背景
- STM32F107VCT6的RT-Thread开发环境搭建成功
- STM32F10C7VCT6有两路CAN总线
- 调试CAN总线,研究RT-Thread CAN驱动框架的实现方法
移植
首先需要移植并实现RT-Thread 最小系统。
熟悉硬件原理图,确认MSH cmd串口、CAN总线引脚,这里使用CAN1.

通过 STM32CubeMX,配置CAN 引脚,初始化引脚与CAN时钟。

初始化代码
更新后的: stm32f1xx_hal_msp.c 文件。
/**
* @brief CAN MSP Initialization
* This function configures the hardware resources used in this example
* @param hcan: CAN handle pointer
* @retval None
*/
void HAL_CAN_MspInit(CAN_HandleTypeDef* hcan)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
if(hcan->Instance==CAN1)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN CAN1_MspInit 0 */
/* USER CODE END CAN1_MspInit 0 */
/* Peripheral clock enable */
__HAL_RCC_CAN1_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
/**CAN1 GPIO Configuration
PB8 ------> CAN1_RX
PB9 ------> CAN1_TX
*/
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_8;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStruct);
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_9;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_AF_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_HIGH;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStruct);
__HAL_AFIO_REMAP_CAN1_2();
/* USER CODE BEGIN CAN1_MspInit 1 */
/* USER CODE END CAN1_MspInit 1 */
}
}
/**
* @brief CAN MSP De-Initialization
* This function freeze the hardware resources used in this example
* @param hcan: CAN handle pointer
* @retval None
*/
void HAL_CAN_MspDeInit(CAN_HandleTypeDef* hcan)
{
if(hcan->Instance==CAN1)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN CAN1_MspDeInit 0 */
/* USER CODE END CAN1_MspDeInit 0 */
/* Peripheral clock disable */
__HAL_RCC_CAN1_CLK_DISABLE();
/**CAN1 GPIO Configuration
PB8 ------> CAN1_RX
PB9 ------> CAN1_TX
*/
HAL_GPIO_DeInit(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_8|GPIO_PIN_9);
/* USER CODE BEGIN CAN1_MspDeInit 1 */
/* USER CODE END CAN1_MspDeInit 1 */
}
}CAN功能配置
使能RT-Thread CAN驱动框架,这里暂时不使用硬件滤波器(地址过滤)
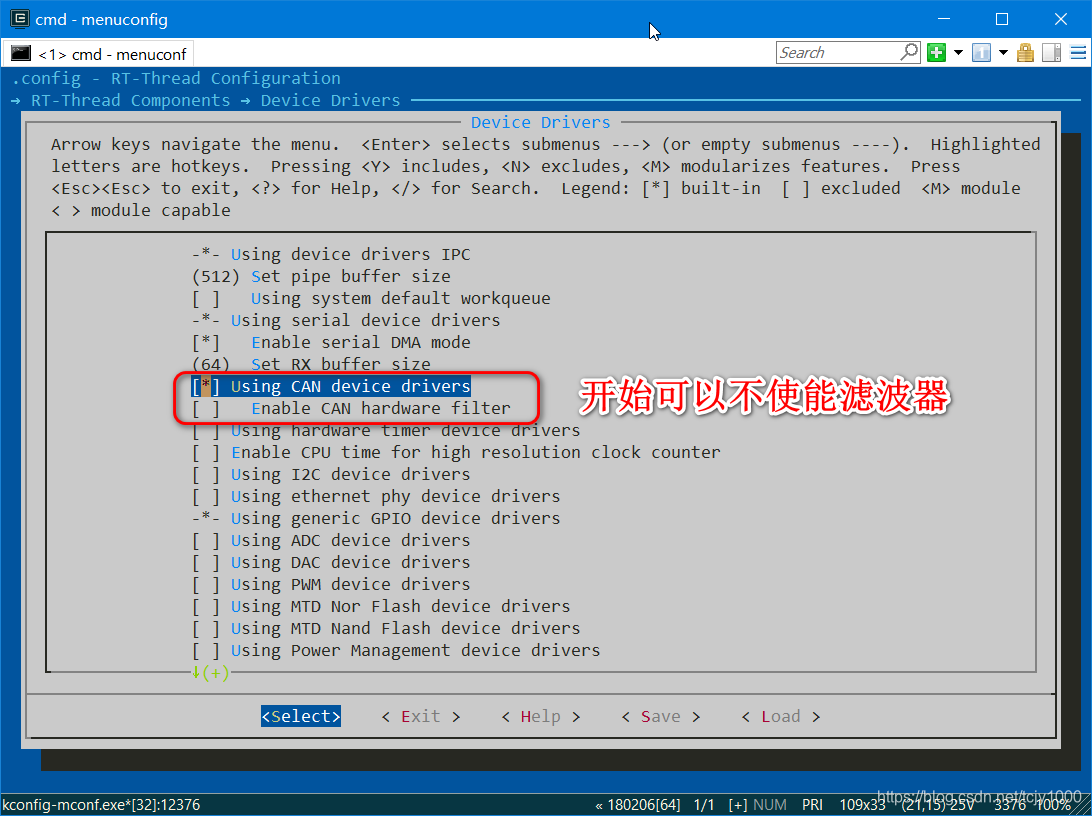

使能CAN
HAL库模块


配置board下的Kconfig文件,使能 宏:BSP_USING_CAN1
menuconfig BSP_USING_CAN
bool "Enable CAN"
select RT_USING_CAN
default n
if BSP_USING_CAN
config BSP_USING_CAN1
bool "Enable CAN1"
default y
config BSP_USING_CAN2
bool "Enable CAN2"
default n
endif

例程
把CAN的测试代码,放在工程目录下。
/*
* 程序清单:这是一个 CAN 设备使用例程
* 例程导出了 can_sample 命令到控制终端
* 命令调用格式:can_sample can1
* 命令解释:命令第二个参数是要使用的 CAN 设备名称,为空则使用默认的 CAN 设备
* 程序功能:通过 CAN 设备发送一帧,并创建一个线程接收数据然后打印输出。
*/
#include <rtthread.h>
#include "rtdevice.h"
#define CAN_DEV_NAME "can1" /* CAN 设备名称 */
static struct rt_semaphore rx_sem; /* 用于接收消息的信号量 */
static rt_device_t can_dev; /* CAN 设备句柄 */
/* 接收数据回调函数 */
static rt_err_t can_rx_call(rt_device_t dev, rt_size_t size)
{
/* CAN 接收到数据后产生中断,调用此回调函数,然后发送接收信号量 */
rt_sem_release(&rx_sem);
return RT_EOK;
}
static void can_rx_thread(void *parameter)
{
int i;
//rt_err_t res;
struct rt_can_msg rxmsg = {0};
/* 设置接收回调函数 */
rt_device_set_rx_indicate(can_dev, can_rx_call);
#if 0
struct rt_can_filter_item items[5] =
{
RT_CAN_FILTER_ITEM_INIT(0x100, 0, 0, 1, 0x700, RT_NULL, RT_NULL), /* std,match ID:0x100~0x1ff,hdr 为 - 1,设置默认过滤表 */
RT_CAN_FILTER_ITEM_INIT(0x300, 0, 0, 1, 0x700, RT_NULL, RT_NULL), /* std,match ID:0x300~0x3ff,hdr 为 - 1 */
RT_CAN_FILTER_ITEM_INIT(0x211, 0, 0, 1, 0x7ff, RT_NULL, RT_NULL), /* std,match ID:0x211,hdr 为 - 1 */
RT_CAN_FILTER_STD_INIT(0x486, RT_NULL, RT_NULL), /* std,match ID:0x486,hdr 为 - 1 */
{0x555, 0, 0, 1, 0x7ff, 7,} /* std,match ID:0x555,hdr 为 7,指定设置 7 号过滤表 */
};
struct rt_can_filter_config cfg = {5, 1, items}; /* 一共有 5 个过滤表 */
/* 设置硬件过滤表 */
res = rt_device_control(can_dev, RT_CAN_CMD_SET_FILTER, &cfg);
RT_ASSERT(res == RT_EOK);
#endif
while (1)
{
/* hdr 值为 - 1,表示直接从 uselist 链表读取数据 */
rxmsg.hdr = -1;
/* 阻塞等待接收信号量 */
rt_sem_take(&rx_sem, RT_WAITING_FOREVER);
/* 从 CAN 读取一帧数据 */
rt_device_read(can_dev, 0, &rxmsg, sizeof(rxmsg));
/* 打印数据 ID 及内容 */
rt_kprintf("ID:%x", rxmsg.id);
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
rt_kprintf("%2x", rxmsg.data[i]);
}
rt_kprintf("\n");
}
}
int can_sample(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct rt_can_msg msg = {0};
rt_err_t res;
rt_size_t size;
rt_thread_t thread;
char can_name[RT_NAME_MAX];
if (argc == 2)
{
rt_strncpy(can_name, argv[1], RT_NAME_MAX);
}
else
{
rt_strncpy(can_name, CAN_DEV_NAME, RT_NAME_MAX);
}
/* 查找 CAN 设备 */
can_dev = rt_device_find(can_name);
if (!can_dev)
{
rt_kprintf("find %s failed!\n", can_name);
return RT_ERROR;
}
/* 初始化 CAN 接收信号量 */
rt_sem_init(&rx_sem, "rx_sem", 0, RT_IPC_FLAG_FIFO);
/* 以中断接收及发送方式打开 CAN 设备 */
res = rt_device_open(can_dev, RT_DEVICE_FLAG_INT_TX | RT_DEVICE_FLAG_INT_RX);
RT_ASSERT(res == RT_EOK);
/* 创建数据接收线程 */
thread = rt_thread_create("can_rx", can_rx_thread, RT_NULL, 1024, 25, 10);
if (thread != RT_NULL)
{
rt_thread_startup(thread);
}
else
{
rt_kprintf("create can_rx thread failed!\n");
}
msg.id = 0x78; /* ID 为 0x78 */
msg.ide = RT_CAN_STDID; /* 标准格式 */
msg.rtr = RT_CAN_DTR; /* 数据帧 */
msg.len = 8; /* 数据长度为 8 */
/* 待发送的 8 字节数据 */
msg.data[0] = 0x00;
msg.data[1] = 0x11;
msg.data[2] = 0x22;
msg.data[3] = 0x33;
msg.data[4] = 0x44;
msg.data[5] = 0x55;
msg.data[6] = 0x66;
msg.data[7] = 0x77;
/* 发送一帧 CAN 数据 */
size = rt_device_write(can_dev, 0, &msg, sizeof(msg));
if (size == 0)
{
rt_kprintf("can dev write data failed!\n");
}
return res;
}
void can_send_test(void)
{
struct rt_can_msg msg = {0};
rt_size_t size;
static rt_uint8_t num = 0;
msg.id = 0x78; /* ID 为 0x78 */
msg.ide = RT_CAN_STDID; /* 标准格式 */
msg.rtr = RT_CAN_DTR; /* 数据帧 */
msg.len = 8; /* 数据长度为 8 */
/* 待发送的 8 字节数据 */
msg.data[0] = 0x00;
msg.data[1] = num++;
msg.data[2] = 0x22;
msg.data[3] = 0x33;
msg.data[4] = num++;
msg.data[5] = 0x55;
msg.data[6] = 0x66;
msg.data[7] = 0x77;
/* 发送一帧 CAN 数据 */
size = rt_device_write(can_dev, 0, &msg, sizeof(msg));
if (size == 0)
{
rt_kprintf("can dev write data failed!\n");
}
}
/* 导出到 msh 命令列表中 */
MSH_CMD_EXPORT(can_sample, can device sample);
MSH_CMD_EXPORT(can_send_test, can send test);
调试
- 这里使用USB-CAN,上位机使用USB_CAN TOOL 工具进行调试。
- 注意CAN波特率设置,这里默认配置为1Mbps。
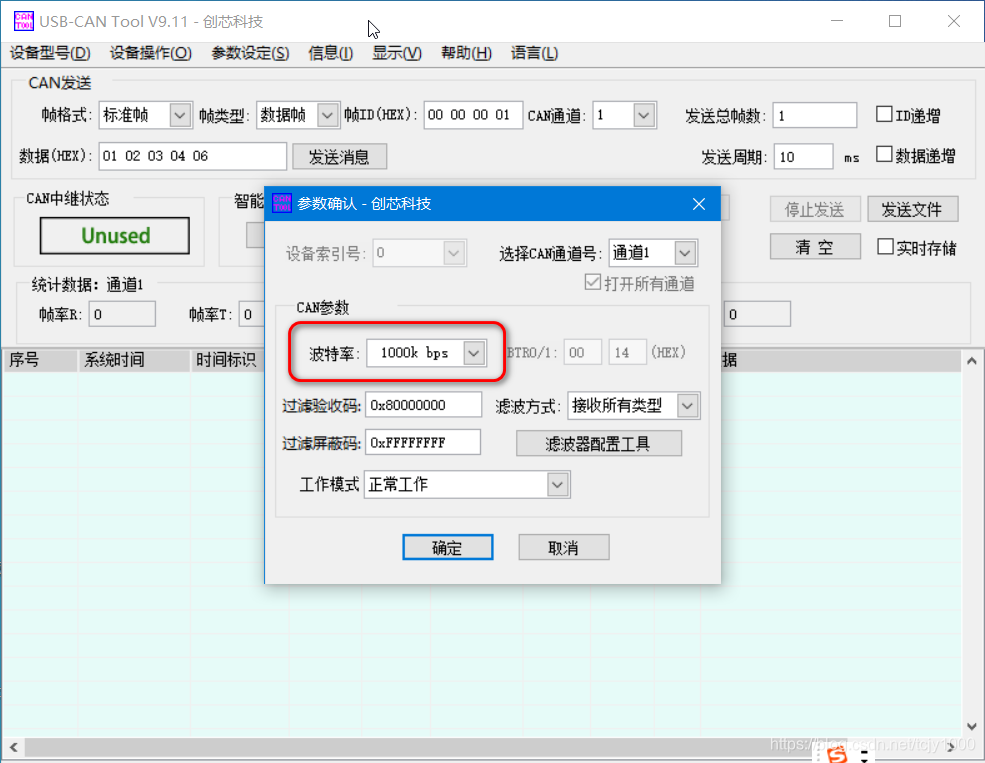
开启CAN通信
CAN测试命令,需要手动输入。
can_sample : 开启CAN Demo通信
can_send_test : 发送CAN数据帧

CAN适合双向通信!多主机、多从机通信。

CAN双向通信初步成功。
总结
- CAN本身属于串行通信的一种。
- CAN使用硬件滤波器,可以过滤不必要的CAN节点的通信,从而不被频繁的总线通信所中断。
- CAN本身的特性,适合多个主机通信。
- 注意CAN的接线方式:CANH <----> CANH CANL <-----> CANL。差分总线,可以不共GND。