堆的应用一:topk问题
文章目录
前言
堆的应用(topk)会涉及到大量的堆的知识:如果有不理解的可以参考 : 堆的模拟实现
一、题目
在N个数中找出最大的前K个数 或者 在N个数中找出最小的前K个数
要求:时间复杂度优化到 O(N)

二、思路+图解
1.思路一:
先排降序,前10个数就是最大的前10个。时间复杂度 : O(N*logN)
2.思路二:
N个数插入大堆,pop k次,每次堆顶的数据就为前 K 个。 时间复杂度 : O(N+logN*K)–>证明如下:

3.思路三:
假设N非常大,N=10亿,内存中存不下这些数,他们存在文件中。k=100,思路一和思路二都不能用了(存不下)
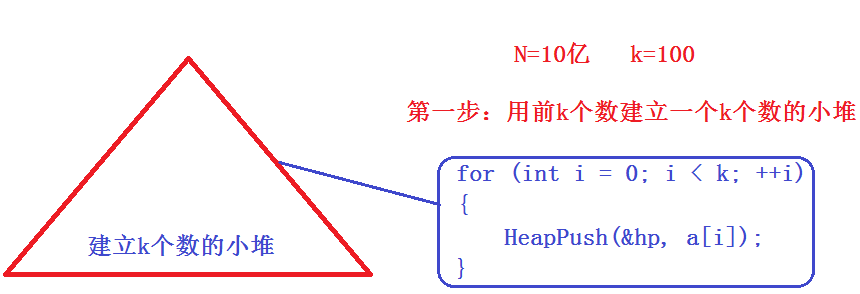

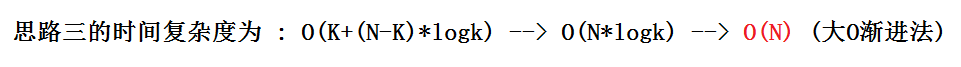
实数图解
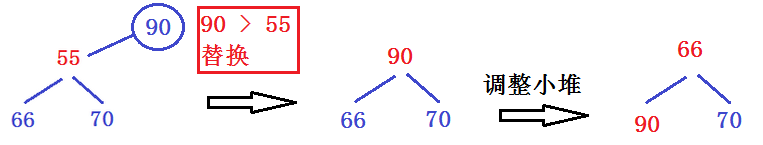
为了方便,我们把 N 为 5 , 把 k 设为 3,即在5个数中找出最大的前 3 个数字!
这五个数分别为 66 12 70 55 90
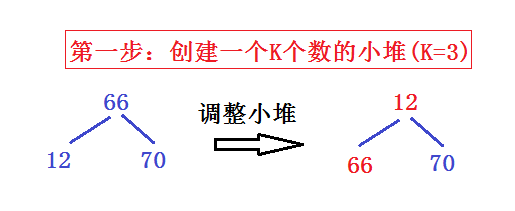
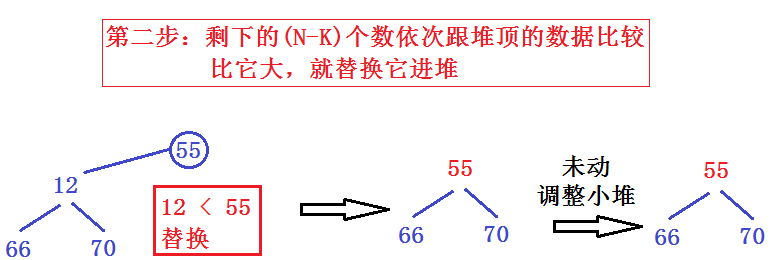
再依次重复第二步:直到N-K个数都和堆顶元素比较,这样既节省空间又加快效率
三、代码测试-源代码
1.生成100w个随机数字
这里我们用 rand 和 srand 两个函数来生成随机数!
代码如下(示例):
int n = 1000000;
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
srand(time(0));
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
a[i] = rand() % 1000000;
}
2.设置10个比100w大的数字
这里随机找100w里的坐标来改变数字大小!
代码如下(示例):
a[5] = 1000000 + 1;
a[1231] = 1000000 + 2;
a[5355] = 1000000 + 3;
a[51] = 1000000 + 4;
a[15] = 1000000 + 5;
a[2335] = 1000000 + 6;
a[9999] = 1000000 + 7;
a[76] = 1000000 + 8;
a[423] = 1000000 + 9;
a[3144] = 1000000 + 10;
3.topk函数的实现
代码如下(示例):
void PrintTopK(int* a, int n, int k)
{
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
// 创建一个K个数的小堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
// 剩下的N-K个数跟堆顶的数据比较,比他大,就替换他进堆
for (int i = k; i < n; ++i)
{
if (a[i] > HeapTop(&hp))
{
//HeapPop(&hp);
//HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
hp.a[0] = a[i];
AdjustDown(hp.a, hp.size, 0);
}
}
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapDestroy(&hp);
}
4.整体源代码
代码如下(示例):
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
HPDataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}HP;
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child);//向上调整
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent);//向下调整
void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py);//交换
void HeapInit(HP* hp);//初始化堆
void HeapDestroy(HP* hp);//销毁堆
void HeapPush(HP* hp, HPDataType x);//尾插数据
void HeapPop(HP* hp);//删除堆顶的数据
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* hp);//取堆顶的数据
void HeapPrint(HP* hp);//打印堆(数组)
bool HeapEmpty(HP* hp);//判断堆是否为空
int HeapSize(HP* hp);//堆结点个数
void Swap(HPDataType * px, HPDataType * py)
{
HPDataType tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
}
void HeapInit(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
}
void HeapDestroy(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
free(hp->a);
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child)
{
assert(a);
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
//while (parent >= 0)
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[child] > a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void HeapPrint(HP* hp)
{
for (int i = 0; i < hp->size; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", hp->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void HeapPush(HP* hp, HPDataType x)
{
assert(hp);
if (hp->size == hp->capacity)
{
size_t newCapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;
HPDataType* tmp = realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
hp->a = tmp;
hp->capacity = newCapacity;
}
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1);
}
bool HeapEmpty(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size == 0;
}
int HeapSize(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size;
}
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(hp));
return hp->a[0];
}
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < n)
{
// 选出左右孩子中小的那一个
if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] < a[child])
{
++child;
}
// 如果小的孩子小于父亲,则交换,并继续向下调整
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 删除堆顶的数据
void HeapPop(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(hp));
Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;
AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);
}
// 在N个数找出最大的前K个 or 在N个数找出最小的前K个
void PrintTopK(int* a, int n, int k)
{
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
// 创建一个K个数的小堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
// 剩下的N-K个数跟堆顶的数据比较,比他大,就替换他进堆
for (int i = k; i < n; ++i)
{
if (a[i] > HeapTop(&hp))
{
//HeapPop(&hp);
//HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
hp.a[0] = a[i];
AdjustDown(hp.a, hp.size, 0);
}
}
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapDestroy(&hp);
}
void TestTopk()
{
int n = 1000000;
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
srand(time(0));
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
a[i] = rand() % 1000000;
}
// 再去设置10个比100w大的数
a[5] = 1000000 + 1;
a[1231] = 1000000 + 2;
a[5355] = 1000000 + 3;
a[51] = 1000000 + 4;
a[15] = 1000000 + 5;
a[2335] = 1000000 + 6;
a[9999] = 1000000 + 7;
a[76] = 1000000 + 8;
a[423] = 1000000 + 9;
a[3144] = 1000000 + 10;
PrintTopK(a, n, 10);
}
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文介绍了 堆排序的应用之一:topk问题!
如果我的博客对你有所帮助记得三连支持一下,感谢大家的支持!
