排序
各种排序代码实现
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
int testTime = 500000;//测试次数
int size = 100;
int scope = 100;
boolean flag = true;
for(int i = 0; i < testTime; i++){
int[] a = generateRandomArray(size, scope);
int[] b = copyArray(a);
heapSort2(a);
compare(b);
if(isEqual(a, b) == false){
flag = false;
print(a);
print(b);
break;
}
}
System.out.println(flag);
}
//测试
public static void compare(int[] a){
Arrays.sort(a);
}
/*
归并排序
O(N*logN) O(N) 稳定
递归的时间复杂度估计之
master公式: T(N) = a*T(N/b) + O(N^d)
log(b, a) = d ---> O((N^d)*logN)
log(b, a) < d ---> O(N^d)
log(b, a) > d ---> O(N^(log(b, a)))
a是调用子问题次数,N是父问题规模,N/b是子问题规模,O(N^d)是除了调用子问题之外的时间复杂度。
从形式上来看,也可以看出来这个公式表明父问题平均分成了规模相同的若干个子问题才可以用下面的结论。
*/
public static void mergeSort(int[] a){
if(a == null || a.length < 2){
return;
}
mergeSort(a, 0, a.length-1);
}
public static void mergeSort(int[] a, int l, int r){
if(l == r){
return;
}
int mid = l + ((r-l)>>1);
mergeSort(a, l, mid);
mergeSort(a, mid+1, r);
merge(a, l, mid, r);
}
public static void merge(int[] a, int l, int mid, int r){
int i = l;
int j = mid + 1;
int[] tmp = new int[r-l+1];
int cnt = 0;
while(i <= mid && j <= r){
if(a[i] <= a[j]){
tmp[cnt++] = a[i++];
}else{
tmp[cnt++] = a[j++];
}
}
while(i <= mid){
tmp[cnt++] = a[i++];
}
while(j <= r){
tmp[cnt++] = a[j++];
}
for(int k = 0; k < cnt; k++){
a[k+l] = tmp[k];
}
}
/*
选择排序
O(N^2) O(1) 不稳定,如8 2 8 7 9第二次选择7与8交换导致两个8与原来的顺序颠倒
*/
public static void selectSort(int[] a){
if(a == null || a.length < 2){
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++){
int minIndex = i;
for(int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++){
minIndex = a[j] < a[minIndex] ? j : minIndex;
}
swap(a, minIndex, i);
}
}
public static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j){
int tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
/*
冒泡排序
O(N^2) O(1) 稳定
*/
public static void bubbleSort(int[] a){
if(a == null || a.length < 2){
return;
}
for(int i = a.length - 1; i >= 1; i--){
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++){
if(a[j] > a[j+1]){
swap(a, j, j+1);
}
}
}
}
/*
插入排序
O(N)-O(N^2) O(1) 稳定
*/
public static void insertSort(int[] a){
if(a == null || a.length < 2){
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++){
for(int j = i-1; j >= 0 && a[j+1] < a[j]; j--){
swap(a, j, j+1);
}
}
}
/*
快速排序
O(N*logN)-O(N^2) O(logN)-O(N)
不稳定,比如6,6,6,4序列,当前数是第一个6,划分参考值是5,6>5,和大于区左边数4交换
*/
public static void quickSort(int[] a){
if(a == null || a.length < 2){
return;
}
quickSort(a, 0, a.length-1);
}
public static void quickSort(int[] a, int l, int r){
if(l < r){
int[] tmp = partition(a, l, r);
quickSort(a, l, tmp[0]-1);
quickSort(a, tmp[1]+1, r);
}
}
public static int[] partition(int[] a, int l, int r){
int small = l - 1;
int big = r + 1;
int cur = l;
int pivot = l + (int)(Math.random()*(r-l+1));
int v = a[pivot]; // 没改进前,v也不可是a[l],因为a[l]可能交换到后面导致a[l]值变化
while(cur < big){
if(a[cur] > v){
swap(a, cur, --big);
}else if(a[cur] < v){
swap(a, cur++, ++small);
}else{
cur++;
}
}
return new int[]{
small+1, big-1};
}
/*
堆排序(直接用JavaAPI)
O(N*logN) O(1) 不稳定,不稳定,如4 1 2 2第一步形成小根堆,就已不稳定了
*/
public static void heapSort1(int[] a){
if(a == null || a.length < 2){
return;
}
//默认就是小根堆,下面的比较器没必要传入,下面是为了帮助用大根堆的时候这样用
PriorityQueue<Integer> que = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(100, new Comparator<Integer>(){
public int compare(Integer x, Integer y){
return x - y;
}
});
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
que.add(a[i]);
}
int cnt = 0;
while(!que.isEmpty()){
a[cnt++] = que.poll();
}
}
/*
堆排序(手动实现)
*/
public static void heapSort2(int[] a){
if(a == null || a.length < 2){
return;
}
//1.先把数组调成大根堆
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
heapInsert(a, i);
}
//2.大根堆堆顶元素和堆尾元素交换,堆大小减1,堆顶元素下沉操作
int heapSize = a.length;
swap(a, 0, --heapSize);
//3.重复2操作,直到堆大小为0
while(heapSize > 0){
heapify(a, 0, heapSize);
swap(a, 0, --heapSize);
}
}
public static void heapInsert(int[] a, int index){
while(a[index] > a[(index-1)/2]){
swap(a, index, (index-1)/2);
index = (index-1)/2;
}
}
public static void heapify(int[] a, int index, int heapSize){
int left = 2*index + 1;
while(left < heapSize){
int right = left + 1;
int big = left;
if(right < heapSize && a[right] > a[left]){
big = right;
}
if(a[index] >= a[big]){
big = index;
}
if(big == index){
break;
}
swap(a, big, index);
index = big;
left = 2*index + 1;
}
}
//产生随机数组,数组大小自己设定,数组中元素的值范围是[0, scope]
//Math.random()---double---[0,1)
//Math.random()*x---double---[0,x)
//(int)(Math.random()*x)---int---[0,x-1]
public static int[] generateRandomArray(int size, int scope){
int[] a = new int[(int)((size+1)*Math.random())];
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
a[i] = (int)((scope+1)*Math.random()) - (int)(scope*Math.random());
}
return a;
}
//拷贝数组
public static int[] copyArray(int[] a){
if(a == null){
return null;
}
int[] b = new int[a.length];
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
b[i] = a[i];
}
return b;
}
//测试
public static boolean isEqual(int[] a, int[] b){
if(a != null && b == null){
return false;
}
if(a == null && b != null){
return false;
}
if(a == null && b == null){
return true;
}
if(a.length != b.length){
return false;
}
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
if(a[i] != b[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void print(int[] a){
if(a == null){
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
快排的partition过程:
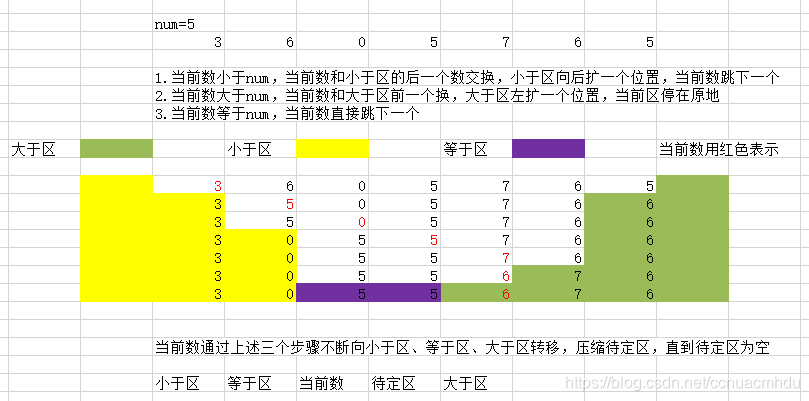
上面各种排序的过程中用了对数器:
1,有一个你想要测的方法a;
2,实现复杂度不好但是容易实现的方法b;
3,实现一个随机样本产生器;
4,把方法a和方法b跑相同的随机样本,看看得到的结果是否一样;
5,如果有一个随机样本使得比对结果不一致,打印样本进行人工干预,改对方法a或者方法b;
6,当样本数量很多时比对测试依然正确,可以确定方法a已经正确。
各种排序算法分析
稳定性
排序之后原来相等元素的相对顺序不变,则是稳定排序,否则不稳定。不基于比较的排序(桶排序)是稳定的。
冒泡排序:严格比右边相邻数大的时候才与右边相邻数交换,就可保证稳定;如果与右边相邻数相等也与右边的相邻数交换,那就不稳定了。
插入排序:严格比左边小的时候才往前搜索插入就能稳定;如果相等的话也往前继续搜索并插入,那就不稳定了。
选择排序:不稳定。 8 1 8 7 9 简单选择排序: 第二次外循环8和8的相对顺序就发生了改变。
归并排序:左右两侧合并的时候,当左右两侧值相等的时候,先合并左侧的数,就可用保证稳定;如果先合并右边的数就不稳定了。
快速排序:不稳定。比如6,6,6,4序列,当前数是第一个6,划分参考值是5,由于6大于5,会和大于区左边一个数4交换,导致不稳定。
堆排序:不稳定。在堆上调整的过程本身就不是稳定的,堆排序的第一步把不断调成大根堆的过程中,比如序列7,3,6,6形成大根堆的过程中,就已经不稳定了。
堆
1,堆结构就是用数组实现的完全二叉树结构
2,完全二叉树中如果每棵子树的最大值都在顶部就是大根堆
3,完全二叉树中如果每棵子树的最小值都在顶部就是小根堆
用数组表示完全二叉树,a[i]的左孩子是a[i2+1],a[i]的右孩子是a[i2+2],a[i]的父亲是a[(i-1)/2]。
堆的大小可以用一个专用的变量表示,和相应数组大小不一样。
heapInsert:对于大根堆(小根堆类似)来说:往堆里面新插入某元素。需要不断看他的父亲,比父亲大就要和父亲交换。此函数还可以解决某个元素变大的情况,某元素变大了,也需要类似的调整。
//往上浮
//index表示新插入堆的元素对应到数组中的下标,或者也可表示值变大的元素下标
public static void heapInsert(int[] a, int index){
//注意当index=0的时候,while的循环条件变成了a[0]>a[0]显然不成立,while循环结束
while(a[index] > a[(index-1)/2]){
swap(a, index, (index-1)/2);
index = (index-1)/2;
}
}
heapify:对于大根堆(小根堆类似)来说:某个元素变小的话,得往下沉,和自己的左右孩子比较,如果比孩子小,与最大的且比自己大的孩子交换,不断重复这个过程,要注意左右孩子未必都存在,还要注意会不会越界,由于是完全二叉树,如果没左孩子,必定没右孩子。
//往下沉
public static void heapify(int[] a, int index, int heapSize){
int left = index*2+1;
while(left < heapSize){//保证不越界
int right = left + 1;//右孩子
int largest = left;//largest表示父亲、左右孩子三者中的最大值对应的下标
if(right < heapSize && a[right] > a[left]){//如果右孩子且右孩子比左孩子大
largest = right;
}
if(a[index] >= a[largest]){//此处用了等号,父亲不比孩子小就不要下沉了
largest = index;
}
//以上求出来了父亲、左右孩子三者中的最大值对应的下标是largest
if(largest == index){//如果父亲、左右孩子三者中的最大值就是父亲,就不需要调整了
break;
}
swap(a, largest, index);
index = largest;//更新当前节点
left = index*2 + 1;//更新当前节点的左孩子,循环求解
}
}
问题:已经建好的大根堆,要求弹出最大的那个数。
只需要把最大的数和堆的最后一个数交换,然后把这个最大的数给用户,然后做一次heapify就又变成大根堆了。
问题:已经建立号的大根堆,某个数变了,但不知道变大还是变小了,要求重新调整到大根堆。
只需要进行尝试,分别尝试heapInsert和heapify,这两个显然只有一个能做成,就调成大根堆了。时间复杂度还是O(logN)
小和问题
小和问题
在一个数组中,每一个数左边比当前数小的数累加起来,叫做这个数组的小和。求一个数组 的小和。例子:[1,3,4,2,5] 1左边比1小的数,没有; 3左边比3小的数,1; 4左边比4小的数,1、3; 2左边比2小的数,1; 5左边比5小的数,1、3、4、2; 所以小和为1+1+3+1+1+3+4+2=16
思路:常规暴力求解法时间复杂度是O(N^2),这里考虑了归并排序把时间复杂度下降到O(NlogN)。关键思想是直接计算出贡献值,看例子好说清楚,比如1,2,3,4,这样的有序序列,按照常规暴力求法是:1 + (1+2) + (1+2+3),按照贡献的话,对于1,2,3,4这样有序序列,1对2,3,4的均有贡献,2对3,4均有贡献,3对4有贡献,那么13+22+31就可以了。而归并排序是对两个有序序列的合并,如果左侧当前值严格小于右侧当前值的话,就可以直接求出左侧当前值对右侧所有相应值的贡献。这样通过归并排序就可以解决问题了。
public static int mergeSort(int[] a){
if(a == null || a.length < 2){
return 0;
}
return mergeSort(a, 0, a.length-1);
}
public static int mergeSort(int[] a, int left, int right){
if(left == right){
return 0;
}
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
return mergeSort(a, left, mid)
+ mergeSort(a, mid+1, right)
+ merge(a, left, mid, right);
}
public static int merge(int[] a, int left, int mid, int right){
int[] help = new int[right-left+1];
int index = 0;
int i = left;
int j = mid + 1;
int res = 0;
while(i <= mid && j <= right){
if(a[i] < a[j]){
res += a[i]*(right-j+1);
help[index++] = a[i++];
}else{
help[index++] = a[j++];
}
}
while(i <= mid){
help[index++] = a[i++];
}
while(j <= right){
help[index++] = a[j++];
}
for(int k = 0; k < help.length; k++){
a[k+left] = help[k];
}
return res;
}
节省了暴力求解的比较浪费,因为某个数对一个有序序列的贡献可以直接计算出来,不需要一次一次加一次次比较了。要理解关键代码,如果左边当前数对右边当前数有贡献,那么左边当前数对右边当前数及其右边所有数都有贡献;如果左边当前数对右边当前数没有贡献,那么左边当前数及其右边所有数对右边当前数均无贡献。
逆序对问题
在一个数组中,左边的数如果比右边的数大,则这两个数构成一个逆序对,请打印所有逆序对。
思路:类似于小和问题,只需要确定某个数左侧所有比他小的数,构成逆序对。
核心代码:
public static ArrayList<String> mergeSort(int[] a){
if(a == null || a.length < 2){
return new ArrayList<String>();
}
return mergeSort(a, 0, a.length-1);
}
public static ArrayList<String> mergeSort(int[] a, int left, int right){
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<String>();
if(left == right){
return res;
}
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
ArrayList<String> list1 = mergeSort(a, left, mid);
ArrayList<String> list2 = mergeSort(a, mid+1, right);
ArrayList<String> list3 = merge(a, left, mid, right);
for(int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++){
res.add(list1.get(i));
}
for(int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++){
res.add(list2.get(i));
}
for(int i = 0; i < list3.size(); i++){
res.add(list3.get(i));
}
return res;
}
public static ArrayList<String> merge(int[] a, int left, int mid, int right){
int[] help = new int[right-left+1];
int index = right-left;
int i = mid;
int j = right;
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
while(i >= left && j >= mid+1){
if(a[i] > a[j]){
for(int k = mid+1; k <= j; k++){
list.add("("+a[i]+","+a[k]+")");
}
help[index--] = a[i--];
}else{
help[index--] = a[j--];
}
}
while(i >= left){
help[index--] = a[i--];
}
while(j >= mid+1){
help[index--] = a[j--];
}
for(int k = 0; k < help.length; k++){
a[k+left] = help[k];
}
return list;
}
二分
代码实现
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int v){
if(a == null || a.length == 0){
return -1;
}
int l = 0;
int r = a.length;
while(l <= r){
int mid = l + ((r-l)>>1);
if(v == a[mid]){
return mid;
}else if(v < a[mid]){
r = mid - 1;
}else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
有序数组中找>=某数的最左侧位置

import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] a = new int[]{
1,2,2,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,4,4};
int index = binarySearch(a, 2);
System.out.println(index);//1
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int v){
if(a == null || a.length == 0){
return -1;
}
int left = 0;
int right = a.length-1;
int index = -1;
while(left <= right){
int mid = left +( (right - left) >> 1);
if(a[mid] >= v){
index = mid;
right = mid-1;
}else{
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return index;
}
}
局部最小值问题
任意两个相邻的数都不一样。找到一个局部最小值。
局部最小值的三种情况:
(1)a[0] < a[1],a[0]就是局部最小;
(2)a[n-1] < a[n-2], a[n-1]就是局部最小;
(3)a[i-1] > a[i] && a[i] < a[i+1],a[i]就是局部最小。
下面是一个例子,如果两头都不是局部最小,那么呈现如下形势,头部下降趋势,而尾部是上升趋势,那么在中间必定存在局部最小吗?答案是的。以下面的例子看,如果第一个900开始如果一直都不是局部最小,必是一直下降的趋势,最多下降到第二个900,而第二个900到第二个1000是上升的,那么这种极端的情况下第二个900必定是局部最小的。除了这个极端的情况,在第二个900之前就有局部最小了。
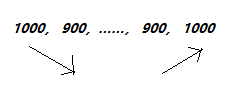
二分思路:如果a[mid]不是局部最小,那么a[mid] > a[mid-1] || a[mid] > a[mid+1],那么在a[0…mid-1],或a[mid+1, n-1]必有局部最小,不断二分即可。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] a = new int[]{
1000,900,600,300,900,1000};
int index = binarySearch(a);
System.out.println(index);//3
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] a){
if(a == null || a.length == 0){
return -1;
}
if(a.length == 1){
return 0;
}
if(a[0] < a[1]) {
return 0;
}
if(a[a.length - 1] < a[a.length - 2]){
return a.length-1;
}
int left = 0;
int right = a.length-1;
while(left <= right){
int mid = left +( (right - left) >> 1);
if(a[mid] > a[mid+1]){
left = mid + 1;
}else if(a[mid] > a[mid-1]){
right = mid-1;
}else{
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
改进算法入手角度:数据样本的特殊性(本题就是任意两个相邻的数不同)和标准的特殊性,导致了能够一分为二的状况就可以二分。(二分的必要条件不是数组是否有序)
注明:二分法中mid = left + ((right-left)>>1);或写成mid = left + (right-left)/2;不要写成mid = (left+right)/2,因为当left和right比较大的时候,比如20亿左右,两个相加就越界了。
注明:移位的时候,>>是用符号位1或0补齐左侧(对应正负数),而>>>无论正负都是用0补齐左侧。
贪心
字符串拼接问题
给定一个字符串类型的数组strs,找到一种拼接方式,使得把所有字符串拼起来之后形成的字符串具有最小的字典序。
【贪心策略】把所有单词按照字典序排序,然后直接连起来,这种策略是错误的。比如字符串"da"和字符串"d",若按照这种策略拼接结果是"dda",正确答案是"dad"。
【贪心策略】str1+str2的字典序小于str2+str1,那么拼接策略是str1+str2,否则拼接策略是str2+str1
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static String lowestString(String[] strs) {
if(strs == null || strs.length == 0){
return "";
}
Arrays.sort(strs, new Comparator<String>(){
public int compare(String s1, String s2){
return (s1 + s2).compareTo(s2 + s1);
}
});
String res = "";
for(int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++){
res += strs[i];
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String[] strs = {"d", "da"};
System.out.println(lowestString(strs));
}
}
金条分割问题
一块金条切成两半,是需要花费和长度数值一样的铜板的。比如长度为20的金条,不管切成长度多大的两半,都要花费20个铜板。一群人想整分整块金条,怎么分最省铜板?
例如,给定数组{10,20,30},代表一共三个人,整块金条长度为10+20+30=60。金条要分成10,20,30三个部分。 如果先把长度60的金条分成10和50,花费60;再把长度50的金条分成20和30,花费50;一共花费110铜板。但是如果先把长度60的金条分成30和30,花费60;再把长度30金条分成10和20,花费30;一共花费90铜板。输入一个数组,返回分割的最小代价。
【贪心策略】就是哈夫曼编码的过程,一次拿出最小的两个拼,即可。。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int leastMoney(int[] a) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
pq.add(a[i]);
}
int sum = 0;
int cur = 0;
while(pq.size() >= 2){
cur = pq.poll() + pq.poll();
sum += cur;
pq.add(cur);
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] a = {10, 20, 30};
System.out.println(leastMoney(a));
}
}
安排最多的项目问题
一些项目要占用一个会议室宣讲,会议室不能同时容纳两个项目的宣讲。给你每一个项目开始的时间和结束的时间(给你一个数组,里面是一个个具体的项目),你来安排宣讲的日程,要求会议室进行的宣讲的场次最多。返回这个最多的宣讲场次。
【贪心策略】结束早的项目优先安排
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static class Program {
public int start;
public int end;
public Program(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
public static class ProgramComparator implements Comparator<Program> {
@Override
public int compare(Program o1, Program o2) {
return o1.end - o2.end;
}
}
public static int bestArrange(Program[] programs, int start) {
Arrays.sort(programs, new ProgramComparator());
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < programs.length; i++){
if(start < programs[i].start){
res++;
start = programs[i].end;
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
}
}
数据流中随时可取得中位数问题
【贪心策略】准备两个堆,一个大根堆,一个小根堆,第一个数进入大根堆,如果当前数小于等于大根堆堆顶就进入大根堆,否则进入小根堆,如果两个堆大小的差达到了2,就从数目多的那个堆里弹出一个数进入另一个堆。
上述策略保证了两个堆中的数的个数是当前总数的一半。如果两个堆大小相同,那么中位数就是两个堆顶和的平均值,如果两个堆的大小不等,那么中位数就是数较多的那个堆的堆顶。
package class07;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Code06_MadianQuick {
public static class MedianHolder {
private PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new MaxHeapComparator());
private PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new MinHeapComparator());
private void modifyTwoHeapsSize() {
if (this.maxHeap.size() == this.minHeap.size() + 2) {
this.minHeap.add(this.maxHeap.poll());
}
if (this.minHeap.size() == this.maxHeap.size() + 2) {
this.maxHeap.add(this.minHeap.poll());
}
}
public void addNumber(int num) {
if (maxHeap.isEmpty() || num <= maxHeap.peek()) {
maxHeap.add(num);
} else {
minHeap.add(num);
}
modifyTwoHeapsSize();
}
public Integer getMedian() {
int maxHeapSize = this.maxHeap.size();
int minHeapSize = this.minHeap.size();
if (maxHeapSize + minHeapSize == 0) {
return null;
}
Integer maxHeapHead = this.maxHeap.peek();
Integer minHeapHead = this.minHeap.peek();
if (((maxHeapSize + minHeapSize) & 1) == 0) {
return (maxHeapHead + minHeapHead) / 2;
}
return maxHeapSize > minHeapSize ? maxHeapHead : minHeapHead;
}
}
public static class MaxHeapComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
if (o2 > o1) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
public static class MinHeapComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
if (o2 < o1) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
// for test
public static int[] getRandomArray(int maxLen, int maxValue) {
int[] res = new int[(int) (Math.random() * maxLen) + 1];
for (int i = 0; i != res.length; i++) {
res[i] = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue);
}
return res;
}
// for test, this method is ineffective but absolutely right
public static int getMedianOfArray(int[] arr) {
int[] newArr = Arrays.copyOf(arr, arr.length);
Arrays.sort(newArr);
int mid = (newArr.length - 1) / 2;
if ((newArr.length & 1) == 0) {
return (newArr[mid] + newArr[mid + 1]) / 2;
} else {
return newArr[mid];
}
}
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i != arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean err = false;
int testTimes = 200000;
for (int i = 0; i != testTimes; i++) {
int len = 30;
int maxValue = 1000;
int[] arr = getRandomArray(len, maxValue);
MedianHolder medianHold = new MedianHolder();
for (int j = 0; j != arr.length; j++) {
medianHold.addNumber(arr[j]);
}
if (medianHold.getMedian() != getMedianOfArray(arr)) {
err = true;
printArray(arr);
break;
}
}
System.out.println(err ? "Oops..what a fuck!" : "today is a beautiful day^_^");
}
}
项目利润最大问题
输入:
正数数组costs
正数数组profits
正数k
正数m
含义:
costs[i]表示i号项目的花费
profits[i]表示i号项目在扣除花费之后还能挣到的钱(利润)
k表示你只能串行的最多做k个项目
m表示你初始的资金
说明:
你每做完一个项目,马上获得的收益,可以支持你去做下一个项目。
输出:
你最后获得的最大钱数。
【贪心策略】先把所有项目按照花费大小进入小根堆。
然后把小根堆中能够做的项目(花费小于等于当前资金)按照利润大小进入大根堆,从大根堆中挑选一个项目做了。重复该步骤即可。
package class07;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Code05_IPO {
public static class Node {
public int p;
public int c;
public Node(int p, int c) {
this.p = p;
this.c = c;
}
}
public static class MinCostComparator implements Comparator<Node> {
@Override
public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) {
return o1.c - o2.c;
}
}
public static class MaxProfitComparator implements Comparator<Node> {
@Override
public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) {
return o2.p - o1.p;
}
}
public static int findMaximizedCapital(int k, int W, int[] Profits, int[] Capital) {
Node[] nodes = new Node[Profits.length];
for (int i = 0; i < Profits.length; i++) {
nodes[i] = new Node(Profits[i], Capital[i]);
}
PriorityQueue<Node> minCostQ = new PriorityQueue<>(new MinCostComparator());
PriorityQueue<Node> maxProfitQ = new PriorityQueue<>(new MaxProfitComparator());
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.length; i++) {
minCostQ.add(nodes[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
while (!minCostQ.isEmpty() && minCostQ.peek().c <= W) {
maxProfitQ.add(minCostQ.poll());
}
if (maxProfitQ.isEmpty()) {
return W;
}
W += maxProfitQ.poll().p;
}
return W;
}
}
位运算
异或
位运算异或:相同为0不同为1,等价说成无进位相加。
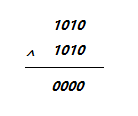
1)0^N == N,N^N == 0
2)异或运算满足交换律和结合率
a^b^c = a^(b^c) = b^a^c = a^c^b
解释:对于每个位上的数要么是0,要么是1,若干个数的某一位一起进行异或,如果有偶数个1异或之后得0,如果有奇数个1,异或之后得1。这个结论是显然的,因为异或运算不像加减运算,没有进位发生,结果仅仅取决于当前位。所以自然满足交换律和结合律了,几个数做异或运算,和这几个数的运算顺序和结合顺序没有关系。
3)不用额外变量交换两个数
int tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
//设x=a, y=b
a = a^b; //a=x^y, b=y
b = a^b;//b=x^y^y=y^y^x=0^x=x, a=x^y
a = a^b;//a=x^y^y=x
坑:下面的代码有坑。如果i和j相同,会导致a[i]=a[j]=0。
public static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j){
a[i] = a[i]^a[j];
a[j] = a[i]^a[j];
a[i] = a[i]^a[j];
}
4)一个数组中有一种数出现了奇数次,其他数都出现了偶数次,怎么找到这一个数
把所有的数异或起来,就是所求。偶数次出现的数自己和自己异或就是0。最终只剩下一个奇数次出现的那个数。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] a = new int[]{1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2,3,3,6};
System.out.println(oddNumber(a));
}
public static int oddNumber(int[] a){
int res = 0;
for(int x : a){
res ^= x;
}
return res;
}
}
5)一个数组中有两种数出现了奇数次,其他数都出现了偶数次,怎么找到这两个数
思路:设定出现奇数次的这两个数分别是a,b,那么所有数异或后的结果就是x = a^b,由于a,b不相同,那么x必然存在是1的位,假设是第6位是1,那么这个1不是a的1,就是b的1;现在把所有第6位是1的数都异或起来,得到的结果必定是a或b,如果结果是a,那么把结果和x异或,得到b,如果结果是b,那么结果和x异或,得到a。
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] a =new int[]{1,1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3,6};
oddNumber(a);
}
public static void oddNumber(int[] a){
int res1 = 0;
for(int x : a){
res1 ^= x;
}
int right1 = res1 & (~res1 + 1);
int res2 = 0;
for(int x : a){
if((x & right1) == 0){
res2 ^= x;
}
}
System.out.println(res2 + "," + (res2^res1));
}
}
注明:10100 & (~10110 + 1) = 10100 & (01011+00001) = 01100 & 10101 = 00100。
e & (~e+1)的作用是提取出e的从右边数第一个为1的位,并把其他位全部置0得到的数。
位图
用位存放信息,可应用到布隆过滤器,处理大规模url黑名单问题。
int[] arr = new int[10]; // 32bit * 10 -> 320 bits
// arr[0] int 0 ~ 31
// arr[1] int 32 ~ 63
// arr[2] int 64 ~ 95
int i = 178; // 想取得178个bit的状态
int numIndex = i / 32; // 对应数组下标
int bitIndex = i % 32; // 对应数的哪位(从高位到低位)
// 拿到178位的状态
int s = (arr[numIndex] && (1 << (31 - bitIndex))) == 0 ? 0 : 1;
// 请把178位的状态改成1
arr[numIndex] = arr[numIndex] | (1 << (31 - bitIndex));
// 请把178位的状态改成0
arr[numIndex] = arr[numIndex] & (~(1 << (31 - bitIndex)));
链表
反转单链表和双向链表
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
// for test
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head1 = new Node(2);
Node node1 = new Node(1);
Node node2 = new Node(6);
head1.next = node1;
node1.next = node2;
printList(head1);
printList(reverseList(head1));
DoubleNode head2 = new DoubleNode(2);
DoubleNode doubleNode1 = new DoubleNode(1);
DoubleNode doubleNode2 = new DoubleNode(6);
head2.last = null;
head2.next = doubleNode1;
doubleNode1.next = doubleNode2;
doubleNode1.last = head2;
doubleNode2.next = null;
doubleNode2.last = doubleNode1;
printDoubleList(head2);
printDoubleList(reverseDoubleList(head2));
}
//单链表
public static class Node{
public int v;
public Node next;
public Node(int v){
this.v = v;
}
}
public static Node reverseList(Node head){
Node pre = null;
Node cur = head;
Node tmp = null;
while(cur != null){
tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
public static void printList(Node head){
while(head != null){
System.out.print(head.v + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//双向链表
public static class DoubleNode{
public int v;
public DoubleNode last;
public DoubleNode next;
public DoubleNode(int v){
this.v = v;
}
}
public static DoubleNode reverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head){
DoubleNode pre = null;
DoubleNode cur = head;
DoubleNode tmp = null;
while(cur != null){
tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
cur.last = tmp;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
public static void printDoubleList(DoubleNode head){
DoubleNode tail = null;
while(head != null){
System.out.print(head.v + " ");
tail = head;//为了记录最后一个节点
head = head.next;
}
System.out.print("| ");
while(tail != null){
System.out.print(tail.v + " ");
tail = tail.last;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
打印有序链表的公共部分
//两个有序链表的公共部分打印,两个指针指向两个链表,往后走,
//如果相等就打印,并共同往后移,如果不等,小的往后移动
public static void printCommon(Node head1, Node head2){
while(head1 != null && head2 != null){
if(head1.v == head2.v){
System.out.print(head1.v + " ");
head1 = head1.next;
head2 = head2.next;
}else if(head1.v < head2.v){
head1 = head1.next;
}else{
head2 = head2.next;
}
}
}
判断一个链表是否为回文结构
给定一个单链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构。
【例子】1->2->1,返回true; 1->2->2->1,返回true;15->6->15,返回true;1->2->3,返回false。
【优化】如果链表长度为N,时间复杂度达到O(N),额外空间复杂度达到O(1)。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(1);
print(head1);
System.out.println(isPalindrome1(head1));
System.out.println(isPalindrome2(head1));
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head1));
System.out.println("==============================");
head1.next.next.next = new Node(1);
print(head1);
System.out.println(isPalindrome1(head1));
System.out.println(isPalindrome2(head1));
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head1));
}
public static class Node{
public int v;
public Node next;
public Node(int v){
this.v = v;
}
}
/*
方案一:利用栈,额外空间复杂度O(N)
*/
public static boolean isPalindrome1(Node head){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
while(head != null){
if(head.v != stack.pop().v){
return false;
}
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
/*
方案二:利用栈,额外空间复杂度是O(N/2)
利用快慢指针,只把后一半压入栈,然后再和前一半比较。
关于快慢指针的走法,只需要列出两种情况(奇数和偶数个节点)搞一下就明白了
*/
public static boolean isPalindrome2(Node head){
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return true;
}
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head;
while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow = slow.next;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while(slow != null){
stack.push(slow);
slow = slow.next;
}
slow = head;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
if(stack.pop().v != slow.v){
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
/*
方案三:利用快慢指针,找到链表中点,把后一半链表反转,然后前后两半同时遍历对比
额外空间复杂度是O(1)
*/
public static boolean isPalindrome3(Node head){
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return true;
}
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head;
while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
Node mid = slow;//记录链表中点
//翻转后一半链表
Node pre = mid;
Node cur = mid.next;
while(cur != null){
Node tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
cur = head;
Node tail = pre;//记录尾部节点,以便后续再把链表反转回来
while(pre != mid){
if(pre.v != cur.v){
return false;
}
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
//把后一半链表重新反转成原始状态
pre = null;
cur = tail;
while(cur != mid){
Node tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return true;
}
public static void print(Node head){
while(head != null){
System.out.print(head.v + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式
【题目】给定一个单链表的头节点head,节点的值类型是整型,再给定一个整数pivot。实现一个调整链表的函数,将链表调整为左部分都是值小于pivot的节点,中间部分都是值等于pivot的节点,右部分都是值大于pivot的节点。
【进阶】在实现原问题功能的基础上增加如下的要求
【要求】调整后所有小于pivot的节点之间的相对顺序和调整前一样
【要求】调整后所有等于pivot的节点之间的相对顺序和调整前一样
【要求】调整后所有大于pivot的节点之间的相对顺序和调整前一样
【要求】时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)。
方案一:把链表中的数放在数组中,完成partition后再放回链表。
方案二:具体见代码说明吧
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head1 = new Node(7);
head1.next = new Node(9);
head1.next.next = new Node(1);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(8);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
print(head1);
//Node res1 = listPartition1(head1, 5);
Node res1 = listPartition2(head1, 5);
print(res1);
}
public static class Node{
public int v;
public Node next;
public Node(int v){
this.v = v;
}
}
//方案二:准备六个指针,分别是小于区、等于区、大于区的头尾指针,每个区做完
// 比划分边界值小就放在小于区,比划分值大就放在大于区,否则放入等于区,最后合并即可
public static Node listPartition2(Node head, int pivot){
Node smallHead = null;
Node smallTail = null;
Node equalHead = null;
Node equalTail = null;
Node bigHead = null;
Node bigTail = null;
//注意下面一个区仅仅有一个节点的时候头和尾是一样的,如果再新加一个,
//只需要加入尾部,尾指针后移即可,头指针一直是头指针不变。
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.v < pivot){
if(smallHead == null){
smallHead = smallTail = cur;
}else{
smallTail.next = cur;
smallTail = cur;
}
}else if(cur.v > pivot){
if(bigHead == null){
bigHead = bigTail = cur;
}else{
bigTail.next = cur;
bigTail = cur;
}
}else{
if(equalHead == null){
equalHead = equalTail = cur;
}else{
equalTail.next = cur;
equalTail = cur;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
//下面就是把三个区合并的问题了,关键问题是有的区可能不存在!
//最简单粗暴的方法就是分类讨论,8种情况
if(smallTail != null && equalTail != null && bigTail != null){
//111
smallTail.next = equalHead;
equalTail.next = bigHead;
bigTail.next = null;
return smallHead;
}else if(smallTail != null && equalTail != null && bigTail == null){
//110
smallTail.next = equalHead;
equalTail.next = null;
return smallHead;
}else if(smallTail != null && equalTail == null && bigTail != null){
//101
smallTail.next = bigHead;
bigTail.next = null;
return smallHead;
}else if(smallTail != null && equalTail == null && bigTail == null){
//100
smallTail.next = null;
return smallHead;
}else if(smallTail == null && equalTail != null && bigTail != null){
//011
equalTail.next = bigHead;
bigTail.next = null;
return equalHead;
}else if(smallTail == null && equalTail != null && bigTail == null){
//010
equalTail.next = null;
return equalHead;
}else if(smallTail == null && equalTail == null && bigTail != null){
//001
bigTail.next = null;
return bigHead;
}else{
//000
return head;
}
}
//方案一:把链表节点放在了数组中,对数组做partition
public static Node listPartition1(Node head, int pivot){
if(head == null){
return head;
}
int len = 0;
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
len++;
cur = cur.next;
}
Node[] a = new Node[len];
int i = 0;
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
a[i++] = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
//在数组中进行partition
arrPartition(a, pivot);
//放回原链表
i = 1;
for(; i < a.length; i++){
a[i-1].next = a[i];
}
a[i-1].next = null;
return a[0];
}
public static void arrPartition(Node[] a, int pivot){
int left = -1;
int right = a.length;
int cur = 0;
while(cur < right){
if(a[cur].v < pivot){
swap(a, ++left, cur++);
}else if(a[cur].v > pivot){
swap(a, --right, cur);
}else{
cur++;
}
}
}
public static void swap(Node[] a, int i, int j){
Node tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
public static void print(Node head){
while(head != null){
System.out.print(head.v + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
上面方案二的最后那一段分类讨论可以优化如下:
// small and equal reconnect
if (sT != null) {
sT.next = eH;
eT = eT == null ? sT : eT;
}
// all reconnect
if (eT != null) {
eT.next = bH;
}
return sH != null ? sH : eH != null ? eH : bH;
复制含有随机指针节点的链表
【题目】一种特殊的单链表节点类描述如下
class Node {
int value;
Node next;
Node rand;
Node(int val) {
value = val;
}
}
rand指针是单链表节点结构中新增的指针,rand可能指向链表中的任意一个节
点,也可能指向null。给定一个由Node节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点
head,请实现一个函数完成这个链表的复制,并返回复制的新链表的头节点。
【要求】时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)
方案一:利用HashMap,额外空间复杂度是O(N)
方案二:额外空间复杂度优化到O(1),方法是把链表的每个节点复制一份插入到原节点后面。这种结构就能起到原来使用HashMap的作用了!因为复制的备份就在原节点后面。原来是查HashMap,现在就变成了查一个节点的前一个节点。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head.random = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 1 -> 6
head.next.random = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 2 -> 6
head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; // 3 -> 5
head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; // 4 -> 3
print(head);
//Node res1 = copyListWithRandom1(head);
Node res1 = copyListWithRandom2(head);
print(res1);
}
public static class Node{
public int v;
public Node next;
public Node random;
public Node(int v){
this.v = v;
}
}
//方案一:利用哈希表,额外空间复杂度是O(N)
public static Node copyListWithRandom1(Node head){
HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.v));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
//方案二:额外空间复杂度是O(1)
public static Node copyListWithRandom2(Node head){
if(head == null){
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
Node tmp = null;
while(cur != null){
tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = new Node(cur.v);
cur.next.next = tmp;
cur = tmp;
}
cur = head;
Node pre = null;
Node post = null;
//先把复制的新链表的random设置好
while(cur != null){
pre = cur;
post = cur.next;
if(pre.random == null){
post.random = null;
}else{
post.random = pre.random.next;
}
cur = cur.next.next;
}
//新旧两个链表现在在一块,需要分开
cur = head;
Node copy = null;
while(cur != null){
tmp = cur.next.next;
copy = cur.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
if(tmp == null){
copy.next = null;
}else{
copy.next = tmp.next;
}
cur = cur.next.next;
}
return head.next;
}
public static void print(Node head){
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.v + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.random == null){
System.out.print("-");
}else{
System.out.print(cur.random.v+" ");
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
两个单链表相交的一系列问题
【题目】给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2。请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的第一个节点。如果不相交,返回null
【要求】如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static class Node{
public int v;
public Node next;
public Node(int v){
this.v = v;
}
}
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2){
if(head1 == null || head2 == null){
return null;
}
Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1);
Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2);
if(loop1 == null && loop2 == null){
return noLoop(head1, head2);
}
if(loop1 != null && loop2 != null){
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);
}
return null;
}
//判断是否有环,有环的话返回第一个入环节点,无环返回null,使用HashSet
/*
public static Node getLoopNode(Node head){
HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<Node>();
while(head != null){
if(!set.add(head)){
return head;
}
}
return null;
}
*/
//判断是否有环,有环的话返回第一个入环节点,无环返回null,额外空间复杂度是O(1)
public static Node getLoopNode(Node head){
if(head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
return null;
}
Node slow = head.next;
Node fast = head.next.next;
while(slow != fast){
if(fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null){
return null;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
fast = head;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
//无环求相交节点
public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2){
if(head1 == null || head2 == null){
return null;
}
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while(cur1 != null){
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur2 != null){
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
//cur1为较长的链表,cur2是较短的链表
if(n > 0){
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
}else{
cur1 = head2;
cur2 = head1;
}
n = Math.abs(n);
//长链表先走n步
while(n != 0){
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur1 != cur2){
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
//两个有环链表的相交节点
public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2){
Node cur1 = null;
Node cur2 = null;
//如果两个链表的入环节点相同
if(loop1 == loop2){
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while(cur1 != loop1){
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur2 != loop2){
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
if(n > 0){
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
}else{
cur1 = head2;
cur2 = head1;
}
n = Math.abs(n);
while(n != 0){
cur1 = cur1.next;
n--;
}
while(cur1 != cur2){
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}else{
//两个链表的入环节点不同
cur1 = loop1.next;
while(cur1 != loop1){
if(cur1 == loop2){
return loop1;//入环节点不同且相交,返回loop1或loop2都可以
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
return null;//两链表各自成环,不相交
}
}
public static void print(Node head){
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.v + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->null
Node head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
// 0->9->8->6->7->null
Node head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).v);
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->4...
head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next; // 7->4
// 0->9->8->2...
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next; // 8->2
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).v);
// 0->9->8->6->4->5->6..
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).v);
}
}
解题策略
1.判断有环无环
2.两个链表都无环
3.两个链表一个有环另一个无环
4.两个链表都有环
总的来说都有两个解决方式:一个是通过HashSet,额外空间复杂度是O(N);另一个方法是优化到O(1)。具体描述如下:
判环方法1:利用HashSet法,额外空间复杂度O(N)。遍历链表,不断向HashSet里加入节点,如果当前节点已经在HashSet里存在,就是入环节点了,如果遍历到链表最后到null,说明无环。
判环方法2:利用快慢指针也可以优化到O(1)。快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,如果快指针走到null,说明无环。如果快慢指针能够走到相遇,说明有环,相遇之后,慢指针停在原地,快指针变成链表头,两个指针都一次一步,直到相遇,相遇点就是入环点。
下面三种情况可以用HashSet解决:先把一个链表所有节点入HashSet,然后遍历另一个链表,第一个已经在HashSet的节点就是第一个相交节点。
两个链表都无环:单链表每个节点只有一个指针指向下一个,那么两个链表如果相交,一旦相交,之后就一直在一起了。所以,对于两个链表都无环的话,可以先看尾部节点,如果不同必不相交,如果相同只要找到相交的第一个节点即可,长链表先走差值步(两个链表长度差),然后两个链表一起走到第一个相交节点就OK了。
一个有环一个无环:两链表一个有环另一个有环,一定不相交
两个链表都有环:两个链表都有环,只有三种情况如下:
1)两个链表各自成环,不相交;两个入环节点不一样,让其中一个入环节点往后走,走回自己的过程中如果遇到了另一个入环节点,说明是情况3),如果没有遇到另一个入环节点,说明两个链表各自成环。
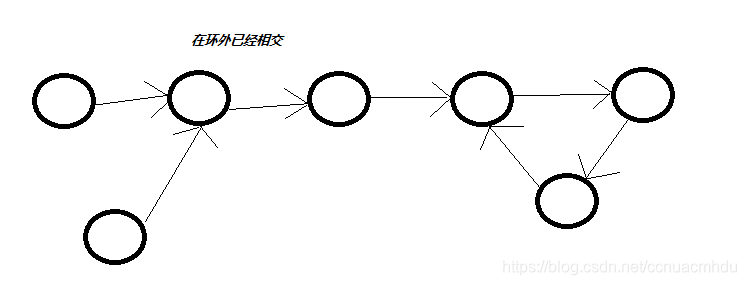
2)两个链表在环外已经相交;两个链表的入环节点相同,即可判断此情况。遍历链表,找到入环点,把入环点作为结束点,这就转化成两个无环链表找第一个相交点的问题了。
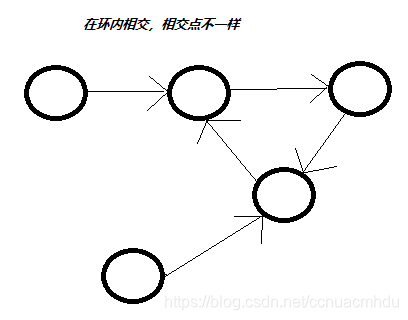
3)两个链表在环内相交。让其中一个入环节点往后走,走回自己的过程中遇到了另一个入环节点。两链表的相交节点返回任意一个入环节点即可。
只给单链表的一个节点,怎么删除这个节点
把后继节点的值给该节点,把后继节点删掉。这样做其实有问题,如果没有后继节点自然删不掉,还有问题就是其实这并没有对该节点的内存空间释放,错误地把后继节点的内存空间释放了,这是比较危险的操作,因为如果有其他节点找该节点的后继节点,那就会出错。
二叉树
二叉树递归遍历
二叉树节点没有指向父节点的指针,所以从上往下走容易,而从下往上走不能走,所以需要栈来记录以前走过的路。递归方式直接使用系统栈,非递归方式压自己的栈。
二叉树非递归遍历
先序深度遍历(非递归)
先把头节点入栈。然后:不断重复下面的步骤:
1.拿出栈顶元素
2.打印该元素
3.压入右孩子和左孩子
后序深度遍历(非递归)
准备两个栈A,B。先把头节点入栈A。然后:不断重复下面的步骤:
1.拿出A栈顶元素
2.把该元素压入栈B
3.压入左孩子和右孩子到栈A
入栈B的顺序就是根-右孩子-左孩子,最后把元素依依次从栈B中弹出就是左孩子-根-右孩子的顺序,即后序遍历结果。
中序深度遍历(非递归)
准备一个栈。总体上来说,把左边界入栈,依次出栈(左-中),转向右边,再左边界入栈出栈(右)。
二叉树遍历代码实现
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static class Node{
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public static void preOrderRecursive(Node root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
preOrderRecursive(root.left);
preOrderRecursive(root.right);
}
public static void inOrderRecursive(Node root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
inOrderRecursive(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
inOrderRecursive(root.right);
}
public static void postOrderRecursive(Node root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
postOrderRecursive(root.left);
postOrderRecursive(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
}
public static void preOrderUnRecursive(Node root){
if(root != null){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
root = stack.pop();
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
if(root.right != null){
stack.push(root.right);
}
if(root.left != null){
stack.push(root.left);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
//中序遍历(非递归)。左边界全部压栈,依次出栈(左-中),转向右侧入栈出栈(右)
public static void inOrderUnRecursive(Node root){
if(root != null){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while(!stack.isEmpty() || root != null){
if(root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}else{
root = stack.pop();
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
root = root.right;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void postOrderUnRecursive(Node root){
if(root != null){
Stack<Node> stack1 = new Stack<Node>();
Stack<Node> stack2 = new Stack<Node>();
stack1.push(root);
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
root = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(root);
if(root.left != null){
stack1.push(root.left);
}
if(root.right != null){
stack1.push(root.right);
}
}
while(!stack2.isEmpty()){
System.out.print(stack2.pop().val + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
//宽度遍历求最大宽度
public static int treeBFS(Node root){
if(root != null){
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
HashMap<Node, Integer> levelMap = new HashMap<Node, Integer>();
int maxWidth = 0;
int curLevel = 0;
int curWidth = 0;
queue.add(root);
levelMap.put(root, 1);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
root = queue.poll();
//System.out.print(root.val+" ");
if(root.left != null){
queue.add(root.left);
levelMap.put(root.left, levelMap.get(root)+1);
}
if(root.right != null){
queue.add(root.right);
levelMap.put(root.right, levelMap.get(root)+1);
}
if(levelMap.get(root) > curLevel){
curLevel = levelMap.get(root);
curWidth = 1;
}else{
curWidth++;
}
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, curWidth);
}
return maxWidth;
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(5);
head.left = new Node(3);
head.right = new Node(8);
head.left.left = new Node(2);
head.left.right = new Node(4);
head.left.left.left = new Node(1);
head.right.left = new Node(7);
head.right.left.left = new Node(6);
head.right.right = new Node(10);
head.right.right.left = new Node(9);
head.right.right.right = new Node(11);
// recursive
System.out.println("==============recursive==============");
System.out.print("pre-order: ");
preOrderRecursive(head);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("in-order: ");
inOrderRecursive(head);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("post-order: ");
postOrderRecursive(head);
System.out.println();
// unrecursive
System.out.println("============unrecursive=============");
preOrderUnRecursive(head);
inOrderUnRecursive(head);
postOrderUnRecursive(head);
System.out.println("============BFS=============");
System.out.println(treeBFS(head));
}
}
二叉树解题套路
能够把流程定义成检查每个节点为头的子树是否符合同一标准并且答案在其中。
套路判搜索二叉树
二叉树及其所有子树都是搜索二叉树,左孩子小于根,根小于右孩子。二叉树的中序遍历结果是严格递增序,就是搜索二叉树。
搜索二叉树满足二叉树解题套路,即检查每个节点为头的二叉树是否是搜索二叉树。所以用套路写。可能性分析:对每个节点来说,左孩子是搜索二叉树;右孩子是搜索二叉树;左孩子的最大值小于当前节点;右孩子的最小值大于当前节点。信息整合:左孩子是否是搜索二叉树及最大值,右孩子是否是搜索二叉树及最小值。
public class Main{
public static class Node{
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public static boolean isBST(Node root){
return process(root).isBST;
}
public static class ReturnType{
public boolean isBST;
public int max;
public int min;
public ReturnType(boolean isBST, int max, int min){
this.isBST = isBST;
this.max = max;
this.min = min;
}
}
public static ReturnType process(Node root){
if(root == null){
return new ReturnType(true, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
ReturnType leftData = process(root.left);
ReturnType rightData = process(root.right);
boolean isBST = leftData.isBST
&& rightData.isBST
&& leftData.max < root.val
&& root.val < rightData.min;
int min = Math.min(root.val, Math.min(leftData.min, rightData.min));
int max = Math.max(root.val, Math.max(leftData.max, rightData.max));
return new ReturnType(isBST, max, min);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Node head = new Node(5);
head.left = new Node(3);
head.right = new Node(8);
head.left.left = new Node(2);
head.left.right = new Node(4);
head.left.left.left = new Node(1);
head.right.left = new Node(7);
head.right.left.left = new Node(6);
head.right.right = new Node(10);
head.right.right.left = new Node(9);
head.right.right.right = new Node(11);
System.out.println(isBST(head));
}
}
套路判平衡二叉树
左孩子是平衡二叉树,右孩子是平衡二叉树,左孩子和右孩子的高度差小于等于1。
public class Main{
public static class Node{
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public static boolean isBST(Node root){
return process(root).isBalanced;
}
public static class ReturnType{
public boolean isBalanced;
public int height;
public ReturnType(boolean isBalanced, int height){
this.isBalanced = isBalanced;
this.height = height;
}
}
public static ReturnType process(Node root){
if(root == null){
return new ReturnType(true, 0);
}
ReturnType leftData = process(root.left);
ReturnType rightData = process(root.right);
int height = Math.max(leftData.height, rightData.height) + 1;
boolean isBalanced = leftData.isBalanced
&& rightData.isBalanced
&& Math.abs(leftData.height - rightData.height) <= 1;
return new ReturnType(isBalanced, height);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Node head = new Node(5);
head.left = new Node(3);
head.right = new Node(8);
head.left.left = new Node(2);
head.left.right = new Node(4);
head.left.left.left = new Node(1);
head.right.left = new Node(7);
head.right.left.left = new Node(6);
head.right.right = new Node(10);
head.right.right.left = new Node(9);
head.right.right.right = new Node(11);
System.out.println(isBST(head));
}
}
套路判满二叉树
public class Main{
public static class Node{
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public static class ReturnType{
public int height;
public int nodeNumber;
public ReturnType(int height, int nodeNumber){
this.height = height;
this.nodeNumber = nodeNumber;
}
}
public static boolean isFull(Node root){
ReturnType type = process(root);
int height = type.height;
int nodeNumber = type.nodeNumber;
return (1 << height) - 1 == nodeNumber;
}
public static ReturnType process(Node root){
if(root == null){
return new ReturnType(0, 0);
}
ReturnType leftData = process(root.left);
ReturnType rightData = process(root.right);
int height = Math.max(leftData.height, rightData.height) + 1;
int nodeNumber = leftData.nodeNumber + rightData.nodeNumber + 1;
return new ReturnType(height, nodeNumber);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Node head = new Node(5);
head.left = new Node(3);
head.right = new Node(8);
head.left.left = new Node(2);
head.left.right = new Node(4);
head.right.left = new Node(7);
head.right.right = new Node(10);
System.out.println(isFull(head));
}
}
判完全二叉树
1)任意一个节点有右孩子没有左孩子,判定为不是完全二叉树
2)遇到第一个只有左孩子的节点或叶子节点起,后续节点都是叶子节点才是完全二叉树,否则不是。
解决方案:BFS
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static class Node{
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public static boolean isCBT(Node root){
if(root == null){
return true;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
boolean flag = false;//标记当前是否已经开始进入只有左孩子的节点或叶子节点
queue.add(root);
Node tmp = null;
Node left = null;
Node right = null;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
tmp = queue.poll();
left = tmp.left;
right = tmp.right;
//如果有右孩子且无左孩子,判定为false
if(right != null && left == null){
return false;
}
//如果已经进入叶子节点或只有左孩子的节点的情况下,出现了非叶子节点,判定为false
if(flag == true && (left != null || right != null)){
return false;
}
if(left != null){
queue.add(left);
}
if(right != null){
queue.add(right);
}else{
flag = true;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Node head = new Node(5);
head.left = new Node(3);
head.right = new Node(8);
head.left.left = new Node(2);
//head.left.right = new Node(4);
head.right.left = new Node(7);
head.right.right = new Node(10);
System.out.println(isCBT(head));
}
}
找二叉树两节点的最低公共祖先
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static class Node{
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
private static HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
public static Node lowestAncestor(Node root, Node n1, Node n2){
//遍历二叉树root,把每个节点和其父亲作为一对,存入哈希表
if(root != null){
map.put(root, null);
}
setMap(root);
//把n1及其父亲加入HashSet,然后从n2开始向上查找所有父亲,只要在HashSet中存在就是最低公共父亲
HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<Node>();
while(map.containsKey(n1)){
set.add(n1);
n1 = map.get(n1);
}
while(!set.contains(n2)){
n2 = map.get(n2);
}
return n2;
}
private static void setMap(Node root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
if(root.left != null){
map.put(root.left, root);
}
if(root.right != null){
map.put(root.right, root);
}
setMap(root.left);
setMap(root.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Node head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(2);
head.right = new Node(3);
head.left.left = new Node(4);
head.left.right = new Node(5);
head.right.left = new Node(6);
head.right.right = new Node(7);
head.right.right.left = new Node(8);
Node o1 = head.left.right;
Node o2 = head.right.left;
System.out.println("o1 : " + o1.val);
System.out.println("o2 : " + o2.val);
System.out.println("ancestor : " + lowestAncestor(head, o1, o2).val);
}
}
找后继节点
【题目】 现在有一种新的二叉树节点类型如下:
public class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int val) {
value = val;
}
}
该结构比普通二叉树节点结构多了一个指向父节点的parent指针。
假设有一棵Node类型的节点组成的二叉树,树中每个节点的parent指针都正确地指向自己的父节点,头节
点的parent指向null。
只给一个在二叉树中的某个节点node,请实现返回node的后继节点的函数。
在二叉树的中序遍历的序列中, node的下一个节点叫作node的后继节点。
解法:
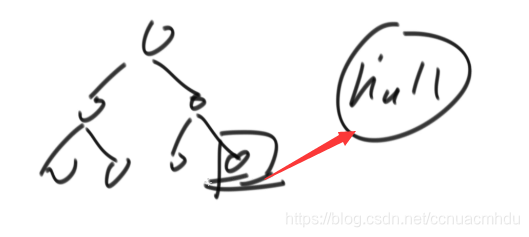
如果某节点有右孩子,那么该节点的后继节点是右子树的最左孩子;如果某节点没有右孩子,那么该节点的后继节点是作为另一个节点的左孩子对应的父节点。
 注意整棵树的最右节点没有后继节点,标记为null。
注意整棵树的最右节点没有后继节点,标记为null。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
}
public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node root){
if(root == null){
return root;
}
if(root.right != null){
return getMostLeft(root.right);
}else{
Node parent = root.parent;
//下面的parent != null一句,是为了下面图中的情况,一直向上判定完了都没有,后继是null
while(parent != null && parent.left != root){
root = parent;
parent = root.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
public static Node getMostLeft(Node root){
if(root == null){
return root;
}
while(root.left != null){
root = root.left;
}
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Node head = new Node(6);
head.parent = null;
head.left = new Node(3);
head.left.parent = head;
head.left.left = new Node(1);
head.left.left.parent = head.left;
head.left.left.right = new Node(2);
head.left.left.right.parent = head.left.left;
head.left.right = new Node(4);
head.left.right.parent = head.left;
head.left.right.right = new Node(5);
head.left.right.right.parent = head.left.right;
head.right = new Node(9);
head.right.parent = head;
head.right.left = new Node(8);
head.right.left.parent = head.right;
head.right.left.left = new Node(7);
head.right.left.left.parent = head.right.left;
head.right.right = new Node(10);
head.right.right.parent = head.right;
Node test = head.left.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left.left.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left.right.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right.left.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right.right; // 10's next is null
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test));
}
}

二叉树的序列化和反序列化
就是内存里的一棵树如何变成字符串形式,又如何从字符串形式变成内存里的树
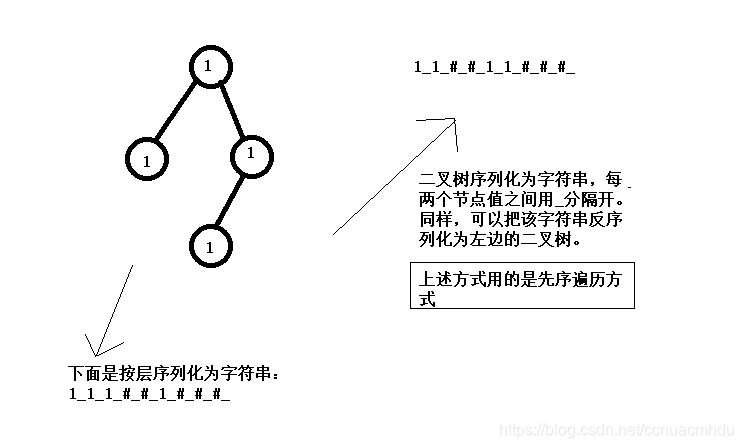
先序序列化
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
}
//先序序列化
public static String serialByPre(Node root){
if(root == null){
return "#_";
}
String res = root.value + "_";
res += serialByPre(root.left);
res += serialByPre(root.right);
return res;
}
//先序反序列化
public static Node deserializeByPre(String preStr){
String[] values = preStr.split("_");
return buildTreeByPreStr(values, 0);
}
public static Node buildTreeByPreStr(String[] values, int i){
if(values[0].equals("#")){
return null;
}
Node root = new Node(Integer.valueOf(values, i++));
root.left = buildTreeByPreStr(values, i++);
root.right = buildTreeByPreStr(values, i++);
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
}
}
按层序列化
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
}
//层序序列化
public static String serializeByLevel(Node root){
if(root == null){
return "#_";
}
String res = root.value + "_";
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
root = queue.poll();
if(root.left != null){
res += root.left.value + "_";
queue.add(root.left);
}else{
res += "#_";
}
if(root.right != null){
res += root.right.value + "_";
queue.add(root.right);
}else{
res += "#_";
}
}
return res;
}
//层序反序列化
public static Node deserializeByLevel(String levelStr){
String[] values = levelStr.split("_");
int index = 0;
Node root = generateNodeByStr(values[i++]);
if(root == null){
return null;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.add(root);
Node tmp = null;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
tmp = queue.poll();
tmp.left = generateNodeByStr(values[i++]);
tmp.right = generateNodeByStr(values[i++]);
if(tmp.left != null){
queue.add(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right != null){
queue.add(tmp.right);
}
}
return root;
}
public static Node generateNodeByStr(String str){
if(str.equals("#")){
return null;
}
return new Node(Integer.valueOf(str));
}
public static void main(String[] args){
}
}
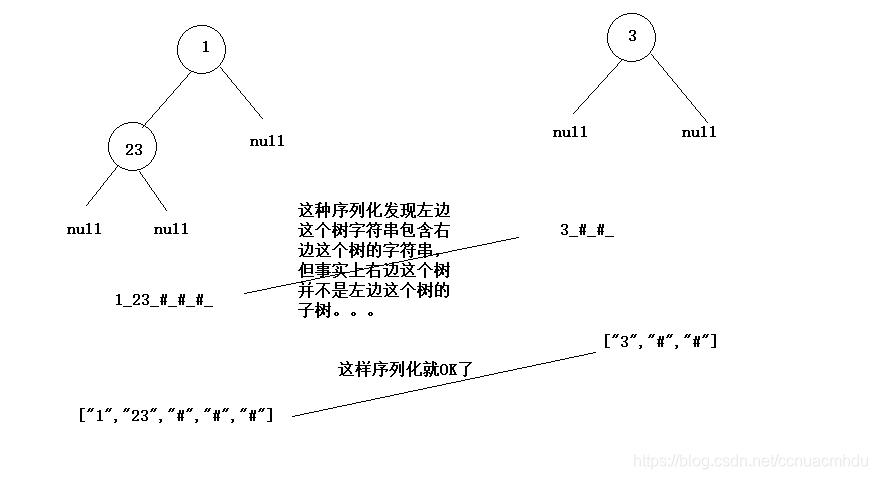
判二叉树A是否为二叉树B的子树
暴力方法:拿着B的任意个节点去遍历,同时遍历A,如果匹配上了就是,否则不是。
KMP方法:先把树序列化成字符串,看看其中一个树的字符串是否被另一棵树的字符串所包含。
折纸问题
请把一段纸条竖着放在桌子上,然后从纸条的下边向上方对折1次,压出折痕后展开。此时折痕是凹下去的,即折痕突起的方向指向纸条的背面。如果从纸条的下边向上方连续对折2次,压出折痕后展开,此时有三条折痕,从上到下依次是下折痕、下折痕和上折痕。给定一个输入参数N,代表纸条都从下边向上方连续对折N次。请从上到下打印所有折痕的方向。例如:N=1时,打印: down N=2时,打印: down down up
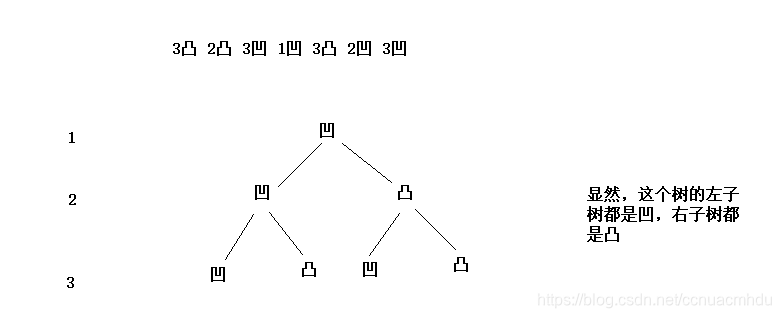
显然中序遍历这个树,就对应了折纸的所有折痕。左孩子代表是上方的,右孩子代表是下方的。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
//i:第i层,n:一共n层,flag:false表示下面节点(右孩子-凸),true表示上面节点(左孩子-凹)
public static void printAll(int i, int n, boolean flag){
print(1, n, true);
}
public static void print(int i, int n, boolean flag){
if(i <= n){
print(i+1,n,true);
System.out.println(flag == true ? "凹" : "凸");
print(i+1,n,false);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
printAll(1,3,true);
}
}
暴力递归到动态规划
动态规划就是暴力尝试减少重复计算的技巧整,而已这种技巧就是一个大型套路先写出用尝试的思路解决问题的递归函数,而不用操心时间复杂度这个过程是无可替代的,没有套路的,只能依靠个人智慧,或者足够多的经验。
但是怎么把尝试的版本,优化成动态规划,是有固定套路的,大体步骤如下:
- 1)找到什么可变参数可以代表一个递归状态,也就是哪些参数一旦确定,返回值就确定了
- 2)把可变参数的所有组合映射成一张表,有 1 个可变参数就是一维表,2 个可变参数就是二维表,…
- 3)最终答案要的是表中的哪个位置,在表中标出
- 4)根据递归过程的 base case,把这张表的最简单、不需要依赖其他位置的那些位置填好值
- 5)根据递归过程非base case的部分,也就是分析表中的普遍位置需要怎么计算得到,那么这张表的填写顺序也就确定了
- 6)填好表,返回最终答案在表中位置的值
机器人达到指定位置方法数
【题目】
假设有排成一行的 N 个位置,记为 1~N,N 一定大于或等于 2。开始时机器人在其中的 M 位置上(M 一定是 1-N 中的一个),机器人可以往左走或者往右走,如果机器人来到 1 位置, 那么下一步只能往右来到 2 位置;如果机器人来到 N 位置,那么下一步只能往左来到 N-1 位置。
规定机器人必须走 K 步,最终能来到 P 位置(P 也一定是 1~N 中的一个)的方法有多少种。给定四个参数 N、M、K、P,返回方法数。
【举例】
N=5,M=2,K=3,P=3
上面的参数代表所有位置为 1 2 3 4 5。机器人最开始在 2 位置上,必须经过 3 步,最后到达 3 位置。走的方法只有如下 3 种: 1)从2到1,从1到2,从2到3 2)从2到3,从3到2,从2到33)从2到3,从3到4,从4到3
所以返回方法数 3。 N=3,M=1,K=3,P=3上面的参数代表所有位置为 1 2 3。机器人最开始在 1 位置上,必须经过 3 步,最后到达 3位置。怎么走也不可能,所以返回方法数 0。
【暴力尝试】
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int robot(int n, int m, int k, int p){
if(n < 2 || m < 1 || m > n || k < 1 || p <1 || p > n){
return 0;
}
return process(n, m, k, p);
}
//在m位置,走k次,走到p的方法数?
public static int process(int n, int m, int k, int p){
if(k == 0){
return m == p ? 1 : 0;
}
if(m == 1){
return process(n, m+1, k-1, p);
}
if(m == n){
return process(n, --m, --k, p);
}
return process(n, m+1, k-1, p) + process(n, m-1, k-1, p);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(process(5,2,3,3));
}
}
【转成dp】
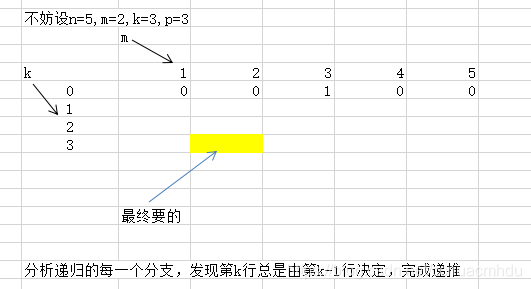 `
`
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int robot(int n, int m, int k, int p){
if(n < 2 || m < 1 || m > n || k < 1 || p <1 || p > n){
return 0;
}
return process(n, m, k, p);
}
//在m位置,走k次,走到p的方法数?
public static int process(int n, int m, int k, int p){
if(k == 0){
return m == p ? 1 : 0;
}
if(m == 1){
return process(n, m+1, k-1, p);
}
if(m == n){
return process(n, m-1, k-1, p);
}
return process(n, m+1, k-1, p) + process(n, m-1, k-1, p);
}
public static int dp(int n, int m, int k, int p){
if(n < 2 || m < 1 || m > n || k < 1 || p <1 || p > n){
return 0;
}
int[][] d = new int[k+1][n+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
d[0][i] = (i == p ? 1 : 0);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <=n; j++){
if(j == 1){
d[i][j] = d[i-1][j+1];
}else if(j == n){
d[i][j] = d[i-1][j-1];
}else{
d[i][j] = d[i-1][j+1] + d[i-1][j-1];
}
}
}
return d[k][m];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(robot(5,2,3,3));
System.out.println(dp(5,2,3,3));
}
}`
换钱的最少货币数
【题目】
给定数组 arr,arr 中所有的值都为正数且不重复。每个值代表一种面值的货币,每种面值的货币可以使用任意张,再给定一个整数 aim,代表要找的钱数,求组成 aim 的最少货币数。
package class07;
public class Code02_CoinsMin {
public static int minCoins1(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) {
return -1;
}
return process(arr, 0, aim);
}
// 当前考虑的面值是arr[i],还剩rest的钱需要找零
// 如果返回-1说明自由使用arr[i..N-1]面值的情况下,无论如何也无法找零rest
// 如果返回不是-1,代表自由使用arr[i..N-1]面值的情况下,找零rest需要的最少张数
public static int process(int[] arr, int i, int rest) {
// base case:
// 已经没有面值能够考虑了
// 如果此时剩余的钱为0,返回0张
// 如果此时剩余的钱不是0,返回-1
if (i == arr.length) {
return rest == 0 ? 0 : -1;
}
// 最少张数,初始时为-1,因为还没找到有效解
int res = -1;
// 依次尝试使用当前面值(arr[i])0张、1张、k张,但不能超过rest
for (int k = 0; k * arr[i] <= rest; k++) {
// 使用了k张arr[i],剩下的钱为rest - k * arr[i]
// 交给剩下的面值去搞定(arr[i+1..N-1])
int next = process(arr, i + 1, rest - k * arr[i]);
if (next != -1) { // 说明这个后续过程有效
res = res == -1 ? next + k : Math.min(res, next + k);
}
}
return res;
}
public static int minCoins2(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) {
return -1;
}
int N = arr.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][aim + 1];
// 设置最后一排的值,除了dp[N][0]为0之外,其他都是-1
for (int col = 1; col <= aim; col++) {
dp[N][col] = -1;
}
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 从底往上计算每一行
for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) { // 每一行都从左往右
dp[i][rest] = -1; // 初始时先设置dp[i][rest]的值无效
if (dp[i + 1][rest] != -1) { // 下面的值如果有效
dp[i][rest] = dp[i + 1][rest]; // dp[i][rest]的值先设置成下面的值
}
// 左边的位置不越界并且有效
if (rest - arr[i] >= 0 && dp[i][rest - arr[i]] != -1) {
if (dp[i][rest] == -1) { // 如果之前下面的值无效
dp[i][rest] = dp[i][rest - arr[i]] + 1;
} else { // 说明下面和左边的值都有效,取最小的
dp[i][rest] = Math.min(dp[i][rest],
dp[i][rest - arr[i]] + 1);
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][aim];
}
// for test
public static int[] generateRandomArray(int len, int max) {
int[] arr = new int[(int) (Math.random() * len) + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * max) + 1;
}
return arr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int len = 10;
int max = 10;
int testTime = 10000;
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
int[] arr = generateRandomArray(len, max);
int aim = (int) (Math.random() * 3 * max) + max;
if (minCoins1(arr, aim) != minCoins2(arr, aim)) {
System.out.println("ooops!");
break;
}
}
}
}
排成一条线的纸牌博弈问题
【题目】
给定一个整型数组 arr,代表数值不同的纸牌排成一条线。玩家 A 和玩家 B 依次拿走每张纸 牌,规定玩家 A 先拿,玩家 B 后拿,但是每个玩家每次只能拿走最左或最右的纸牌,玩家 A 和 玩家 B 都绝顶聪明。请返回最后获胜者的分数。
【举例】
arr=[1,2,100,4]。
开始时,玩家 A 只能拿走 1 或 4。如果玩家 A 拿走 1,则排列变为[2,100,4],接下来玩家 B可以拿走 2 或 4,然后继续轮到玩家 A。如果开始时玩家 A 拿走 4,则排列变为[1,2,100],接下 来玩家 B 可以拿走 1 或 100,然后继续轮到玩家 A。玩家 A 作为绝顶聪明的人不会先拿 4,因为 拿 4 之后,玩家 B 将拿走 100。所以玩家 A 会先拿 1,让排列变为[2,100,4],接下来玩家 B 不管 怎么选,100 都会被玩家 A 拿走。玩家 A 会获胜,分数为 101。所以返回 101。arr=[1,100,2]。
开始时,玩家 A 不管拿 1 还是 2,玩家 B 作为绝顶聪明的人,都会把 100 拿走。玩家 B 会获胜,分数为 100。所以返回 100。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int win1(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(f(arr, 0, arr.length - 1), s(arr, 0, arr.length - 1));
}
public static int f(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
if (i == j) {
return arr[i];
}
return Math.max(arr[i] + s(arr, i + 1, j), arr[j] + s(arr, i, j - 1));
}
public static int s(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
if (i == j) {
return 0;
}
return Math.min(f(arr, i + 1, j), f(arr, i, j - 1));
}
public static int win2(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][] f = new int[arr.length][arr.length];
int[][] s = new int[arr.length][arr.length];
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
f[j][j] = arr[j];
for (int i = j - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
f[i][j] = Math.max(arr[i] + s[i + 1][j], arr[j] + s[i][j - 1]);
s[i][j] = Math.min(f[i + 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
}
}
return Math.max(f[0][arr.length - 1], s[0][arr.length - 1]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 9, 1 };
System.out.println(win1(arr));
System.out.println(win2(arr));
}
}
象棋中马的跳法
【题目】
请同学们自行搜索或者想象一个象棋的棋盘,然后把整个棋盘放入第一象限,棋盘的最左下角是(0,0)位置。那么整个棋盘就是横坐标上9条线、纵坐标上10条线的一个区域。给你三个参数,x,y,k,返回如果“马”从(0,0)位置出发,必须走k步,最后落在(x,y)上的方法数有多少种?
package class07;
public class Code04_HorseJump {
public static int getWays(int x, int y, int step) {
return process(x, y, step);
}
public static int process(int x, int y, int step) {
if (x < 0 || x > 8 || y < 0 || y > 9) {
return 0;
}
if (step == 0) {
return (x == 0 && y == 0) ? 1 : 0;
}
return process(x - 1, y + 2, step - 1)
+ process(x + 1, y + 2, step - 1)
+ process(x + 2, y + 1, step - 1)
+ process(x + 2, y - 1, step - 1)
+ process(x + 1, y - 2, step - 1)
+ process(x - 1, y - 2, step - 1)
+ process(x - 2, y - 1, step - 1)
+ process(x - 2, y + 1, step - 1);
}
public static int dpWays(int x, int y, int step) {
if (x < 0 || x > 8 || y < 0 || y > 9 || step < 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][][] dp = new int[9][10][step + 1];
dp[0][0][0] = 1;
for (int h = 1; h <= step; h++) {
for (int r = 0; r < 9; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < 10; c++) {
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r - 1, c + 2, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r + 1, c + 2, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r + 2, c + 1, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r + 2, c - 1, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r + 1, c - 2, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r - 1, c - 2, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r - 2, c - 1, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r - 2, c + 1, h - 1);
}
}
}
return dp[x][y][step];
}
public static int getValue(int[][][] dp, int row, int col, int step) {
if (row < 0 || row > 8 || col < 0 || col > 9) {
return 0;
}
return dp[row][col][step];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 7;
int y = 7;
int step = 10;
System.out.println(getWays(x, y, step));
System.out.println(dpWays(x, y, step));
}
}
Bob的生存概率
【题目】
给定五个参数n,m,i,j,k。表示在一个N*M的区域,Bob处在(i,j)点,每次Bob等概率的向上、下、左、右四个方向移动一步,Bob必须走K步。如果走完之后,Bob还停留在这个区域上,就算Bob存活,否则就算Bob死亡。请求解Bob的生存概率,返回字符串表示分数的方式。
package class07;
public class Code05_BobDie {
public static String bob1(int N, int M, int i, int j, int K) {
long all = (long) Math.pow(4, K);
long live = process(N, M, i, j, K);
long gcd = gcd(all, live);
return String.valueOf((live / gcd) + "/" + (all / gcd));
}
public static long process(int N, int M, int row, int col, int rest) {
if (row < 0 || row == N || col < 0 || col == M) {
return 0;
}
if (rest == 0) {
return 1;
}
long live = process(N, M, row - 1, col, rest - 1);
live += process(N, M, row + 1, col, rest - 1);
live += process(N, M, row, col - 1, rest - 1);
live += process(N, M, row, col + 1, rest - 1);
return live;
}
public static long gcd(long m, long n) {
return n == 0 ? m : gcd(n, m % n);
}
public static String bob2(int N, int M, int i, int j, int K) {
int[][][] dp = new int[N + 2][M + 2][K + 1];
for (int row = 1; row <= N; row++) {
for (int col = 1; col <= M; col++) {
dp[row][col][0] = 1;
}
}
for (int rest = 1; rest <= K; rest++) {
for (int row = 1; row <= N; row++) {
for (int col = 1; col <= M; col++) {
dp[row][col][rest] = dp[row - 1][col][rest - 1];
dp[row][col][rest] += dp[row + 1][col][rest - 1];
dp[row][col][rest] += dp[row][col - 1][rest - 1];
dp[row][col][rest] += dp[row][col + 1][rest - 1];
}
}
}
long all = (long) Math.pow(4, K);
long live = dp[i + 1][j + 1][K];
long gcd = gcd(all, live);
return String.valueOf((live / gcd) + "/" + (all / gcd));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 10;
int M = 10;
int i = 3;
int j = 2;
int K = 5;
System.out.println(bob1(N, M, i, j, K));
System.out.println(bob2(N, M, i, j, K));
}
}
矩阵的最小路径和—讲解状态压缩
下面这个题目会给出状态压缩,对空间进行优化。空间优化其实就是覆盖掉了一些值。覆盖掉了就找不到原来的路径信息了哦。
【题目】
给定一个矩阵 m,从左上角开始每次只能向右或者向下走,最后到达右下角的位置,路径上所有的数字累加起来就是路径和,返回所有的路径中最小的路径和。
【举例】
如果给定的 m 如下: 1359 8134 5061 8840
路径 1,3,1,0,6,1,0 是所有路径中路径和最小的,所以返回12
【求解】
1.暴力递归
2.改成dp
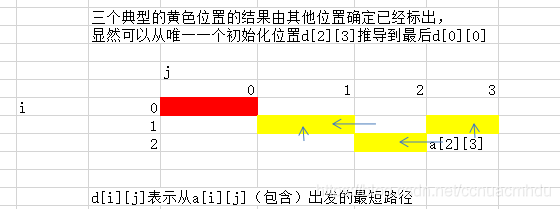
3.状态压缩
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int minPathSum0(int[][] a){
if(a == null || a.length == 0 || a[0] == null || a[0].length == 0){
return 0;
}
int row = a.length;
int col = a[0].length;
return process(a, 0, 0, row, col);
}
//1.首先暴力递归尝试,主要是找准递归结束条件和递归方程
//从a[i][j]出发(包含a[i][j])到右下角节点的路径最小值
public static int process(int[][] a, int i, int j, int row, int col){
if(i == row - 1 && j == col - 1){
return a[i][j];
}else if(i == row - 1){
return a[i][j] + process(a, i, j+1, row, col);
}else if(j == col - 1){
return a[i][j] + process(a, i+1, j, row, col);
}else{
return Math.min(a[i][j] + process(a, i+1, j, row, col),
a[i][j] + process(a, i, j+1, row, col));
}
}
//2.然后把暴力递归改写成动态规划(分析变量和不变量,搞出表,初始化,依赖分析,推导)
public static int minPathSumDP0(int[][] a){
if(a == null || a.length == 0 || a[0] == null || a[0].length == 0){
return 0;
}
int row = a.length;
int col = a[0].length;
int[][] d = new int[row][col];
d[row-1][col-1] = a[row-1][col-1];
for(int i = row - 1; i >= 0; i--){
for(int j = col - 1; j >= 0; j--){
if(i == row - 1 && j + 1 < col){
d[i][j] = d[i][j+1] + a[i][j];
}
if(j == col - 1 && i + 1 < row){
d[i][j] = d[i+1][j] + a[i][j];
}
if(i != row - 1 && j != col - 1){
d[i][j] = Math.min(a[i][j] + d[i+1][j], a[i][j] + d[i][j+1]);
}
}
}
return d[0][0];
}
//3.对动态规划状态进行压缩(根据原始动态规划,观察依赖关系,看看是否需要借助临时变量,本题不需要)
public static int minPathSumDP1(int[][] a){
if(a == null || a.length == 0 || a[0] == null || a[0].length == 0){
return 0;
}
int row = a.length;
int col = a[0].length;
int[] d = new int[col];
d[col-1] = a[row-1][col-1];
for(int i = row - 1; i >= 0; i--){
for(int j = col - 1; j >= 0; j--){
if(i == row - 1 && j + 1 < col){
d[j] = a[i][j] + d[j+1];
}
if(j == col - 1 && i + 1 < row){
d[j] = d[j] + a[i][j];
}
if(i != row - 1 && j != col - 1){
d[j] = Math.min(d[j+1], d[j]) + a[i][j];
}
}
}
return d[0];
}
public static int[][] generateRandomMatrix(int rowSize, int colSize) {
if (rowSize < 0 || colSize < 0) {
return null;
}
int[][] result = new int[rowSize][colSize];
for (int i = 0; i != result.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j != result[0].length; j++) {
result[i][j] = (int) (Math.random() * 10);
}
}
return result;
}
// for test
public static void printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
for (int i = 0; i != matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j != matrix[0].length; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 500000;
boolean flag = true;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
int[][] m = generateRandomMatrix(3, 4);
if(minPathSumDP0(m) != minPathSumDP1(m)){
printMatrix(m);
System.out.println(minPathSumDP0(m));
System.out.println(minPathSumDP1(m));
flag = false;
break;
}
if(minPathSumDP0(m) != minPathSum0(m)){
printMatrix(m);
System.out.println(minPathSumDP0(m));
System.out.println(minPathSum0(m));
flag = false;
break;
}
if(minPathSumDP1(m) != minPathSum0(m)){
printMatrix(m);
System.out.println(minPathSumDP1(m));
System.out.println(minPathSum0(m));
flag = false;
break;
}
}
System.out.println(flag);
}
}
图
DFS、BFS
拓扑排序
最小生成树(prime/kruskal+并查集)
最短路径(dijkstra/bellmanford/floyd)
哈希表
设计RandomPool结构
设计一种结构,在该结构中有如下三个功能:
insert(key):将某个key加入到该结构,做到不重复加入。
delete(key):将原本在结构中的某个key移除。
getRandom():等概率随机返回结构中的任何一个key。
【要求】
Insert、delete和getRandom方法的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
【代码】
import java.util.HashMap;
/*
使用两个Map,一个存放键-编号,另一个存放编号-键
注意删除,把最后一个变成要删除的那个,总量减去1
*/
public class Main {
public static class Pool<K> {
private HashMap<K, Integer> keyIndexMap;
private HashMap<Integer, K> indexKeyMap;
private int size;
public Pool() {
this.keyIndexMap = new HashMap<K, Integer>();
this.indexKeyMap = new HashMap<Integer, K>();
this.size = 0;
}
public void insert(K key) {
if (!this.keyIndexMap.containsKey(key)) {
this.keyIndexMap.put(key, this.size);
this.indexKeyMap.put(this.size++, key);
}
}
public void delete(K key) {
if (this.keyIndexMap.containsKey(key)) {
int deleteIndex = this.keyIndexMap.get(key);
int lastIndex = --this.size;
K lastKey = this.indexKeyMap.get(lastIndex);
this.keyIndexMap.put(lastKey, deleteIndex);
this.indexKeyMap.put(deleteIndex, lastKey);
this.keyIndexMap.remove(key);
this.indexKeyMap.remove(lastIndex);
}
}
public K getRandom() {
if (this.size == 0) {
return null;
}
int randomIndex = (int) (Math.random() * this.size); // 0 ~ size -1
return this.indexKeyMap.get(randomIndex);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pool<String> pool = new Pool<String>();
pool.insert("zuo");
pool.insert("cheng");
pool.insert("yun");
System.out.println(pool.getRandom());
System.out.println(pool.getRandom());
System.out.println(pool.getRandom());
System.out.println(pool.getRandom());
System.out.println(pool.getRandom());
System.out.println(pool.getRandom());
}
}
并查集
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Code04_UnionFind {
// 样本进来会包一层,叫做元素,用户给的是V
public static class Element<V> {
public V value;
public Element(V value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public static class UnionFindSet<V> {
public HashMap<V, Element<V>> elementMap; // 用户的每个V封装成一个Element
// key 某个元素 value 该元素的父
public HashMap<Element<V>, Element<V>> fatherMap; // 元素和父元素
// key 某个集合的代表元素 value 该集合的大小
public HashMap<Element<V>, Integer> sizeMap; // 每个集合根和该集合大小
public UnionFindSet(List<V> list) {
elementMap = new HashMap<>();
fatherMap = new HashMap<>();
sizeMap = new HashMap<>();
for (V value : list) {
Element<V> element = new Element<V>(value);
elementMap.put(value, element);
fatherMap.put(element, element);
sizeMap.put(element, 1);
}
}
// 给定一个ele,往上一直找,把代表元素返回,一路往上找的所有元素的父亲全都改成根
private Element<V> findHead(Element<V> element) {
Stack<Element<V>> path = new Stack<>();
while (element != fatherMap.get(element)) {
path.push(element);
element = fatherMap.get(element);
}
while (!path.isEmpty()) {
fatherMap.put(path.pop(), element);
}
return element;
}
public boolean isSameSet(V a, V b) {
if (elementMap.containsKey(a) && elementMap.containsKey(b)) {
return findHead(elementMap.get(a)) == findHead(elementMap.get(b));
}
return false;
}
public void union(V a, V b) {
if (elementMap.containsKey(a) && elementMap.containsKey(b)) {
Element<V> aF = findHead(elementMap.get(a));
Element<V> bF = findHead(elementMap.get(b));
if (aF != bF) {
Element<V> big = sizeMap.get(aF) >= sizeMap.get(bF) ? aF : bF;
Element<V> small = big == aF ? bF : aF;
fatherMap.put(small, big);
sizeMap.put(big, sizeMap.get(aF) + sizeMap.get(bF));
sizeMap.remove(small);
}
}
}
}
}
有序表
二叉搜索树
仅说明一点,待删除节点的四种情况,待删除节点的左右孩子有空的三种情况比较简单,下面演示待删除节点的左右孩子都不空的情况。


/**
*
* Abstract binary search tree implementation. Its basically fully implemented
* binary search tree, just template method is provided for creating Node (other
* trees can have slightly different nodes with more info). This way some code
* from standart binary search tree can be reused for other kinds of binary
* trees.
*
* @author Ignas Lelys
* @created Jun 29, 2011
*
*/
public class AbstractBinarySearchTree {
/** Root node where whole tree starts. */
public Node root;
/** Tree size. */
protected int size;
/**
* Because this is abstract class and various trees have different
* additional information on different nodes subclasses uses this abstract
* method to create nodes (maybe of class {@link Node} or maybe some
* different node sub class).
*
* @param value
* Value that node will have.
* @param parent
* Node's parent.
* @param left
* Node's left child.
* @param right
* Node's right child.
* @return Created node instance.
*/
protected Node createNode(int value, Node parent, Node left, Node right) {
return new Node(value, parent, left, right);
}
/**
* Finds a node with concrete value. If it is not found then null is
* returned.
*
* @param element
* Element value.
* @return Node with value provided, or null if not found.
*/
public Node search(int element) {
Node node = root;
while (node != null && node.value != null && node.value != element) {
if (element < node.value) {
node = node.left;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
}
return node;
}
/**
* Insert new element to tree.
*
* @param element
* Element to insert.
*/
public Node insert(int element) {
if (root == null) {
root = createNode(element, null, null, null);
size++;
return root;
}
Node insertParentNode = null;
Node searchTempNode = root;
while (searchTempNode != null && searchTempNode.value != null) {
insertParentNode = searchTempNode;
if (element < searchTempNode.value) {
searchTempNode = searchTempNode.left;
} else {
searchTempNode = searchTempNode.right;
}
}
Node newNode = createNode(element, insertParentNode, null, null);
if (insertParentNode.value > newNode.value) {
insertParentNode.left = newNode;
} else {
insertParentNode.right = newNode;
}
size++;
return newNode;
}
/**
* Removes element if node with such value exists.
*
* @param element
* Element value to remove.
*
* @return New node that is in place of deleted node. Or null if element for
* delete was not found.
*/
public Node delete(int element) {
Node deleteNode = search(element);
if (deleteNode != null) {
return delete(deleteNode);
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Delete logic when node is already found.
*
* @param deleteNode
* Node that needs to be deleted.
*
* @return New node that is in place of deleted node. Or null if element for
* delete was not found.
*/
protected Node delete(Node deleteNode) {
if (deleteNode != null) {
Node nodeToReturn = null;
if (deleteNode.left == null) {
// 只要左孩子为空(包含仅左孩子空和左右孩子都空两种情况)
nodeToReturn = transplant(deleteNode, deleteNode.right);
} else if (deleteNode.right == null) {
// 仅右孩子空
nodeToReturn = transplant(deleteNode, deleteNode.left);
} else {
// 左右孩子都不空。deleteNode的右孩子的最左孩子是deleteNode节点的后继结点
Node successorNode = getMinimum(deleteNode.right); // 找deleteNode.right的最左孩子
if (successorNode.parent != deleteNode) {
// deleteNode的后继结点不是deleteNode.right,就不需要下面三行代码
transplant(successorNode, successorNode.right);
successorNode.right = deleteNode.right;
successorNode.right.parent = successorNode;
}
transplant(deleteNode, successorNode);
successorNode.left = deleteNode.left;
successorNode.left.parent = successorNode;
nodeToReturn = successorNode;
}
size--;
return nodeToReturn;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Put one node from tree (newNode) to the place of another (nodeToReplace).
*
* @param nodeToReplace
* Node which is replaced by newNode and removed from tree.
* @param newNode
* New node.
*
* @return New replaced node.
*/
private Node transplant(Node nodeToReplace, Node newNode) {
if (nodeToReplace.parent == null) {
this.root = newNode;
} else if (nodeToReplace == nodeToReplace.parent.left) {
nodeToReplace.parent.left = newNode;
} else {
nodeToReplace.parent.right = newNode;
}
if (newNode != null) {
newNode.parent = nodeToReplace.parent;
}
return newNode;
}
/**
* @param element
* @return true if tree contains element.
*/
public boolean contains(int element) {
return search(element) != null;
}
/**
* @return Minimum element in tree.
*/
public int getMinimum() {
return getMinimum(root).value;
}
/**
* @return Maximum element in tree.
*/
public int getMaximum() {
return getMaximum(root).value;
}
/**
* Get next element element who is bigger than provided element.
*
* @param element
* Element for whom descendand element is searched
* @return Successor value.
*/
// TODO Predecessor
public int getSuccessor(int element) {
return getSuccessor(search(element)).value;
}
/**
* @return Number of elements in the tree.
*/
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
/**
* Tree traversal with printing element values. In order method.
*/
public void printTreeInOrder() {
printTreeInOrder(root);
}
/**
* Tree traversal with printing element values. Pre order method.
*/
public void printTreePreOrder() {
printTreePreOrder(root);
}
/**
* Tree traversal with printing element values. Post order method.
*/
public void printTreePostOrder() {
printTreePostOrder(root);
}
/*-------------------PRIVATE HELPER METHODS-------------------*/
private void printTreeInOrder(Node entry) {
if (entry != null) {
printTreeInOrder(entry.left);
if (entry.value != null) {
System.out.println(entry.value);
}
printTreeInOrder(entry.right);
}
}
private void printTreePreOrder(Node entry) {
if (entry != null) {
if (entry.value != null) {
System.out.println(entry.value);
}
printTreeInOrder(entry.left);
printTreeInOrder(entry.right);
}
}
private void printTreePostOrder(Node entry) {
if (entry != null) {
printTreeInOrder(entry.left);
printTreeInOrder(entry.right);
if (entry.value != null) {
System.out.println(entry.value);
}
}
}
protected Node getMinimum(Node node) {
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
protected Node getMaximum(Node node) {
while (node.right != null) {
node = node.right;
}
return node;
}
protected Node getSuccessor(Node node) {
// if there is right branch, then successor is leftmost node of that
// subtree
if (node.right != null) {
return getMinimum(node.right);
} else {
// otherwise it is a lowest ancestor whose left child is also
// ancestor of node
Node currentNode = node;
Node parentNode = node.parent;
while (parentNode != null && currentNode == parentNode.right) {
// go up until we find parent that currentNode is not in right
// subtree.
currentNode = parentNode;
parentNode = parentNode.parent;
}
return parentNode;
}
}
// -------------------------------- TREE PRINTING
// ------------------------------------
public void printTree() {
printSubtree(root);
}
public void printSubtree(Node node) {
if (node.right != null) {
printTree(node.right, true, "");
}
printNodeValue(node);
if (node.left != null) {
printTree(node.left, false, "");
}
}
private void printNodeValue(Node node) {
if (node.value == null) {
System.out.print("<null>");
} else {
System.out.print(node.value.toString());
}
System.out.println();
}
/*
下面是打印二叉树的形状,可构造一棵简单的二叉树实验下。其实是把二叉树以根为
中心,左旋转90度,每个节点占据1行,依次打印每行的那个节点,显然遍历顺序是
右子树-根-左子树。
*/
private void printTree(Node node, boolean isRight, String indent) {
if (node.right != null) {
printTree(node.right, true, indent + (isRight ? " " : " | "));
}
System.out.print(indent);
if (isRight) {
System.out.print(" /");
} else {
System.out.print(" \\");
}
System.out.print("----- ");
printNodeValue(node);
if (node.left != null) {
printTree(node.left, false, indent + (isRight ? " | " : " "));
}
}
public static class Node {
public Node(Integer value, Node parent, Node left, Node right) {
super();
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public Integer value;
public Node parent;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public boolean isLeaf() {
return left == null && right == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((value == null) ? 0 : value.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Node other = (Node) obj;
if (value == null) {
if (other.value != null)
return false;
} else if (!value.equals(other.value))
return false;
return true;
}
}
}
二叉平衡搜索树
在二叉搜索树基础上,左孩子和右孩子高度差不超过1。在二叉搜索树的基础上,利用左旋和右旋调整,保证二叉搜索树的平衡。AVL树是很严苛的,严格保证左右孩子高度差不超过1,为了进一步提高效率,可以要求平衡性别那么严格,由此而来的SB树就是其中一种。
AVL树、SB树、跳表、KMP、Manacher、Morris遍历等,暂略
参考资料
[1] 《牛客算法基础入门班》
[2] 《牛客算法基础提升班》