInitializer实现上的HandlesTypes注解用于表示感兴趣的一些类
根据这三点规范我们看下SpringBoot的启动流程
-
启动Tomcat
-
spring-web模块中META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer,这个文件中定义了org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
-
这个类实现了ServletContainerInitializer
这里我贴一下关键代码

-
可以看到WebApplicationInitializer是一个接口,那看一下它的实现(如下图),可以看到SpringBootServletInitializer(也就是应用中要继承的类)被创建了实例,并调用了onStartUp()方法
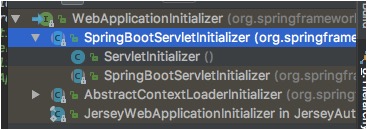
-
咱们把SpringBootServletInitializer关键代码贴出来
public abstract class SpringBootServletInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//创建SpringBuilder
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = this.createSpringApplicationBuilder();
builder.main(this.getClass());
ApplicationContext parent = this.getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (parent != null) {
this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent).");
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, (Object)null);
builder.initializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer[]{
new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent)});
}
builder.initializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer[]{
new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext)});
builder.listeners(new ApplicationListener[]{
new ServletContextApplicationListener(servletContext)});
builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext.class);
//调用configure方法,此方法被子类重写,将SpringBoot主程序传入进来
builder = this.configure(builder);
//使用SpringBuilder创建spring应用
SpringApplication application = builder.build();
if (application.getSources().isEmpty() && AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(this.getClass(), Configuration.class) != null) {
application.getSources().add(this.getClass());
}
Assert.state(!application.getSources().isEmpty(), "No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the configure method or add an @Configuration annotation");
if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) {
application.getSources().add(ErrorPageFilter.class);
}
//启动spring应用,在此方法中通过this.refreshContext(context);来启动ioc容器
return this.run(application);
}
}
Servlet三大组件的注册(Servlet、Filter、Listener)
如果是一个普通的web应用三大组件的注册都是在webapp/web-inf/web.xml中添加配置,而嵌入式的web服务器并没有这个web.xml文件,通过查阅官方文档可以知道,可以通过如下三个组件进行注册ServletRegistrationBean,FilterRegistrationBean,ServletListenerRegistrationBean
这里就贴一下servlet怎么注册,其他就不讲了
public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().println("this is servlet");
}
}
然后在SpringBoot中注册此servlet
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean() {
return new ServletRegistrationBean(new TestServlet(), "/test");// ServletName默认值为首字母小写,即myServlet
}
那这里又引申出一个问题,这个servlet是怎么注册到DispatcherServlet的呢?
这里可以看下DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public ServletRegistrationBean<DispatcherServlet> dispatcherServletRegistration(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet) {
ServletRegistrationBean<DispatcherServlet>
//这里this.serverProperties.getServlet().getServletMapping()的值是"/",既默认dispatcherServlet默认处理当前项目下所有请求
registration = new ServletRegistrationBean<>(
dispatcherServlet,this.serverProperties.getServlet().getServletMapping());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup( this.webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
if (this.multipartConfig != null) {
registration.setMultipartConfig(this.multipartConfig);
}
return registration;
}
看了上面的代码我们可以知道,如果想在SpringBoot中注册多个DispatcherServlet只需要注册ServletRegistrationBean即可,大致代码如下
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean foo() {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
applicationContext.register(FooConfig.class);
dispatcherServlet.setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet, "/foo/*");
servletRegistrationBean.setName("foo");
return servletRegistrationBean;
}
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean bar() {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
applicationContext.register(BarConfig.class);
dispatcherServlet.setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet, "/bar/*");
servletRegistrationBean.setName("bar");
return servletRegistrationBean;
}