第 9 章 哈希表
1、Google 上机题
- 看一个实际需求, google 公司的一个上机题:
- 有一个公司,当有新的员工来报道时,要求将该员工的信息加入(id, 性别, 年龄, 住址…),当输入该员工的 id 时,要求查找到该员工的所有信息
- 要求:不使用数据库,尽量节省内存,速度越快越好 => 哈希表(散列)
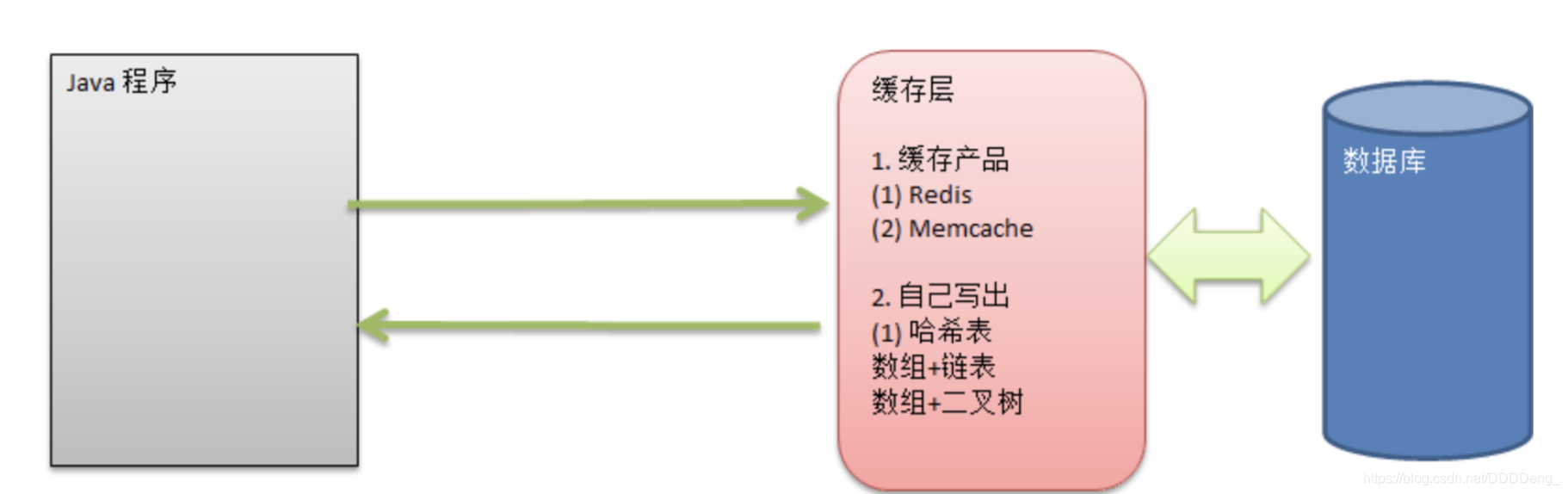
2、哈希表基本介绍
-
散列表(Hash table, 也叫哈希表) ,是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。
-
它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录, 以加快查找的速度。 这个映射函数叫做散列函数, 存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
-
哈希表的核心:private EmpLinkedList[] empLinkedListArray;
-
哈希表编程思路:
- 先根据对象的信息将其散列,得到 hashCode
- 根据对象的 hashCode 值,找到对应的数组下标,其实就是找到存储对象的链表
- 在链表中进行相应的增删改查操作

3、代码实现
3.1、Emp 节点
// 表示一个雇员
class Emp {
public int id;
public String name;
public Emp next; // next默认为null
public Emp(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
3.2、Emp 链表
// 创建EmpLinkedList,表示链表
class EmpLinkedList {
// 头指针,执行第一个Emp,因此我们这个链表的head是直接指向第一个Emp
public Emp head; // 默认为null
// 添加雇员到链表
// 说明
// 1. 假定,当添加雇员时,id是自增长,即id的分配总是从小到大
// 因此我们将该雇员直接加入到本链表的最后即可
public void add(Emp emp) {
if (head == null) {
head = emp;
return;
}
// 如果不是第一个雇员,则使用一个辅助的指针,帮助定位到最后
Emp curEmp = head;
while (true) {
if (curEmp.next == null) {
// 说明到链表最后
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next; // 后移
}
curEmp.next = emp;
}
// 遍历链表的雇员信息
public void list(int no) {
if (head == null) {
// 说明链表为空
System.out.println("第" + (no + 1) + "条链表为空");
return;
}
System.out.println("第" + (no + 1) + "条链表信息为:");
Emp curEmp = head;
while (true) {
System.out.println(curEmp);
if (curEmp.next == null) {
// 说明curEmp已经到最后
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
}
// 根据id查找雇员
// 如果找到,就返回Emp,如果没有找到,就返回null
public Emp findEmpById(int id) {
// 首先判断链表是否为空
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return null;
}
// 辅助指针
Emp curEmp = head;
while (true) {
if (curEmp.id == id) {
// 找到
break;
}
// 退出
if (curEmp.next == null) {
// 说明遍历当前链表没有找到该雇员
curEmp = null;
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
return curEmp;
}
}
3.3、Emp 哈希表
// 创建HashTab管理多条链表
class HashTab {
private EmpLinkedList[] empLinkedListArray;
private int size; // 表示有多少条链表
// 构造器
public HashTab(int size) {
this.size = size;
// 初始化empLinkedListArray
empLinkedListArray = new EmpLinkedList[size];
// 要初始化hashTab中的每一个链表
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
empLinkedListArray[i] = new EmpLinkedList();
}
}
// 添加雇员
public void add(Emp emp) {
// 根据员工id,得到该员工应该添加到哪条链表
int empLinkedListNo = hashFun(emp.id);
// 将emp添加到对应的链表中
empLinkedListArray[empLinkedListNo].add(emp);
}
// 遍历所有的链表,遍历hashtable
public void list() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
empLinkedListArray[i].list(i);
}
}
// 根据输入的id,查找雇员
public void findEmpById(int id) {
// 使用三列函数确定到哪条链表查找
int empLinkedListNO = hashFun(id);
Emp emp = empLinkedListArray[empLinkedListNO].findEmpById(id);
if (emp != null) {
// 找到
System.out.printf("在第%d条链表中找到雇员 id = %d\n", (empLinkedListNO + 1), id);
} else {
System.out.println("在哈希表中,没有找到该雇员!");
}
}
// 编写散列函数,使用一个简单取模法
public int hashFun(int id) {
return id % size;
}
}
3.4、代码测试
public class HashTableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建哈希表
HashTab hashTab = new HashTab(7);
// 写一个简单的菜单
String key = "";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("add : 添加雇员");
System.out.println("list : 显示雇员");
System.out.println("find : 查找雇员");
System.out.println("exit : 退出系统");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key) {
case "add":
System.out.println("输入id");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入名字");
String name = scanner.next();
// 创建雇员
Emp emp = new Emp(id, name);
hashTab.add(emp);
break;
case "list":
hashTab.list();
break;
case "find":
System.out.println("请输入要查找的id");
id = scanner.nextInt();
hashTab.findEmpById(id);
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}