(1)选择排序
①原理:
每一次从无序区间选出最大(或最小)的一个元素,存放在无序区间的最后(或最前),直到全部待排序的数据元素 排完 。
②代码实现:
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 选择排序
*/
public class selectSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={
5,1,25,4,8,11,5,7,5,0};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
select(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
public static void select(int[] array){
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<array.length;j++){
if(array[j]<array[i]){
int tmp=array[j];
array[j]=array[i];
array[i]=tmp;
}
}
}
}
}
运行截图:

③性能分析
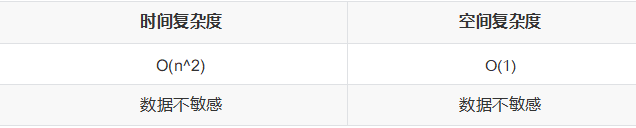 稳定性: 不稳定
稳定性: 不稳定
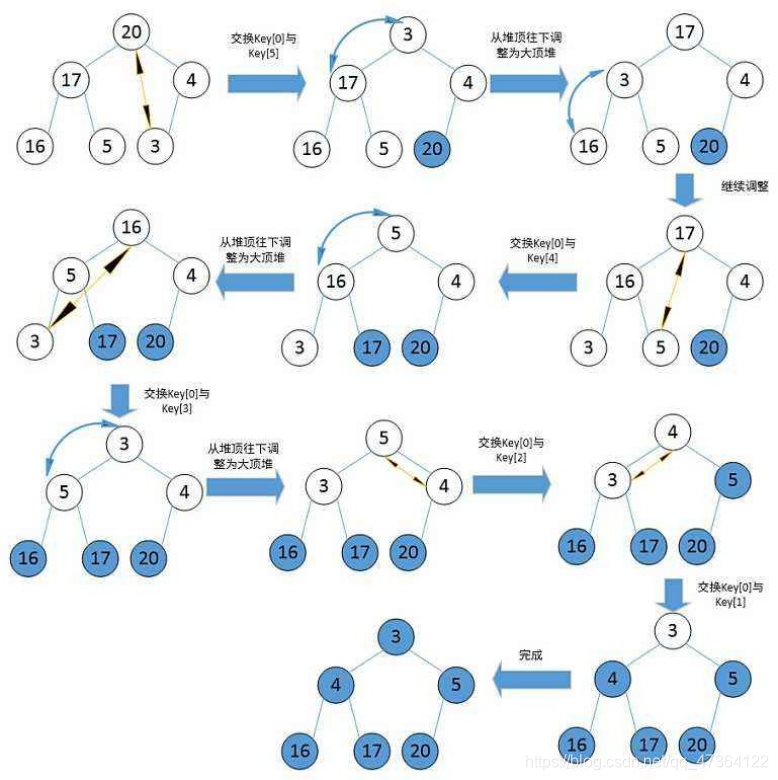
(2)堆排序
①原理:
基本原理也是选择排序,只是不在使用遍历的方式查找无序区间的最大的数,而是通过堆来选择无序区间的最大的数。
注意: 排升序要建大堆;排降序要建小堆。
②代码实现:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HeapSort {
//堆排序测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeapSort heapSort=new HeapSort();
int[] array={
27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
heapSort.createBigHeap(array);
heapSort.show();
System.out.println();
heapSort.heapSort();
heapSort.show();
}
public int[] elem;
public int useDsize;
public HeapSort(){
this.elem=new int[10];
}
//向下调整
public void adjustDown(int parent,int len){
int child=2*parent+1;
while(child<len){
if(child+1<len && this.elem[child]<this.elem[child+1]){
child++;
}
if(this.elem[child]>this.elem[parent]){
int tmp=this.elem[child];
this.elem[child]=this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent]=tmp;
parent=child;
child=parent*2+1;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
//创建大根堆
public void createBigHeap(int[] array){
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
this.elem[i]=array[i];
useDsize++;
}
for (int i = (this.useDsize-1-1)/2; i >=0 ; i--) {
adjustDown(i,this.useDsize);
}
}
//堆排序,先建大堆,后向下调整
public void heapSort() {
int end = this.useDsize - 1;
while (end > 0) {
int tmp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[end];
this.elem[end] = tmp;
adjustDown(0, end);
end--;
}
}
//打印所排序的数组
public void show(){
for(int i=0;i<useDsize;i++){
System.out.print(this.elem[i]+" ");
}
}
}
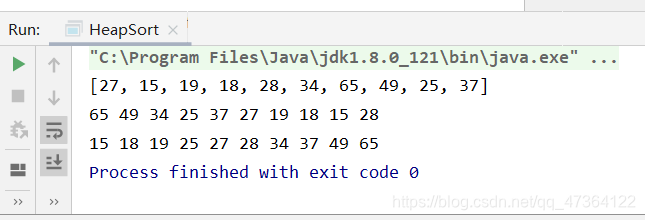
运行截图:
③性能分析
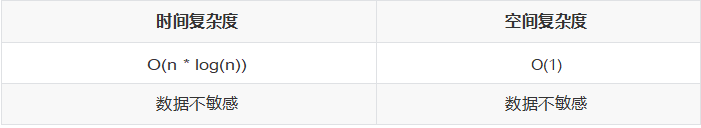 稳定性:不稳定
稳定性:不稳定