Numpy中ndarray运算
问题
如果想要操作符合某一条件的数据,应该怎么做?
1 逻辑运算

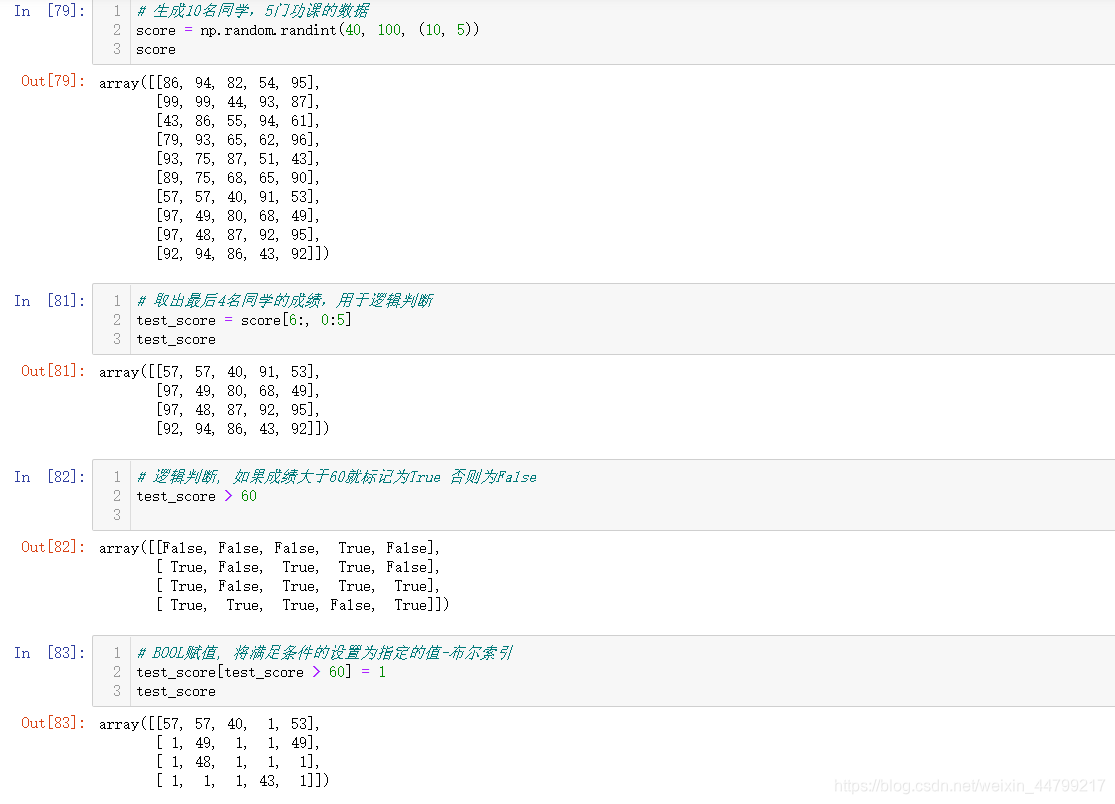
# 生成10名同学,5门功课的数据
>>> score = np.random.randint(40, 100, (10, 5))
# 取出最后4名同学的成绩,用于逻辑判断
>>> test_score = score[6:, 0:5]
# 逻辑判断, 如果成绩大于60就标记为True 否则为False
>>> test_score > 60
array([[ True, True, True, False, True],
[ True, True, True, False, True],
[ True, True, False, False, True],
[False, True, True, True, True]])
# BOOL赋值, 将满足条件的设置为指定的值-布尔索引
>>> test_score[test_score > 60] = 1
>>> test_score
array([[ 1, 1, 1, 52, 1],
[ 1, 1, 1, 59, 1],
[ 1, 1, 44, 44, 1],
[59, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
【数组可以比较逻辑运算,列表不可以】
2 通用判断函数
- np.all()
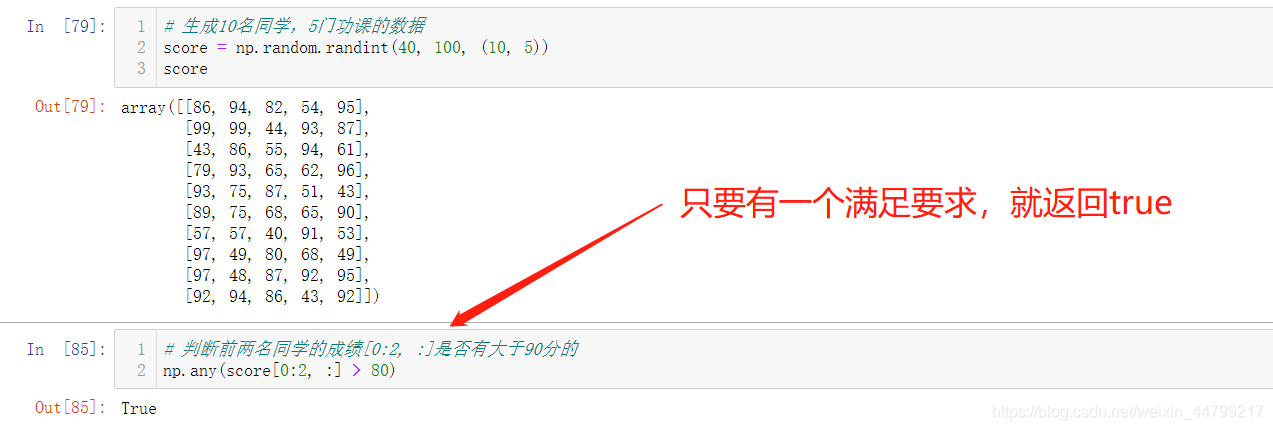
# 判断前两名同学的成绩[0:2, :]是否全及格
>>> np.all(score[0:2, :] > 60)
False

- np.any()
# 判断前两名同学的成绩[0:2, :]是否有大于90分的
>>> np.any(score[0:2, :] > 80)
True
3 np.where(三元运算符)
通过使用np.where能够进行更加复杂的运算
- np.where()
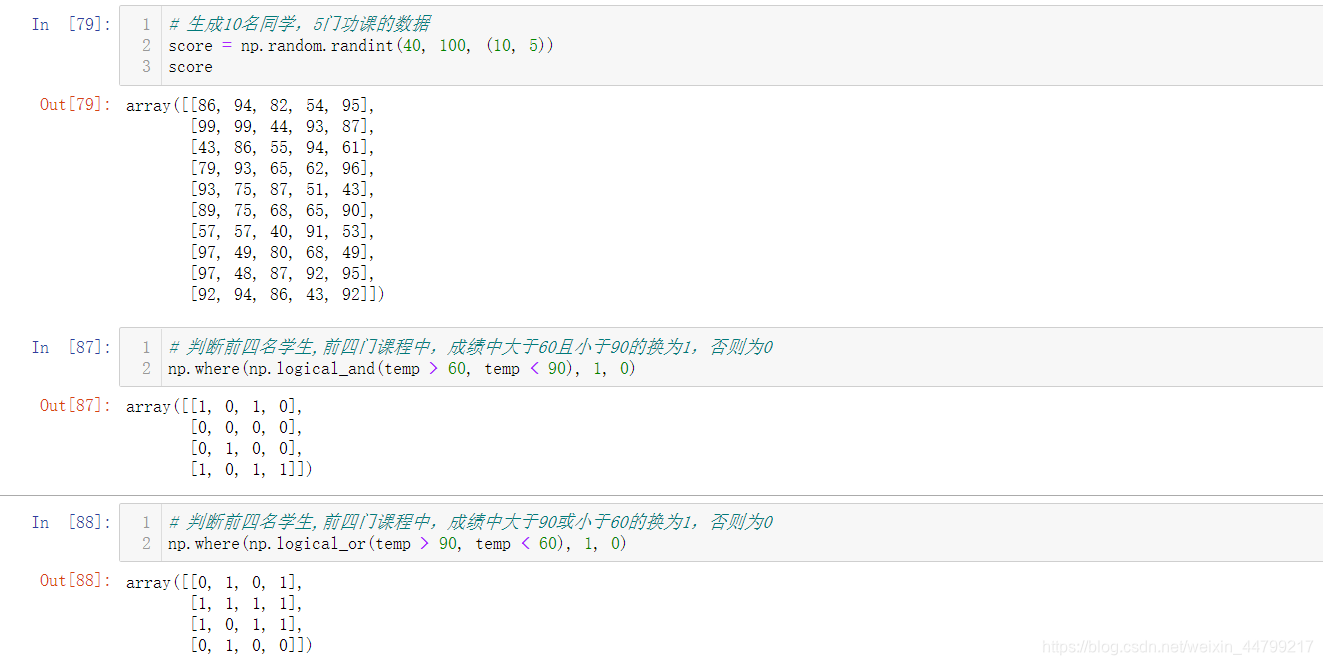
# 判断前四名学生,前四门课程中,成绩中大于60的置为1,否则为0
temp = score[:4, :4]
np.where(temp > 60, 1, 0)

- 复合逻辑需要结合np.logical_and和np.logical_or使用
# 判断前四名学生,前四门课程中,成绩中大于60且小于90的换为1,否则为0
np.where(np.logical_and(temp > 60, temp < 90), 1, 0)
# 判断前四名学生,前四门课程中,成绩中大于90或小于60的换为1,否则为0
np.where(np.logical_or(temp > 90, temp < 60), 1, 0)
4 统计运算
如果想要知道学生成绩最大的分数,或者做小分数应该怎么做?
4.1 统计指标
在数据挖掘/机器学习领域,统计指标的值也是我们分析问题的一种方式。常用的指标如下:
- min(a, axis)
- Return the minimum of an array or minimum along an axis.
- max(a, axis])
- Return the maximum of an array or maximum along an axis.
- median(a, axis) 【中位数】
- Compute the median along the specified axis.
- mean(a, axis, dtype)
- Compute the arithmetic mean along the specified axis.
- std(a, axis, dtype) 【标准差】
- Compute the standard deviation along the specified axis.
- var(a, axis, dtype) 【方差】
- Compute the variance along the specified axis.
4.2 案例:学生成绩统计运算
进行统计的时候,axis 轴的取值并不一定,Numpy中不同的API轴的值都不一样,在这里,axis 0代表列, axis 1代表行去进行统计
# 接下来对于前四名学生,进行一些统计运算
# 指定列 去统计
temp = score[:4, 0:5]
print("前四名学生,各科成绩的最大分:{}".format(np.max(temp, axis=0)))
print("前四名学生,各科成绩的最小分:{}".format(np.min(temp, axis=0)))
print("前四名学生,各科成绩波动情况:{}".format(np.std(temp, axis=0)))
print("前四名学生,各科成绩的平均分:{}".format(np.mean(temp, axis=0)))
结果:

如果需要统计出某科最高分对应的是哪个同学?
- np.argmax(temp, axis=) 【最大值下标】
- np.argmin(temp, axis=) 【最小值下标】
- 【可以写成:temp.argmax(axis=1)】
print("前四名学生,各科成绩最高分对应的学生下标:{}".format(np.argmax(temp, axis=0)))
结果:

5 小结
- 逻辑运算
- 直接进行大于,小于的判断
- 合适之后,可以直接进行赋值
- 通用判断函数
- np.all()
- np.any()
- 统计运算
- np.max()
- np.min()
- np.median()
- np.mean()
- np.std()
- np.var()
- np.argmax(axis=) — 最大元素对应的下标
- np.argmin(axis=) — 最小元素对应的下标