- 遗传算法
建立GeneticAlgorithm.py
import numpy as np
from GAIndividual import GAIndividual
import random
import copy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class GeneticAlgorithm:
'''
The class for genetic algorithm
'''
def __init__(self, sizepop, vardim, bound, MAXGEN, params):
'''
sizepop: population sizepop 种群数量 60
vardim: dimension of variables 变量维度 25
bound: boundaries of variables 变量的边界 -600 600
MAXGEN: termination condition 终止条件 1000
param: algorithm required parameters, it is a list which is consisting of crossover rate, mutation rate, alpha
算法所需的参数,它是由交叉率,变异率,alpha组成的列表
0.9, 0.1, 0.5
'''
self.sizepop = sizepop
self.MAXGEN = MAXGEN
self.vardim = vardim
self.bound = bound
self.population = []
#self.fitness 60行一列 全0填充
self.fitness = np.zeros((self.sizepop, 1))
#25行两列
self.trace = np.zeros((self.MAXGEN, 2))
self.params = params
def initialize(self):
'''
initialize the population 初始化种群
'''
for i in range(0, self.sizepop):
ind = GAIndividual(self.vardim, self.bound)
#生成一个随机染色体
ind.generate()
self.population.append(ind)
def evaluate(self):
'''
evaluation of the population fitnesses
评估种群适合度
'''
for i in range(0, self.sizepop):
#计算染色体适应性
self.population[i].calculateFitness()
self.fitness[i] = self.population[i].fitness
def solve(self):
'''
evolution process of genetic algorithm
遗传算法的演化过程
'''
self.t = 0
self.initialize()
self.evaluate()
best = np.max(self.fitness)
bestIndex = np.argmax(self.fitness)
self.best = copy.deepcopy(self.population[bestIndex])
#取平均适应度
self.avefitness = np.mean(self.fitness)
self.trace[self.t, 0] = (1 - self.best.fitness) / self.best.fitness
self.trace[self.t, 1] = (1 - self.avefitness) / self.avefitness
print("Generation %d: optimal function value is: %f; average function value is %f" % (
self.t, self.trace[self.t, 0], self.trace[self.t, 1]))
while (self.t < self.MAXGEN - 1):
self.t += 1
self.selectionOperation()
self.crossoverOperation()
self.mutationOperation()
self.evaluate()
best = np.max(self.fitness)
bestIndex = np.argmax(self.fitness)
if best > self.best.fitness:
self.best = copy.deepcopy(self.population[bestIndex])
self.avefitness = np.mean(self.fitness)
self.trace[self.t, 0] = (1 - self.best.fitness) / self.best.fitness
self.trace[self.t, 1] = (1 - self.avefitness) / self.avefitness
print("Generation %d: optimal function value is: %f; average function value is %f" % (
self.t, self.trace[self.t, 0], self.trace[self.t, 1]))
print("Optimal function value is: %f; " %
self.trace[self.t, 0])
print ("Optimal solution is:")
print (self.best.chrom)
self.printResult()
def selectionOperation(self):
'''
selection operation for Genetic Algorithm
遗传算法的选择操作
'''
newpop = []
totalFitness = np.sum(self.fitness)
accuFitness = np.zeros((self.sizepop, 1))
sum1 = 0.
for i in range(0, self.sizepop):
accuFitness[i] = sum1 + self.fitness[i] / totalFitness
sum1 = accuFitness[i]
for i in range(0, self.sizepop):
r = random.random()
idx = 0
for j in range(0, self.sizepop - 1):
if j == 0 and r < accuFitness[j]:
idx = 0
break
elif r >= accuFitness[j] and r < accuFitness[j + 1]:
idx = j + 1
break
newpop.append(self.population[idx])
self.population = newpop
def crossoverOperation(self):
'''
crossover operation for genetic algorithm
交叉操作
'''
newpop = []
for i in range(0, self.sizepop, 2):
idx1 = random.randint(0, self.sizepop - 1)
idx2 = random.randint(0, self.sizepop - 1)
while idx2 == idx1:
idx2 = random.randint(0, self.sizepop - 1)
newpop.append(copy.deepcopy(self.population[idx1]))
newpop.append(copy.deepcopy(self.population[idx2]))
r = random.random()
if r < self.params[0]:
crossPos = random.randint(1, self.vardim - 1)
for j in range(crossPos, self.vardim):
newpop[i].chrom[j] = newpop[i].chrom[
j] * self.params[2] + (1 - self.params[2]) * newpop[i + 1].chrom[j]
newpop[i + 1].chrom[j] = newpop[i + 1].chrom[j] * self.params[2] + \
(1 - self.params[2]) * newpop[i].chrom[j]
self.population = newpop
def mutationOperation(self):
'''
mutation operation for genetic algorithm
变异操作。
'''
newpop = []
for i in range(0, self.sizepop):
newpop.append(copy.deepcopy(self.population[i]))
r = random.random()
if r < self.params[1]:
mutatePos = random.randint(0, self.vardim - 1)
theta = random.random()
if theta > 0.5:
newpop[i].chrom[mutatePos] = newpop[i].chrom[
mutatePos] - (newpop[i].chrom[mutatePos] - self.bound[0, mutatePos]) * (1 - random.random() ** (1 - self.t / self.MAXGEN))
else:
newpop[i].chrom[mutatePos] = newpop[i].chrom[
mutatePos] + (self.bound[1, mutatePos] - newpop[i].chrom[mutatePos]) * (1 - random.random() ** (1 - self.t / self.MAXGEN))
self.population = newpop
def printResult(self):
'''
plot the result of the genetic algorithm
画出结果
'''
x = np.arange(0, self.MAXGEN)
y1 = self.trace[:, 0]
y2 = self.trace[:, 1]
plt.plot(x, y1, 'r', label='optimal value')
plt.plot(x, y2, 'g', label='average value')
plt.xlabel("Iteration")
plt.ylabel("function value")
plt.title("Genetic algorithm for function optimization")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
bound = np.tile([[-600], [600]], 25)
ga = GeneticAlgorithm(60, 25, bound, 1000, [0.9, 0.1, 0.5])
ga.solve()建立GAIndividual.py
import numpy as np
import ObjFunction
#个体的遗传算法
class GAIndividual:
'''
individual of genetic algorithm
个体的遗传算法
'''
def __init__(self, vardim, bound):
'''
vardim: dimension of variables 维度变量
bound: boundaries of variables 变量的边界
'''
self.vardim = vardim
self.bound = bound
self.fitness = 0.
def generate(self):
'''
generate a random chromsome for genetic algorithm
为遗传算法生成一个随机染色体
'''
len = self.vardim
rnd = np.random.random(size=len)
self.chrom = np.zeros(len)
for i in range(0, len):
self.chrom[i] = self.bound[0, i] + \
(self.bound[1, i] - self.bound[0, i]) * rnd[i]
def calculateFitness(self):
'''
calculate the fitness of the chromsome
计算染色体的适应性
'''
self.fitness = ObjFunction.GrieFunc(
self.vardim, self.chrom, self.bound)三建立ObjFunction.py
import math
#目标函数
def GrieFunc(vardim, x, bound):
"""
Griewangk function
经典函数girewangk
"""
s1 = 0.
s2 = 1.
for i in range(1, vardim + 1):
s1 = s1 + x[i - 1] ** 2
s2 = s2 * math.cos(x[i - 1] / math.sqrt(i))
y = (1. / 4000.) * s1 - s2 + 1
y = 1. / (1. + y)
return y
#非凸优化函数
def RastFunc(vardim, x, bound):
"""
Rastrigin function
在数学优化中,Rastrigin函数是一个非凸函数,用作优化算法的性能测试问题。这是一个非线性多模态函数的典型例子。它最初由Rastrigin [1]提出作为二维函数,并已被Mühlenbein等人推广。[2]寻找这个函数的最小值是一个相当困难的问题,因为它有很大的搜索空间和大量的局部最小值。
在一个n维域上,它被定义为:
{\ displaystyle f(\ mathbf {x})= An + \ sum _ {i = 1} ^ {n} \ left [x_ {i} ^ {2} -A \ cos(2 \ pi x_ {i})\对]} f(\ mathbf {x})= An + \ sum _ {i = 1} ^ {n} \ left [x_ {i} ^ {2} -A \ cos(2 \ pi x_ {i})\ right]
"""
s = 10 * 25
for i in range(1, vardim + 1):
s = s + x[i - 1] ** 2 - 10 * math.cos(2 * math.pi * x[i - 1])
return s基于遗传算法的多目标算法
#Importing required modules
import math
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def function1(x):
value = -x**2
return value
def function2(x):
value = -(x-2)**2
return value
#Function to find index of list
#函数查找列表的索引
def index_of(a,list):
for i in range(0,len(list)):
if list[i] == a:
return i
return -1
#Function to sort by values 函数根据值排序
def sort_by_values(list1, values):
sorted_list = []
while(len(sorted_list)!=len(list1)):
if index_of(min(values),values) in list1:
sorted_list.append(index_of(min(values),values))
values[index_of(min(values),values)] = math.inf
return sorted_list
#Function to carry out NSGA-II's fast non dominated sort
#函数执行NSGA-II的快速非支配排序
"""基于序列和拥挤距离"""
def fast_non_dominated_sort(values1, values2):
S=[[] for i in range(0,len(values1))]
front = [[]]
n=[0 for i in range(0,len(values1))]
rank = [0 for i in range(0, len(values1))]
for p in range(0,len(values1)):
S[p]=[]
n[p]=0
for q in range(0, len(values1)):
#p > q
if (values1[p] > values1[q] and values2[p] > values2[q]) or (values1[p] >= values1[q] and values2[p] > values2[q]) or (values1[p] > values1[q] and values2[p] >= values2[q]):
if q not in S[p]:
S[p].append(q)
elif (values1[q] > values1[p] and values2[q] > values2[p]) or (values1[q] >= values1[p] and values2[q] > values2[p]) or (values1[q] > values1[p] and values2[q] >= values2[p]):
n[p] = n[p] + 1
if n[p]==0:
rank[p] = 0
if p not in front[0]:
front[0].append(p)
i = 0
while(front[i] != []):
Q=[]
for p in front[i]:
for q in S[p]:
n[q] =n[q] - 1
if( n[q]==0):
rank[q]=i+1
if q not in Q:
Q.append(q)
i = i+1
front.append(Q)
del front[len(front)-1]
return front
#Function to calculate crowding distance
#计算拥挤距离的函数
def crowding_distance(values1, values2, front):
distance = [0 for i in range(0,len(front))]
sorted1 = sort_by_values(front, values1[:])
sorted2 = sort_by_values(front, values2[:])
distance[0] = 4444444444444444
distance[len(front) - 1] = 4444444444444444
for k in range(1,len(front)-1):
distance[k] = distance[k]+ (values1[sorted1[k+1]] - values2[sorted1[k-1]])/(max(values1)-min(values1))
for k in range(1,len(front)-1):
distance[k] = distance[k]+ (values1[sorted2[k+1]] - values2[sorted2[k-1]])/(max(values2)-min(values2))
return distance
#Function to carry out the crossover
#函数进行交叉
def crossover(a,b):
r=random.random()
if r>0.5:
return mutation((a+b)/2)
else:
return mutation((a-b)/2)
#Function to carry out the mutation operator
#函数进行变异操作
def mutation(solution):
mutation_prob = random.random()
if mutation_prob <1:
solution = min_x+(max_x-min_x)*random.random()
return solution
#Main program starts here
pop_size = 20
max_gen = 921
#Initialization
min_x=-55
max_x=55
solution=[min_x+(max_x-min_x)*random.random() for i in range(0,pop_size)]
gen_no=0
while(gen_no<max_gen):
function1_values = [function1(solution[i])for i in range(0,pop_size)]
function2_values = [function2(solution[i])for i in range(0,pop_size)]
non_dominated_sorted_solution = fast_non_dominated_sort(function1_values[:],function2_values[:])
print("The best front for Generation number ",gen_no, " is")
for valuez in non_dominated_sorted_solution[0]:
print(round(solution[valuez],3),end=" ")
print("\n")
crowding_distance_values=[]
for i in range(0,len(non_dominated_sorted_solution)):
crowding_distance_values.append(crowding_distance(function1_values[:],function2_values[:],non_dominated_sorted_solution[i][:]))
solution2 = solution[:]
#Generating offsprings
while(len(solution2)!=2*pop_size):
a1 = random.randint(0,pop_size-1)
b1 = random.randint(0,pop_size-1)
solution2.append(crossover(solution[a1],solution[b1]))
function1_values2 = [function1(solution2[i])for i in range(0,2*pop_size)]
function2_values2 = [function2(solution2[i])for i in range(0,2*pop_size)]
non_dominated_sorted_solution2 = fast_non_dominated_sort(function1_values2[:],function2_values2[:])
crowding_distance_values2=[]
for i in range(0,len(non_dominated_sorted_solution2)):
crowding_distance_values2.append(crowding_distance(function1_values2[:],function2_values2[:],non_dominated_sorted_solution2[i][:]))
new_solution= []
for i in range(0,len(non_dominated_sorted_solution2)):
non_dominated_sorted_solution2_1 = [index_of(non_dominated_sorted_solution2[i][j],non_dominated_sorted_solution2[i] ) for j in range(0,len(non_dominated_sorted_solution2[i]))]
front22 = sort_by_values(non_dominated_sorted_solution2_1[:], crowding_distance_values2[i][:])
front = [non_dominated_sorted_solution2[i][front22[j]] for j in range(0,len(non_dominated_sorted_solution2[i]))]
front.reverse()
for value in front:
new_solution.append(value)
if(len(new_solution)==pop_size):
break
if (len(new_solution) == pop_size):
break
solution = [solution2[i] for i in new_solution]
gen_no = gen_no + 1
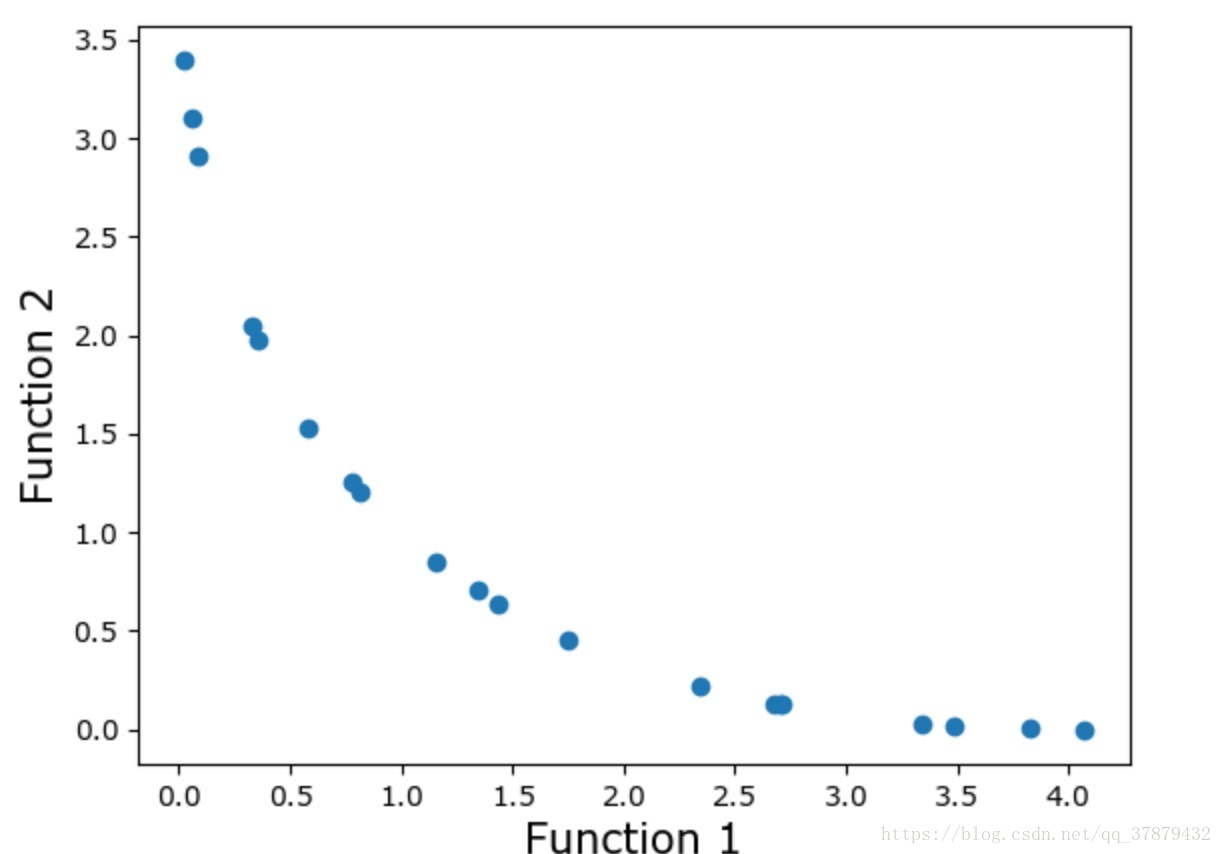
#Lets plot the final front now
function1 = [i * -1 for i in function1_values]
function2 = [j * -1 for j in function2_values]
plt.xlabel('Function 1', fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('Function 2', fontsize=15)
plt.scatter(function1, function2)
plt.show()