英语语法总结
- 第一部分:基础概念
- 第二部分:基础篇
- 2.1 词性一 名词
2.1.1 名词的分类
2.1.2 名词所有格
2.1.3 主谓一致 - 2.2 词性二 代词
2.2.1 人称代词
2.2.2 物主代词
2.2.3 反身代词
2.2.4 指示代词
2.2.5 关系代词
2.2.6 连接代词
2.2.7 不定代词
2.2.8 相互代词
2.2.9 疑问代词 - 2.3 词性三 数词
2.3.1 基数词
2.3.2 序数词
2.3.3 数次的用法大全 - 2.4 词性四 冠词
2.4.1 不定冠词
2.4.2 定冠词
2.4.3 零冠词 - 2.5 词性五 形容词&副词
2.5.1 形容词
2.5.2 副词
2.5.3 形容词、副词的原级、比较级和最高级 - 2.6 词性六 动词
2.6.1 动词的分类
2.6.2 动词的词形变化
2.6.3 动词的时态
2.6.4 动词的语态
2.6.5 非谓语动词
2.6.6 虚拟语气 - 2.7 词性七 连词
(一) 名词性从句之主语从句
(二) 名词性从句之表语从句
(三) 名词性从句之宾语从句
(四) 名词性从句之同位语从句
(五) 状语从句
(六) 定语从句 - 2.8 词性八 介词
(一) 介词主要用法
(二)分类(9种)
(三)句法作用
(四)介词短语在句子中的位置
(五)高频固定词组
(六)易混介词辨析 - 2.9 倒装结构
(一) 全部倒装
(二)部分倒装
- 2.1 词性一 名词
第一部分:基础概念
1.1 词性
- 名词
表人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称
boy,morning,bag,ball,class,orange - 代词
用来代替名词
who,she,you,it - 形容词
表人或事物的性质或特征
good,right,white,orange - 数词
表数目或顺序
own,two,three,first,second,third - 动词
【1 体现语法点最多;2 改变句意;3 变化最丰富】【涉及语法点:时态、语态、非谓语动词、虚拟语气、主谓一致】
表动作或状态
am,is,are,have,see - 副词
修饰动词、形容词或副词;说明时间、地点、程度等。
now,very,here,often,quietly,slowly - 冠词
用在名词前,帮助说明名词。
a,an,the - 介词
表示它后面的名词与其他句子成分的关系。
in,on,from,above,behind - 连词
用来连接词、短语或句子。
and,but,before - 感叹词
表示喜怒哀乐等感情
oh,well,hi,hello.
1.2 句子成分
-
主语
1)是句子所要说的人或物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”;
2)通常用名词或者代词担任。
》 I’m Miss Green. -
谓语
1)说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”;
2)由动词或动词短语担任
》Jack cleans the room every day。 -
表语
1)在系动词后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或“怎么样”;
2)由名词、代词或形容词担任
》My name is Ping Ping. -
宾语
1)表及物动词的对象或结果;
2)由名词或代词担任
》He can spell the word. -
双宾
1)有些及物动词有两个宾语,一个物一个人;
2)指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间接宾语;
3)间接宾语一般放在直接宾语前面。
》He wrote me a letter;同 He wrote a letter to me;(to/for) -
定语【修饰的作用】
1)修饰名词或代词
》Shanghai is a big city;(a big 就是定语) -
状语
1)修饰动词、形容词、副词
》He works hard; -
宾语补足语
1)用来说明宾语怎么样或干什么;
2)由形容词或动词担当
》They usually keep their classromm clean;
》He often helps me do my lessons
》The teacher wanted me to learn French all by myself; -
同位语【铺垫的作用】
1)跟在名词、代词后面用来进一步说明情况
》Where is your classmate Tom?补充一【区分表语&宾语】
动词+宾语
be动词/感官动词+表语
补充二【区分定语&状语】
1 定语
可以是形容词、介词短语、从句-定于从句、动词ed、动词to do、动词ing
2 状语
可以是副词 、介词短语、从句-状语从句、动词ed、动词to do、动词ing
最核心的本质就是看前边是否修饰了名词(如果修饰了名称翻译成“xx的xx”就是定语,否则是状语)
补充三【区分双宾&宾补】
双宾:两个宾语
宾补:宾语的补充说明
格式都是:主+谓+1+2
被动句,双宾可以改成两个被动句
宾补只能改成一个被动句。
1.3 构词法
- 合成法
多个单词合成一个单词;
spaceship,headache,basketball,playground… - 派生法(3种)
1)派生名词:
动词+er/or;动词+ing;动词+(t)ion;形容词+ness;其它
inventor,learner,swimming,kindness
2)派生形容词
名词+y;名词+ful;动词+ing/ed;国名;friendly(ly的不止是副词,少部分是形容词)
snowy,sunny,hopeful,interseting…
3)派生副词
形容词+ly,其他
showly,angrily - 转换法
1)形容词–>动词
dry干燥的->dry弄干
2)动词–>名词
look,walk
3)名词–>动词
hand 手–>传递,face 脸–>面对
4)形容词–>副词
early,fast
5)副词–>连词
when 什么时候–>当…时候
6)介词–>副词
in 到…里–> 在里面
on 在…上–> 进行,继续
第二部分:基础篇
2.1 词性一 名词
2.1.1 名词分类(两个维度:专有名词&普通名词,可数名词&不可数名词)
1. 专有名词:
1)专有名词是个别的人、物、团体、机构等的专用名称
2)专有名词中实词的第一个字母要大写
3)专有名词若含有普通名词的短语,必须用定冠词the
the Great Wall 长城
4)若姓氏名采用复数形式,表该姓氏一家人
the Greens 格林一家人
2. 普通名词:
1)是许多人或事物的共有名称。
pupil,family,man,foot
3. 可数名词和不可数名词:
1)可数名词是可以用数次进行计数的名词
box,child,orange
2)不可数名词是不可以用数词进行计数的名词
water,news ,oil,information
4. 可数名词的单数和复数形式:
1)可数名词由单数变复数的方法:单数名词尾+s;s/o/x/sh/ch结尾+es;辅音字母加y结尾的,把y变i在加es(family,city,party);以f或fe结尾变fe为v,+es
2)不可数名词一般没有复数形式,说明数量时,要用有关的计量名词
a big of rice --》 two bigs of rice
a piect of paper --》 three pieces of paper
a bottle of milk -》 five bottles of milk
5. 单数-复数
规则
+s;+es;o结尾;y结尾;f/fe结尾
不规则
2.1.2 名词所有格(7个知识点)
1)表名词的所属关系,相当于物主代词 (名词 的 xx)
2)在句子中作定语、宾语或主语
(1)表示人或者其他有生命的东西,常在尾 加 ‘s
》Children’s Day 儿童节
》My sister’s book 姐姐的书
(2)以s或者es结尾的复数名词,只加’。
》Teacher’ Day 教师节
(3)有些表示时间、距离以及世界、国家、城镇等无生命的名词,习惯+’s
》today’s newspaper
》ten minutes’ break
》china’ population
(4)无论表示有生命还是无生命的东西的名词,一般均用介词of短语表示所有关系
》a fine daughter of the Party 党的好女儿
》book’s name ; the name of the book;
(5)’s还可以表示某人的家或某店铺
》my aunt‘s 我阿姨家
》the doctor’s 诊所
(6)两人共有某物,采用 A and B‘s
》lucy and lily’s bedroom
(7)双重所有格“of+名词所有格('s)/名词性物主代词”
》a friend of my father’s .(省略 friends) 我父亲的一位朋友
》a friend of mine.
》 my father’s friend‘s friend/a friend of my father’s friend’s. 我爸爸的一个朋友的朋友
》其中之一,某一个
2.1.3 主谓一致(13个知识点)
1)主语是可数名词单数或者不可数名词,谓语动词用单数
》The computer was a great invention
》The water in the glass is very cold;
2)集体名词作主语
(1) 表示整体概念,谓语动词用单数
》Class Three is a very good class.
(2)表示其中所有成员,谓语动词用复数
》Class Three have a map of china.
3)名词复数和单数长的一样的,如Chinese,Japanese,fish,sheep,people等表示单个时谓语动词用单数,表示许多时,谓语动词用复数
》There is a sheep in the yard
》There are some sheep in the yard;
4)有s结尾,但不是复数,谓语动词用单数
》The news is very exciting 这个消息令人兴奋
5)glasses,shoes,socks,trousers,glovers等名词常用复数形式,谓语用复数
》The trousers are very cheap and I want to take them.
6)a lot of
1) 跟名词复数时谓语动词用复数
2)跟不可数名词时谓语动词用单数
》A lot of students are playing baseball now
》A lot of time was wasted on that work.
7)and
1)连接两个名词作主语时,谓语动词多用复数(绝大部分情况下)
2)但连接的两个名词作为一个整体时,谓语动词多用单数
》The teacher and his son are picking apples now
》Fish and chips is very famous food (炸鱼和薯条经常构成一个整体来卖,就像煎饼果子、刀叉)
8)there be 就近原则
There is a table and four chairs in the room.//此处is单复数是 a table 决定的
补充:
be动词的单复数
缺少从句连词:
例如:有很多人喜欢看电影
》there are many people like to go to movies.应该是
there are many people who like to go to movies.
9)both …and…连接两个事物作主语时,谓语动词一般用复数
Both you and I are required to be here tomorrow.
10)主语中有with的短语时,谓语动词单复数由with之前的人物决定
A women with a 7-year-old child was standing at the side of road.
11)either…or…或者neither…nor…连接两个人物作句子主语时,谓语动词就近原则
》Either you or he is right
》Neither you nor I am going there.
12)表示一段时间或长度概念的复数名词作主语时,谓语动词一般用单数
》Two months is not a short time.
》Two thousand kilometers is quite a long distance.
13)主语中由half of…/(three quarters) of…/all (of) the…等词语时,谓语动词的单复数由名词决定
1)Over three quarters of the information on the Internet is in English.
2)A third of the students were playing near the lake.
[补充:主谓一致-“就近原则” 5个]
1)there be
2) neither…nor
3)either…or
4)not only … but also
5)not … but
>There is a boy in the classroom
>Neither you nor I am wrong
>Either they or jim is going to shanghai next saturday
>Not only you but (also) he is wrong
>Not you but your father is to blame
[主谓一致-“就远原则” 8个]
as well as;(together/along) with;rather than;except;besidesd;including;in addition ;apart from
>The president of the college ,together with the deans,is planning a conference for the prurpose of laying down certain regulations.
>All the students,including Tom,are leaving.
[补充:单复数意义不同的名词]
advice 忠告; advices 消息
air 空气: airs 风度,神气
ash 灰烬; ashes 骨灰
beef 牛肉; beeves 食用牛,菜牛
custom 习惯,风俗 customs 海关,关税
damage 损害 damages 赔偿金
effect 效果 effects 动产,家产
copper 铜 coppers 铜钱
fetter 脚镣 fetters 囚禁,束缚
experience 经验 experiences 经历
foot 脚 foots 渣滓
force 力 forces 军队,兵力
2.2 词性二 代词
2.2.1 人称代词(5个知识点主格,宾格,主/宾格,顺序,it):人称代词代替人和事物的名称,分主格和宾格两种形式
1. 主格:句中作主语,表语
》Are they from Brazil? //主语
》Where have they gone? //表语
》It’s he! //表语
2. 宾格:用来作及物动词或介词的宾语
》Who teachers you Ecglish this year?
》We often write letters to her.
3. 人称代词作表语或放在比较状语从句连词than或as之后,可用主格/宾格
-Who is it?
-It’s I/me.
4. 人称代词顺序:“you->he->I”
》Both he and I are working at that computer company
-Who will go there?
-You and me .
5. 代词it
1)指人/物
2)表示“时间、天气、温度、距离、情况”等含义
3)作形式主语/宾语:替代作主语或宾语的不定式、动名词或名词性从句(非谓语动词、名词性从句会再次出现的哦)
-What’s the weather like today?
-It’s fine.
-What’s the time?
-It’s 12:00
-It’s a long way to go.
-It took him three days to clean his house.//非谓语动词作主语,it作形式主语
-It is very clear that the public want to know when these men can go into space.//形式主
-We found it very difficult to learn a foreign language well.//形式宾
2.2.2 物主代词(形容词性物主代词,名词性物主代词,双重所有格):说明事物所属关系的代词
1. 形容词性物主代词:作名词的修饰语,后加名词(修饰的作用,翻译成 xx的)
>Is that your umbrella?
>I often go to see my aunt on Sundays.
>They are their books.
2. 名词性物主代词(名词性物主代词 = 形容词性物主代词+名词):
相当于名词,既代替事物又表明所属关系;
在句子中作主语,宾语或表语
后面不可以跟名词。
>This is your cup,but where is mine?
>Your classroom is very big,but ours is rather small.
3. 双重所有格:of + 名词性物主代词(名词的双重所有格是 of+’s)
>A friend of mine came to see me yesterday.
>My friend came to see me yesterday.
前者强调朋友当中的其中之一,后者强调我的某一个朋友
2.2.3 反身代词(作宾语,作同位语):表示 ”…自己“
1 反身代词在句子中作宾语表示反射。(指一个动作回到该动作执行者本身)
>Don’t play with the knife,you might hurt yourself.
2 在句子中作同位语表示强调(即用来强调名词或代词)
>They story itself is good.Only he didn’t tell it well.
小结一下 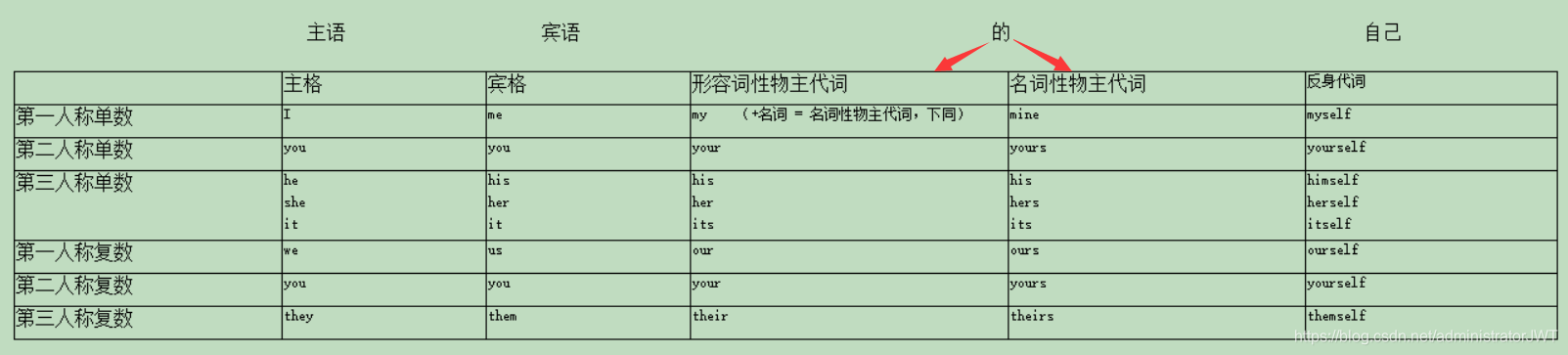
2.2.4 指示代词(单数,复数,含义):指说明近处或远处、上文或下文、以前或现在的人或事物

》 That model pane is made of plastic.
》 Remember never to do such things.
》 Do the same as the teacher tells you.
2.2.5 关系代词:用来引导定语从句的代词叫关系代词
1 关系代词 who/whom,which,that等
在从句中担任一定的成分
起连接作用
》 The student who is drawing a picture is in Grade One.
2 关系代词who/whom指人
》Do you know the man who is wearing a red hat?
3 关系代词which指物
》Have you found the book which you lost several days ago?
4 关系代词that即可指人也可指物
》Can you see the man/dog that is running along the river bank.
2.2.6 连接代词:用来引导宾语从句、主语从句或表语从句的连接词称连接代词
英语中连接代词主要有:
what,who,whom ,which ,whose
注意:定语从句中,用什么连词跟中文意思无关
名词性/状语从句,用什么连词跟中文意思有关
2.2.7 不定代词:代替或修饰不特指的人或事物的代词叫不定代词。在句中作主语宾语表语定语和状语
1 单数:some,any ,none,each,every,one,either,neither,so,the other,another
2 不可数:much,little,a little ,all
3 复数:many,few,a few,ones,both,others,the others
4 符合不定代词12个:something,someone,somebody,anything,anyone,anybody,nothing,nobody,no one,everything,everyone,everybody
5 易混不定代词12组:
1 some和any
1 some
.肯定句中,表 ”几个“、”一些“,”某个“
.疑问句中,表建议、请求希望得到肯定回答
.修可数或不可数名词
》I have some work to do today.
》They will go there some day.
》Would you like some cuffee with sugar?
2 any
.疑问句中,表”任何一个“,”任何一些“
.肯定句中,表”任何的“
.修可数或不可数名词
》They didn’t have any friends here.
》Have you got some questions to ask?
》Come here with any friend.
2 no 和 none
1 no
.作定语,表”没有“,修可数名词或不可数名词
》There is no time left .Please hurry up.
》They had no reading books to lend.
[补充:there be 结构的”有“是指”地方,客观存在的事物“,have的”有“,是指人]
2 none
.只独立使用,句中可作主语、宾语和表语,意思是”没有一个人(或事物)“,表复数或单数
》None of them is/are in the classroom
》I have many books ,but none is interesting.
3 all 和 both
all和both在句中作主语宾语表语定语等…
. all:指三者或三者以上的人或物,代替或修饰可数名词或不可数名词
. both : 指两个人或物,用来代替或修饰可数名词
》I know all of the four British students in their schook.
-Would you like one or that one?
-Both.
注意:”all/both + of the +名词(复数)“,其中of可以省略
》All (of) (the) boys are naughty.
是男孩都调皮
4 every和each
every:形容词,只做定语修单数名词,”每一个“,表整体概念
each:形容词/代词,可做主语/宾语/定语等,”每个“或”各个“,表单个概念
》Every one of the studnets in his class studies very hard.
他班上每个学生学习都很用功。
》They are very busy.Each of them has something to do.
他们很忙,人人都有事做。
5 either和neither
都可做主语,宾语和定语等,都可用作单数
either:两个中间的任何一个
neither:either的否定形式,两个都不
》I don’t care much for what to drink.Either of the two will do.
-Will you go there by bus or by car?
-Neither.
6 other ,the other 和another
.other:”另一“,”其余“,有复数形式。做主语、宾语和定语【不同种类】
.another:”另外“,”又一个“,表示增加,作宾语和定语。【同种类】
.ther other:只有两个时用the other,且语法为”one…the other“
》You have had several cakes.Do you really want another one?//同种类,还是cakes
》I have eaten 4 cakes,but I still want other.//不同种类,不是cakes
》This one of your socks.Where is the other one?
7 others和the others
.others:其余的人/物,指大部分
.the others:其余的人/物,指全部
》A few students are playing aoccer while others are watching them.//剩余的一部分在看
》Two of the ten boys are standing and the others are sitting round them.//剩余8个全部在坐着
8 many和much
many :很多,与可数名词复数连用
much:很多,与不可数名词连用
》I don’t have many friends here.
》Many died in the bus accident.
》We can learn much with the help of him.
9 few,little,a few,a little
.few/little:几乎没有,否定的意思
.a few/a little:有些,肯定的意思
.few/a few:与可数名词连用或替可数的事物
.little/a little:与不可数名词连用或替不可数的事物
(有 a 肯,没 a 否,小样的,不可数)
》He is very poor and he has little money.
他很穷,几乎没钱
》Don’t worry.There is still a little time left.
别急,还有一点时间呢。
10 somebody,something,anything,nothing,everything,everybody
.somebody,something,someone 一般用于肯定句中
.anything,anybody,anyone 一般用于疑问句、否定句和条件状语从句中
.修饰符合不定代词的定语,应放在他们后边
》Hey,lily,There is someone ouside the door//门外有人
》He has nothing much to do tody.//他今天没做多少事
11 a lot of ,lots of ,a number of,large numbers of ,a great deal of ,plenty of “大量,许多”
.a lot of ,lots of ,plety of :即可修不可数名词也可修可数名词的复数
.a number of /large numbers of :只能修可数名词复数形式
.a great deal of:只能修不可数名词。
》 al lot of people think that time is money.
》I don’t have to do it in a hurry because I have plenty of time.
》I have a number of letters to write today.
》I spend a great deal of time/money on shopping.
12 none,no one,nobody
.on one/nobody:指人,后不跟of短语,谓语动词用单数形式
.none:指人/物,后可跟of短语,谓语动词可用单数也可用复数
》No one knows how he managed to get the ticket.
》Nobody handed in his/their composition(s) yesterday.
》None of my friends came to see me that day.
2.2.8 相互代词:each other,one another
》We must help each other when we are in trouble.
我们身处困境时要相互帮助
》They sat there without talking to one another/each other 。
他们坐在哪儿,户型不说话
2.2.9 疑问代词
.引导疑问句:who,whom,whose,what ,which,whoever…
.疑问代词不分单复数
》Who is(are) in that playhouse?
》What colors do they have?
词性三:数词(基数词,序数词,数次的用法归纳):作句子中的主语、宾语、表语和定语
2.3.1 基数词
表示数目的词叫基数词
一千—one thousand
一万—ten thousand
十万—one hundred thousand
百万—one million
千万—then million
亿 —one hundred million
1 百位和十位之间要加and;十万位和万位,亿位和千万位之间通常也加and
2 英语用千、百万等单位计数,大数字从右向左看,每隔三位划一逗号,倒数第一个逗号之前用thousand,
倒数第二个逗号之前用million,倒数第三个逗号之前用billion
练习:七百八十二亿 四千零八万 四千七百六十九
78240084769 — 78,240,084,769
78 billion 2 hundred and 40 million 84 thousand 7 hundred and 69.
2.3.2 序数词
表示顺序的数词叫序数词
通常在基数词后+th,表示第。。。
1000th – one thousandth
注意三点:
两位以上的序数词仅个位部分用序数词,其余部分仍用基数词
》thirty-sixth
使用序数词时一般加定冠词the
》I’m in the third grade.
序数词作”几分之几“时,有复数形式
》1/5 – one fifth;
》2/3 – two thirds;
2.3.3 数次的用法大全
1 表示年份
》2002:twenty thousand and two
2 表示日期
12月1日:Dec.1st或the first of December;
3 表示时刻
5:15 – five fifteen或a quarter past five
4 表示编号
Room 105 – Room one 0 five;
Bus No.13 – Bus Number Thrteen.
5 小数
5.7 – five point seven
0.16 – zero point one six
6 “半”
1/2 – half
半小时 – half an hour
7 序数词前面加the时,表示顺序,加a/an时,表示”再一,又一“
The third lesson is rather difficult.
第三课相当难
Shall we read the text a third time?
我们把课文读第三遍,好吗?
2.4 词性四 冠词(定冠词、不定冠词、零冠词)
2.4.1 不定冠词a/an的5种用法
不定冠词a/an用在单数名词前面
a用在辅音开头的词前面
an用在元音开头的词前面(aeiou)
(1) 表某一个人或物,但不具体说明何人何物
There is a dog lying on the ground.
(2) 表示某类人或物,以区别于其他类
A elephant is much stronger than a man
大象比人强壮多了,不能译为:一个大象比一个人强壮
(3)表示某类人或事务中的任何一个
He is a teacher of English
(4) 表示“一”这个数量
There is a table and four chairs in that dining-room.
(5) 固定搭配
a bit
a little
**2.4.2 定冠词the的12种用法 **
(1)表特指的人或事物
The man with a flower in his hand is Jack.
(2)谈话双方都熟悉的人或事物
Look at the blackboard,lily.
(3)复述前面提到过的人或事物
There is a man under the tree.The man is called Robert.
(4)表示世界上独一无二的事物
The earth turns around the sun.
(5)用在表示方位的名词前面
There will be strong wind to the south of the Yangtze River.
(6)在序数词和形容词最高级的前面
Who is the first one to go?
Of all the stars,the sun is the nearest to the earth.
(7)用在江河、海洋、山脉的前面
I have never been to the Himalaya Mountains.喜马拉雅山
(8)用在含有普通名词的专有名词前面
He is from the United States of America.
(9)用在姓氏之前表示一家人
The Greens are going to Mount Emei next mounth.
(10)same之前一般用the
Lucy and lily look the save.
看上去长得一样。
(11) 固定短语
at the same time
in the end
(12)乐器名称前面
He began to play the violin at the age of 5.
2.4.3 零冠词的9种情况
(1)专有名词和第一次使用的不可数名词前通常不用
China is a very large country.
Man needs air and water.
(2)名词前已有指示、物主、不定代词作定语时
My pen is much more expensive than yours.
(3)周、月或季节名前一般不用
They usually plant trees on the hills in spring.
(4)(第一次使用的)复数名词表人或事物的类别时
Men are cleverer than monkeys.
(5)三餐前不用
We have breakfast at home and lunch at school.
(6)节假日前一般不用
On Children’s Day the boys often get presents from their parents.
(7)球类名词前不用
The children play football one Saturday afternoons.
(8)城市建筑物名称前不用
They are now at People’s Cinema.
(9)一些习惯用语中不用
at/to/from/out of /after/for school;
in/to/for/after class;
2.5 词性五 形容词&副词
2.5.1 形容词
形容词定义:用来说明或修饰名词、代词的词称为形容词
形容词的句法作用:作定语、表语以及宾语补足语
2.5.1.1 在句中的位置(4点)
(1)多方名词之前;音节少的词放在音节多的词之前(作定语)
a big yellow wooden wheel
一个黄色的大木轮
(2)作表语时,放系动词之后(作表语,系动词、感官动词之后)
The price sounds reasonable.
这个价格听起来算是合理
(3) 作宾语补足语时,放宾语之后(作宾补,宾语之后)
We must try our best to keep our environment clean
我们必须尽力保持我们的环境整洁
(4) 后置的两种情况(作定语)
1 修饰复合不定代词放代词之后
Something serious has happened to him
2 与表示“长、宽、高、重、老、距离”的词连用时,形容词后置
He’s 1.8 meters tall.
2.5.1.2 7组易混词辨析
(1)interested与interesting
interesting:令…感兴趣的(本身)
interested:对…感兴趣的(其他)
The man is very interesting and all the children like him.
I am interested in science.
(2)good与well
作定语或表语用good
表身体好或作状语用well
Doing sports is good for us.作表语
Study well and make progress every day.作状语
-How are you?
-I am very well.身体
(3)too much 与 much too
too much : 太多的,修饰事物数量
much too : 太过、过分,修饰形容词或副词
I am full beacuse I have had too much rice.
That coat is much too dear.
(4)dear
形容词:可爱的、亲爱的、贵的
a dear friend 亲爱的
What a dear little boy 可爱的
The sweater is much too dear 贵的
感叹词:表 惊愕、奇怪、惊奇
Oh ,dear! I‘ve lost my pen.
Dear!Dear!I’m sorry to hear that
名词:可爱的人,亲爱的人
Did you have a goog time at work,dear?
(5)quick,fast与soon
quick 与 fast:速度快
soon: 时间快
After a quick breakfast,he hurried to school leaving his bag at home 速度
A train is much faster than a bus 速度
His father will be back to China very soon 时间
(6)lonely 孤独的寂寞的(后果)
alone 独自的,单独的(事实)
He lives alone but he doesn’t feel lonely
He is lonely person.You can not easily get on well with him
(7)living,alive,live ,lively
living:活着的,现存的;一摸一样的,逼真的;=lively 强烈的,活泼的
live:指东西活的。=living 现场的,实况的
alive:指人活着的
lively:有生气的,活泼的,可爱的,快活的,生动的,真实的
We have a living hope that you will succeed.强烈的
Is she still alive?(人)活着的
This is a live fish.(东西)活着的
She is as lively as a kitten .可爱的
He gave a lively description of the football match.生动的
2.5.2 副词
2.5.2.1 定义
说明事情发生的时间、地点、原因、方式等含义
说明其它形容词或副词程度的词叫副词
2.5.2.2 副词的分类
时间副词、程度副词、频度副词、方式副词、地点方位副词、连接副词、疑问副词、关系副词
2.5.2.3 4组易混副词辨析
1 too,also,either,nor “也”
too:肯定句和疑问句的末尾,用逗号隔开;
also:肯定句中谓语动词之前;
either:否定句末尾,用逗号隔开;
nor:否定句,句首;(倒装)
Are you American,too?
He is not happy and I am not happy ,either.
He didn’t watch the football game,Nor did I.(倒装 谓+主)
You can also find the market is very good.
2 sometimes,sometime,some time,some times
sometimes:有时,用于一般现在时
sometime:将来的某时
some times:数次(time只有在表示次数的时候才加s)
somt time:一些时间
Sometimes they go hiking in the mountains.有时
I will stay here some time .一些时间
I will meet your father sometime.未来的某时间
3 farther ,further
表地点、方向或距离时同义,“更远,较远”
further还表 更多、更进一步,额外的意思
They decided to go farther/further the next day.//具体
This problem will be further discussed.//抽象
4 most,mostly
most:(形容词和名词) 大多数的,大部分的
(副词) 最,十分,很
mostly:(副词)主要的,多半的,大部分的
I was at home most of the time when I was free.
This is the most exciting part of the film.
She is mostly out on Sundays.
2.5.3 形容词、副词的原级、比较级和最高级
2.5.3.1 规则变化
单音节和部分双音节 形容词和副词,在原级的后面在er,est构成比较级和最高级
两个音节或两个以上的音节的,在原级前加more,most
2.5.3.2 不规则变化
good better best 好的,更好的,最好的
bad worse worst 糟糕的,更糟糕的,最糟糕的
little less least 少的,更少的,最少的
2.5.3.3 固定句型 (12个)
1 同级比较
as…as,the same…as:与。。。一样
She has written as many essays as her brother(has).
no more …than,not … any more than :与。。。不一样
The hert is no more intelligent than the stomach,for they are both controlled by the brain.
2 the more…,the more…:越。。。越。。。
more and more:越来越
As the internet becomes more and more commercialized,it is the interest of business to universalize access -after all ,the more people online ,the more potential customers there are.
3 表最高程度
否定词+more:十分,非常
I can’t agree with you more.
no+名词+more…than 没有什么比。。。更
No tool is more powerful for understanding the natural world than the scientific method
more …than +anyone/anything else,比其他任何。。。都。。。
He did more work this morning than anyone else.
nothing as…as/nothing like 没有比。。。更。。。
Nothing in the present-day world is so popular as Internet.
the only +名词 独一无二的
He is the only man for this study.
4 表倍数
倍数+as+形容词或副词+as
An ordinary subway train,approaching the station,can be twice as loud as the loudest jet.
倍数+名词+of
The bridge is three times the length of that one.
倍数+比较级+than
This hole is three times deeper than that one .
5 (just)as…,so… :正如…所以…
Just as the soil is a part of the earth,so is the atmosphere.(so后边多用倒装)
6 not … so much as …:与其说A不如说B/是B,而不是A
not A so much as B
not so much A as B
7 more than
i.more than +动词或名词:不仅是,不止是(not only)
more than earn their salaries.
Beacuse of it’s intimacy,radio is usually more than just a medium;it is a companion.
收音机与我们生活息息相关,所以它不仅是媒体,更是我们的伙伴。
ii.more than +数字:多于…(over)
more than 100 years.
iii.more than +形容词:非常
The USA remains more than capable of holding lraq down,while confronting North
korea and Iran-its next main targets.
美国在推翻伊拉克的同时,完全有实力可以与接下来的主要目标朝鲜和伊朗对抗。
8 nothing more than :只不过是
The individual TV viewer invariably senses that he or she is nothing more than
an anonymous,statistically insignificant part of a huge and diverse audience.
每位电视观众总会觉得,在众多形形色色的观众当中,自己只不过是无足轻重的一份子
9 no less than /nothing less than:不亚于…,相当于…
10 more than 。。。can :简直不能
I love you more than I can say.
11 the+比较级…,the +比较级…,越…越…
The more trees we plant,the better it will be .
The harder you try,the greater your progress is.
12 one of the +最高级+名词(复数):最…之一
One of the oldest houses has been burnt in a fire.(谓语动词用单数,因为主语是One)
2.5.1 形容词
2.6 词性六 动词(动词的分类,动词的词形变化,动词的语法(时态,语态,非谓语动词,虚拟语气))
2.6.1 动词的分类
2.6.1.1 实义动词
表实在的意义
表动作或状态
在句中独立作谓语
They eat a lot of potatoes.
2.6.1.2 系动词
本身有一定词义
be动词&感官动词
His father is a teacher.
Twins usually look the same.
3 助动词
本身没有词义,不能独立作谓语,只和主要动词一起构成谓语动词
表否定、疑问、时态、语态等
有人称、单复数和时态的变化
He doesn’t speak English.
We are playing basketball.
I will go home.
4 情态动词
本身有意义,不独立作谓语,和动词一起构成谓语动词
没有人称和单复数的变化,有些情态动词有过去式
You can keep the books for two weeks.
2.6.1.2 动词的词性变化
原型->过去式->过去分词
be(am,is) was been
be(are) were been
lose lost lost
make made made
put put put
…
2.6.2 动词的时态
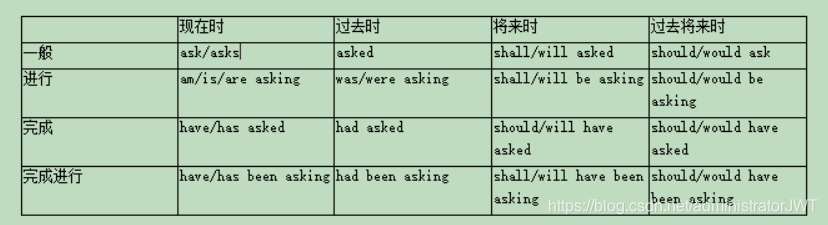
先记住以下六个,所有复杂时态都是这6个中某几个的组合
1 一般过去时
2 现在完成时 1 一般现在时
3 过去完成时 2 现在进行时 一般将来时
过去--------------------》现在---------------------》将来
2.6.1.3.1 一般现在时
经常或习惯发生的 动作或状态
i.常用的时间状语
They go to the Palace Museum once a year.
They often discuss business in the evening.
ii.表客观真理、事实、人的技能或现在的状态时句子中一般不用时间状语
The earth turns round the sun.
Light travels faster than sound.
iii.表十分确定会发生(如安排好的事情);
用一般现在表将来,句子中可以有将来的时间
The train for Haikou leaves at 8:00 in the morning.
iiii.时间状语从句和条件状语从句,用一般现在表将来
Please ring me up as soon as you arrive in Germany.
If it rains tomorrow,we will have to stay at home.
2.6.1.3.2 一般过去时
表过去的动作或状态
可能式一次性的,也可能经常发生
When he went into the room,he saw a stranger talking with his father.
He came to our city in the year 2000.
2.6.1.3.3 一般将来时
表将来某一时刻或经常发生的动作或状态
will表动作与人的主观愿望无关。
shall用于第一人称,will用于所有人称。
am/is/are going to +动词原形;am/is/are to +动词原形;be about to +动词原形:表打算或准备要做的事情,或主观判断
2.6.1.3.4 现在进行时
i. be(am/is/are)+现在分词
I am writing a long novel.
ii.表即将发生的动作,一般指近期安排好的事情
What are you doing tomorrow?
iii.表频繁发生或反复进行的动作,常与always等频度副词连用,以表示赞扬、不满或讨厌等感情色彩
He is always borrowing money from me and frogetting all about it some time later.
这里就要翻译成总是借钱不还的不满的感情。
2.6.1.3.5 过去进行时
i. was/were+现在分词
ii.过去进行时的时间状语
iii.用于宾语从句或时间状语从句中,表示与主句动作同时进行而且延续时间较长。句子中通常不用时间状语从句
2.6.1.3.6 现在完成时
i.have/has+done
ii.时间状语
I have never seen such fine pictures before.
He has just gone to England.
iii.表在过去开始一直延续到现在的动作或状态
I have been away from my hometown for thirty years.//延续到现在,说明离开家乡三十年还没有回家
Uncle Wang has worked in the factory since it opeded. //延续到现在,一直在工厂工作,现在也在
iiii.在完成时中,一个瞬间动词(一次性动作)不能与表示一段时间的状语连用,此时须将该瞬间动词改为延续性
瞬间性动作的完成时 延续性动词或状态动词的完成时
Have (already) gone to -> Have been in/at…for(two years)
Has come to -> Has been here since(1990)
2.6.1.3.7 过去完成时
表示的时间是过去的过去
i. 助动词had+动词的过去分词
ii.时间状语
iii.过去完成时常用于宾语从句,after引导的从句中或从句是before引导的从句中
2.6.1.3.8 过去将来时
i. should 或would+动词原型构成
ii.时间状语
iii.在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中不可以用过去将来时,应该用一般过去时
iiii.表示纯粹的将来时用would/should;表示打算或主观认为的事情用was/were going to do
She told me she would be 18 the next month.
She told me that she was going to have a walk with her pet dog.
2.6.1.3.9 现在完成进行时
i.指一个从过去开始一直延续到现在并由可能继续下去的动作;它具有现在完成时和现在进行时双重特征
ii.have/has+been+动词的现在分词
I have been swimming in the cold water for about two hours.
How lone have you been waiting here?
2.6.3 动词的语态(定义,构成,用法,主动改为被动的方法)
2.6.1.4.1 定义
主语是动作的执行者(即某人做某事),叫主语语态
主语是动作的承受者(即某事被做),叫被动语态
2.6.1.4.2 构成
i.助动词be+动词的过去分词
ii.助动词be有时态,人称和数的变化
iii.被动语态后的by有时可以省略
2.6.1.4.3 被动语态的用法
i.不知道谁是动作的执行者时,用被动语态,省略by短语
ii.众所周知是谁做时,用被动语态,省略by短语
iii.强调动作的承受者,句尾加by短语
A man was killed in the accident.
Rice is also grown in this palce.
It was written by Lu Xun.
2.6.1.4.4 主动语态改被动语态的方法
步骤一.将主动语态的宾语改为被动语态的主语
步骤二.将主动语态的谓语动词改为 be+过去分词的结构
步骤三.将主动语态的主语改为介词by之后的宾语,放在谓语动词之后(有时可省略)。
i.双宾的被动语态
步骤一.把间接宾语改为被动语态的主语,直接宾语仍保留原为
步骤二.把直接宾语改为主动语态的主语,间接宾语前加介词to/for。
His teacher gave hime a dictionary.
->
He was given a dictionary by his teacher.
A dictionary was diven to he by him by his teacher.
ii.加to:不带to的动词不定式做宾语补足语的主动语态(感官动词、使役动词比较多),改为被动语态时不定式前要加to
The boss made the poor man work 12 hours a day.
->
The poor man was made to work 12 hours a day.
iii.带符合宾语的动词
一般把主动语态的宾语改为主语,宾语补足语在被动语态中做主语补足语
I paint the house white.
The house is painted white by me.
iiii.动词短语作谓语
短语动词是不可分割的整体,改为被动语态时要保持其完整性,介词或副词不可遗漏
The girl takes good care of her little brother.
The girl’s little brother is taken care of by her.
2.6.4 非谓语动词(to do不定式,ed过去分词,ing现在分词)
非谓语动词包括不定式、动名词和分词三种形式;
分词包括现在分词和过去分词;
在句中不能作谓语,其它句子成分;
2.6.1.5.1 非谓语动词-动词不定式
1 形式
i.肯定
分为带to(to do)和不带to(do)的动词不定式
ii.否定
not+不定式
2 时态

i.不定式的一般式
表示不定式的动作与谓语动词动作几乎同时发生(v’ == v)
I helped to repair the car.
ii.不定式的完成式
通常表示不定式的动作发生在谓语动词之前 (v’ < v)
I an sorry not to have come to your party last night.
iii.不定式的进行式
表示不定式的动作正在进行,持续中…
It’s nice to be lying on the beach.
iiii.不定式的完成进行式
表示不定式的动作在谓语动作之前;到谓语动作发生时可能停止,也可能继续
He is found to have been working for 4 hours.
3 语态
逻辑主语时动作的发出者,用主动;反之,用被动
She asked the door to be closed.
比较一下
I have some clothes to be washed today.(别人帮忙洗)
I have some clothes to wash. (自己洗)
4 注意
i.there be 句型
在There be 句型中,主语可用不定式修饰;
句中主语是不定式的承受者,常用不定式的主动表示被动。
There is sill a lot of work to do // to be done.
ii.too…to句型
用不定式主动代替被动
The stone is too heavy for me to move.
iii.主语+系动词+形容词+不定式结构
如果表语形容词说明的是主语的内在特征,用主动表被动
The coffee is bitter to taste.
iiii.不定式+(动词+介词)
如果不定式后面跟的是动词+介词的短语动词,介词不可省略
The pen is hard to write with.
5
(1)不定式的句法功能-作主语
>不定式作主语时,表示一个特定的具体的行为
>谓语动词用单三
>动词不定式可以位于句首
>当作主语的动词不定式比较长时,通常用it作形式主语,把不定式置于句末
To live means to create.
To do that sort of things is stupid.
To learn a skill is important for everyone in society.
It is necessary for young students to learn a foreign language.
>It 作形式主语,动词不定式作实际主语的句型结构:
i.It is adj (for sb/sth) to do sth
ii.It’s adj of sb +不定式
iii.It be 名词 +不定式
iiii.It takes sb +some time +to do sth
How rude it was of the boy to jump the queue!
It is friendly of the family to try to make me feel at home in their house.
(2) 不定式句法功能-作表语
>主语和表语同为不定式时,通常主语表条件,表语表结果。
To see is to believe
>作表语常用一下结构:
My wish/job/aim/goal is +不定式
The next step/important thing/problem/measure is +不定式等
My wish is to be a teacher.
Your job is to type the papers in the office.
The next measure is to stop the river from being polluted.
(3) 不定式句法功能-作宾语
>常见的使用动词不定式作宾语的动词有:
agree,choose,decide,hope,fail,wish,refuse,expect,manage,plan,intend,promise,offer,afford,demand,arrange等
>常见“疑问词+不定式”作宾语的动词有:
decide,know,learn,rememer,see,settle,think…
They decide 【to build】 a highway between these two cities.
She offered 【to help】 me when I was in trouble.
>当作宾语的不定式是较长的短语时,常常用it作形式宾语,把不定式放到句末;常用的动词有believe,think,consider,find,feel,make等;
构成句型 动词+it+adj./n + to do sth(it作形式宾,真正的宾语动词不定式放于句末)
I think it necessary for you [to have a good rest] after the long work.
I find it difficult [to understand] him.
(4)不定式句法功能-作宾补
逻辑主语是他前面的宾语
The doctor advised her not [to eat] too mnch sugar.//逻辑主语 her
I wish you [to go] to the meeting with me. //逻辑主语 you
>有一类表示见解,看法的动词,后常接to be型 不定式作宾补,to be可省略
He declared himself (to be) a college student.
The police proved him (to be) a thief.
>hope,demand,suggest等动词后不能接动词不定式做宾补
[误]I hope my san to be back soon.
[正]I hope my san will be back soon.
>在主动结构中,下列动词后作宾补的动词不定式应省略
五看[see,watch,notice,observe,look at]
三使[make,let ,have]
两听[hear,listen to]
一感觉[feel]
His boss made/have/let him [work] all day long.
I heard him [sing] in her bedroom.
I saw him [play] baskball on the playground.
(5)不定式句法功能-作定语
>动词不定式作定语,应位于所修饰词语之后,即-后置定语
>被修饰的名词和用作定语的不定式,可以是逻辑主语也可以使逻辑宾语的关系
Have you got anything [to eat]?//to eat 修饰anything作定语,需后置
Do you have anything [to say/declare]?
>下列名词之后常接动词不定式作定语
ability,attempt,chance,courage,decision,effort,evidence,failure,means,measure,reason,refusal,promise,right,way,wish等
You have no right [to speak].
But she gave up the chance [to go abroad].
He has the ability [to work out] the math question.
I have the courage [to invite] her for dinner.
(6)不定式句法功能-作状语
>作目的状语:不定式的动作稍晚于位于动词的动作
I am saying this [to encourage] you.
I store the food in the fridge [to keep] it fresh.
>in order to 既可以放句首表目的,也可以放在句中
>so as to 只能放在句中
In order to cahth the early bus,I get up early every day.
=I get up early every day so as to catch the early bus.
2.6.1.5.2 非谓语动词-分词(分词作定语,区分现在分词与过去分词;分词作状语,区分一般式与完成式;分词的独立主格结构。)
(1)现在分词作定语(3个知识点)
定语:形容词、介词短语、非谓语动词、定语从句都可以作定语,大部分情况下非谓语动词和定语从句可以互换,然而一下几种情况不可以!
i.现在分词表示的动作和谓语动词的动作是一前一后而不是同时发生,不用现在分词作定语,需要用定语从句。
[误]The teacher criticized the student [having broken] the window.
[正]The teacher criticized the student [who having broken] the window.
[误]Do you know anyone having lost a car?
[正]Don you know anyone [who have lost] a car?
ii.Being 可做状语或补语,不做定语
[误]Anybody [being outside] after ten o’clock will be criticized.
[正]Anybody [who is outside] after ten o’clock will be cirticized.
iii.表经常性动作,不用现在分词作定语
[误] The boy [bringing us] milk everyday is my brother.
[正] The boy [who bings us milk] everyday is my brother.
(2)现在分词作状语
三个知识点
1 与“时间”的关系 -> 一般式;完成式
2 与“主语”的关系 -> 状语;独立主格结构
3 与 “连词” 的关系-> 并列连词;从属连词
具体:
1 与谓语动词的“时间”关系
同时发生用一般式
They secretary worked late into the night,[preparing] a long speech for the president.
He sent me an E-mail,[hoping] to get further information.
先于谓语动词的动作时,现在分词用完成式
[Having suffered from heart] trouble for years,Professor White has to take some medicine with him whenever he goes.
[Having finished his womework] ,the boy went out to play football.
2 现在分词作状语与“主语”的关系
现在分词作状语时,其逻辑主语与句子主语保持一致(主语,宾语,时态,语态)。
如果不一致,分词应有自己的逻辑主语,构成独立主格结构
[looking out of ] the window of our hotel room,we could see lots of mountains around.
They came into the classroom ,[talking and laughing].
Mr.Smith being absent,[the meeting] had to be put off.
//being absent非谓语动词;had to be put off 谓语动词;the meeting 主语;Mr.Smith 逻辑主语
It being a fine day.we all wanted to go outing.
//being a fine 非谓语动词;wanted to 谓语动词;we 主语;it 逻辑主语
3 现在分词作状语时,前面可用连词when,while,once等(连词一般加句子,这里可以加非谓语动词)
[When talking] to you,I always feel happy.
Be careful [while crossing] the street.
4 现在分词作状语时,与主语之间不能有连词or,and ,but
[Having been told] many times ,[but 这里不能加but,应该去掉] he still couldn’t understand it.
(3)过去分词作定语(4个知识点)
1 表情绪的过去分词作定语
Martin’s [confused] sorrows turned to optimism.
He didn’t notice the [surprised] look on her face.
2 一些过去分词用作定语并与其修饰的名词构成固定搭配
boiled water 开水
canned food 罐头食品
required courses 必修课
united front 统一战线
3 过去分词+副词构成复合形容词
a simply-furnished apartment.
strongly-motivated students.
a cautiously-worded statement.
4 有完成意义的过去分词也可以作定语
the risen sun(定语(过去分词)前置+名词) = the sun that has just risen.(名词+定语(定语从句)后置)
an exploded bomb = a bomb that has exploded.
5 注意,有些以-ed结尾的词,并不是过去分词,而是由名词变来的形容词
armored cars 装甲车
a gifted boy 有天赋的孩子
salaried class 工薪阶层
(4)过去分词作状语(4个知识点)
1 过去分词短语作状语多放句首,也可放句尾
[Seen] from the hill,the city looks magnificent.
He soon felt asleep,[exhausted] by the journey.
2 单独的过去分词作状语
Depressed,he went to see his elder sister.
He turned away,[disappointed].
3 过去分词+连词 作状语
I went on talking,[though] continually [interrupted] by George.
They would never do this [unless compelled]
4 过去分词引导状语从句
[Provided(that)] there is no opposition ,we shall hold the meeting there.(这里相当于if)
2.6.5 动词-虚拟语气
表示动作或状态【不是客观存在的事实】,而是说话人的【主观愿望,假设或推测】等。
If I were you,I should study English.
1.虚拟语句在条件从句的用法
i. 一类是真实条件句,一类是非真实条件句,也就是虚拟条件句
ii.如果假设的情况有可能发生的,就是真实条件句,谓语要用陈述语气。
iii.如果假设情况是过去或现在都不存在的,或将来不大可能发生的,则是虚拟语气。
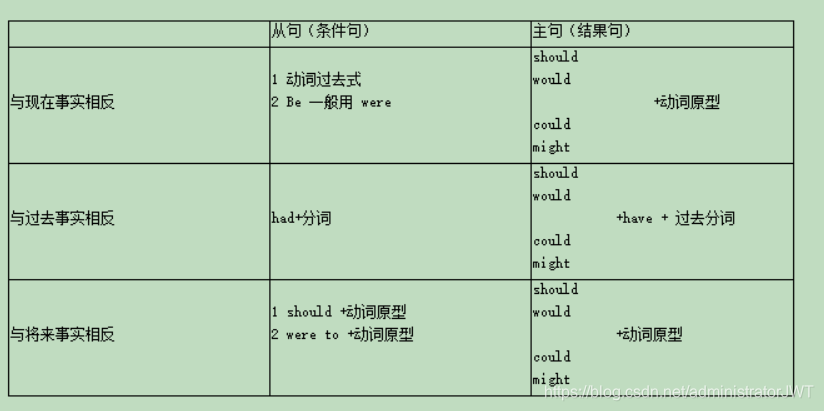
If [he were] here,everything would be all right.//现在
If here mother [had taken] the doctor’s advice,she would /might have got well earlier.//过去
If it [were to rain] tommorrow,the match would be canceled.//将来
注意,有时候省略if,采用部分倒装语序。把had/should/were等动词(不包括行为动词)移到句首
(If it were) Were it to rain to rommorrow,our picnic would be canceled.
(If it had not been) Had it not been for the strom,we would have arrived in time.
(If the earth should) Should the earth stop running,what would happen?
2.虚拟语句在名词性从句中的用法
表希望,愿望等含义的单词出现
I wish I were better-looking.
I wish I had met the fild star just now.
表命令,建议等含义的单词在句中的出现+(should)+to
The young man insisted that I [(should) go] with his fellows.
The doctor advised that he [change] his job.
固定:would rather+did;it be adj. that…(should)+do
3.虚拟语气在状语从句中的用法
[If only] the player had had more courage!
[If only] Daisy would to with me!
He talks [as if] he knew where she was.
It looks [as if] it might show.
She took an unbrella with her [lest/for fear that/in case] it should rain.//以防,万一
4.其它形式的虚拟语气
it is time that…should +do/did
It’s high time that we were off.
would as soon +did/had done
I would just as soon you had told me the truth yesterday.
2.7 词性七 连词
涉及知识点
三大从句: 名词性从句: 1 主语从句
2 宾语从句
3 表语从句
4 同位语从句
状语从句: 1 时间,2 地点,3 原因
4 结果,5 目的,6 条件
7 方式,8 比较,9 让步
定语从句: 1 修饰人
2 修饰物
3 修饰其它
三大从句本质
1 定语从句:“形容词”从句: 1 修饰作用
2 跟形容词相似,翻译成“的”
2 状语从句:“副词”从句: 1 句中的含义
2 时间、地点等9中
3 名词性从句:“名词”从句 1 句中的功能
2 主语/宾语/表语/同位语4种
(一)名词性从句之主语从句
1 引导主语从句连词有 that,whether,who,what,whatever等
2 连词谓语句首不能省略
3 主语从句大多数情况下视为第三人称单数,但在连接代词what引导的主语从句后谓语动词的数跟据句意定。
4 为了防止句子头重脚轻,通常把形式主语it放在主语位置,真正主语后置。
It is certain that he will win the match.
It is true that he has mede a very important discovery in chemistry.
** (二)名词性从句之表语从句**
1 表语从句就是用一个句子作为表语
2 说明主语是什么或怎么样,由名词、形容词或相当于名词或形容词或短语充当。
The problem is how we can get the things we need.
The scissors are not what I need.
What I told his was that I woud find him a good play.
That is what I want to tell you.
** (三)名词性从句之宾语从句**
1 语序:陈述句语句,即“主语+谓语”;
2 时态:
当主句是一般现在时或一般将来时的时候,从句可以是任何时态
当主句是一般过去时的时候,从句时态必须是过去时的范围的时态。
** (四)名词性从句之同位语从句**
1 在复合句中用作同位语的从句叫同位语从句
2 他一般跟在某些名词后边,说明该名词表示的具体内容
I heard the news that our team had won.//我听到了我们队胜利的消息
I had no idea that you were here.//我不知道你在这里
可以跟同位语从句的名词通常有:news ,idea,fact,promise,question,doubt,thought,hope,message,suggestion,words(消息),possibility等
** (五)状语从句**
修饰主句或主句的谓语
一般可分为九大类:分别表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、比较和方式。
掌握引导状语从句常用连接词
1 时间状语从句
常用引导词:when ,as,while,as soon as,before
特殊引导词:the minute,the moment,the second,every
While John was watching TV,his wife was cooking.
Every time I listen to your advice,I get into trouble.
2 地点状语从句
常用引导词:where
特殊引导词:wherever,anywhere,everywhere
Generally,air will be heavily polluted where there are factories.
Wherever you go,you should work hard.
3原因状语从句
常用引导词:because,since ,as
特殊引导词:seeing that,now that ,in that ,considering
My friends dislike me [beacuse] I’m handsome and successful.
Now that everybody has come,let’s begin our conference.
4 目的状语从句
常用引导词:so that ,in order that
特殊引导词:lest,in case,for fear that ,in the hope that
The boss asked the secretary to hurry up with the letters [so that] he could sign them
5 结果状语从句
常用引导词:so…that,such…that
特殊引导词:such that,to the degree that ,to the extend that,to such a degree that
He got up [so] early [that] he caught the first bus.
It’s [such a] good chance that we must not miss it .
To [such an] degree was he excited that he couldn’t sleep last night.
6 条件状语从句
常用引导词:if,unless
特殊引导词:as/so long as,only if,providing/provided that,suppose that,in case that,on condition that.
We’ll start our project [if] the president agree.
You will certainly succeed [so long as ] you keep on trying.
[Provided that] there is no opposition,we shall hold the meeting here.
7让步状语从句
常用引导词:though,although,even if,even though
特殊引导词:as(用在让步状语从句种必须倒装),while(一般用在句首),no matter。。。,in spite of the fact that,while ,whatever,whoever,wherever,whenever,however,whichever.
Much [as] I respect him,I can’t agree to his proposal.
[No matter how] hard he tried,she could not change her mind.
8比较状语从句
常用引导词:as(同级比较),than(不同程度比较)
特殊引导词:the more… the more…;just as…,so…;A is to B what/as X is to Y;no …more than;not A so much as B .
She is as bad-tempered as her mother.
The house is three times as big as ours.
The more you exercise,the healterier you will be.
Food is men what oil is to machine.
9方式状语从句
常用引导词:as,as,if ,how
特殊引导词:the way
(六)定语从句
(1)
定语从句:修饰某一名词或代词的从句。一般紧跟在他所修饰的先行词的后边(有后置也有前置)。
先行词:被定语从句修饰的词叫先行词。
关系词:引导定语从句的词叫关系词。
关系词三个作用:引导定语从句;代替先行词;在定语从句中担当一定的成分。
The man who is shaking hands with my father is policeman.
//who is shaking hands with my father is policeman 是定语从句;修饰“the man”先行词;who是引导定语从句的关系词,代替先行词the man,在定语从句中作主语
(2)关系的代词引导的定语从句
i.who指人,在定语从句中作主语
The boy who are playing football are from Class on.
ii.whom指人,在定语从句中作宾语,常可省略
Li Ming is just a boy (whom) I want to see.
iii.which 指物,在定语从句中作主语或作宾语。作宾语时可省略
Football is a game (which) is liked by most boys.
The factory which makes computers is far away from here.
iiii.that指人时,相当于who或whom,指物时,相当于which。在定语从句中作主语或宾语,作宾语时常可省略。
The number of people that/who come to visit this city each year reaches one million.
iiiii.whose 通常指人,也可指物,在定语从句中作定语
He has a friend whose father is a doctor.
注意,指物时,常用下列结构代替:(whose翻译过来的时候本身就含有“的”)
The classroom [whose door] is broken will soon he repaired.
The classroom the door [of which] is broken will soon he repaired.
Do you like the book [whose cover] is yellow?
Do you like the book the cover [of which] is yellow?
(3)介词+关系代词,引导定语从句
The school (which/that) he once studied [in] is very famous.
The school [in which] he once studied is very famous.
Tomorrow I’ll bring here the magazine (which/that) you asked for.
Tomorrow I’ll bring here the magazine [for which] you asked.
(4) 关系副词引导的定语从句
i.when指时间,在定语从句中作时间状语。
I still remember the day [when] I first came to this school.
The time [when] we got togetter finally arrived.
ii.where指地点,在定语从句中作地点状语
Shanghai is the city [where] I wes bron.
iii.why指原因,在定语从句中作原因状语
Please tell me the reason why you missed the plane.
注意:关系副词引导的定语从句经常可以用“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句来表示
From the years [when/in which] he was going to primary school in the country he had known what he wanted to be when he grew up.
The reason [why/for which] he refused the invitation is quite clear.
(5)限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句:不用逗号“,”与主句隔开;是先行词不可缺少的定语,如删除,主句将失去意义或表达意思不完整;翻译成“的”。
The teacher tould me that Tom was the only person [that] I could depend on.
China is a country [which] has a long histroy.
In the street I saw a man [who] was from Africa.
非限制性定语从句:用逗号“,”与主句隔开;只是对先行词的补充说明,如删除,主句仍能表达完整的意思;通常译成主句的并列句。
His mother [who] loves him very much,is strict with him.
Chain,[which] was founded in 1949,is becoming more and more powerful.
(6)只能用that引导定语从句的情况
1 不定代词
是everything,anything,nothing等不定代词时;或当先行词受every,any,all,some,no,little,few,much等代词修饰时。
2 序数词
[The first place that] they visited in London was the Big Ben.
3 最高级
This is [the best film that] I have ever seen.
4 被 the very,the only 修饰
This is [the very dictionary that] I went to buy.
5 有who,which 等疑问代词时
[Who] is the man [that] is standing by the gate?
[Which] is the T-shirt [that] fits me most?
6 人与动物或人与物
Look at [the man and his donkey that] are walking up the street.
7 定语从句与同位语从句的区别
(1)定语从句修饰限定先行词,它与先行词是修饰的关系;翻译成“的”
同位语从句说明先行词的具体内容,它与先行词是同位的关系。翻译成“是”
The plane [that] has just taken off is for paris.//定语从句
The fact [that] he has already died is quite clear.//同位语从句
(2)定语从句由关系代词或关系副词引导,关系词在从句中担当成分,关系代词在从句中作宾语常可省略
同位语从句主要有连词引导,在从句中一般不担当成分
The news that he tould me is true.//定语从句
The news that he has just died is true.//同位语从句
2.8 介词(6个知识点)
(一) 介词主要用法
1 介词不能独立使用
2 介词之后有名或代词(宾格)或相当于名词的其它词类、短语或从句作它的宾语,即构成介词短语
3 有些介词是由两个以上的词构成的介词短语
out of 从…中出来
because of 因为
(二)分类(9种)
1 地点介词
above 在。。。之前
about 在。。。附近
2 方向介词
across 横越
against 对抗
3 时间介词
about 大约…
after 在。。。以后
4 方式介词
as 作为/当作…
by 用/由/乘坐/被…
5 涉及介词
about 关于…
except 除了…
6 目的介词
for 为了。。。
from 防止。。。
to 为了。。。
7 原因介词
for 因为。。。
with 由于。。。
because of 因为。。。
8 比较介词
as 与。。。一样
like 像。。。一样
than 比。。。一样
9 伴随介词
against 和。。。一起(比赛)
at 在(上班/休息/上学/家)
(三)句法作用
介词短语相当于一个形容词或副词,可用作状语,定语和表语
The man came [down] the stairs.//down作状语
The woman [with] a flower on her head is from the countryside.//定语
The teacher is now [with] the plpils.//表
(四)介词短语在句子中的位置
1 作状语
表时间、地点,可以在句首或句尾
表方向、方式、伴随、涉及、原因、目的、比较,放在句尾
He wanted to find a good job [in] Shanghai the next year.//状语
2 作表语
系动词之后
The letters are [for] you.//表语
3 作定语
被修饰的名词之后
Have you seen a cat [with] a black head and four white legs?//定语
** (五)高频固定词组**
arrive at/in 到达
on foot 步行
** (六)易混介词辨析**
1 时间或地点介词 in ,on ,at
表时间: in,表在某一时间段;在将来时句子中表示一段时间之后;
on,表具体的某一天;
at,表某个时刻或瞬间。
表地点: in,表在某个范围之内;
on,表在某个平面上或与一个面相接触;
at,表在具体的场所或地点。
He was born [on] the morning of May 10th.
I usually get up [at] 7:00 in the morning.
His glasses are right [on] his nose.
He is at the cinema [at] the moment.
2 时间介词after与in:在…之后
after+(具体时刻/从句):表 在。。。时刻之后,常用于一般时态
in+(一段时间):表 在(多久)之后,常用于将来时态
He said that he would be here after 6:00.
My father is coming back from England [in] about a month.
3 时间介词since与for
since+(具体时刻/that-从句):自从。。。起一直到现在
for+(一段时间):总共有。。。之久
Uncle Li has worked in this factory since 1970.
Uncle Li has worked in this factory for over 30 years.
4 方式介词by,in与with – 工具,手段
by:乘坐某交通工具;以。。。方式;在被动句中可以表示动作的执行者
in:使用某语言/文字
with:使用某工具/手段
We see with our eyes and walk with our feet.
Please write that article in English.
Let’s go to the zoo by taxi.
5 through,across与over
through:穿过。。(门洞/人群/树林);通过。。。方式(内部)
across/over:跨越。。(街道/河流);表翻过可用over。(外部)
There is a bridge [across/over] the river.
The vistors went [through] a big gate into another park.
6 as与like 像。。。
as:作为。。。,表职业、职务、作用等事实
like:像。。。一样,表外表,不是事实
Let me speak to you as a father.//说话者是听者的父亲
Let me speak to you like a father.//不是听者的父亲
7 at the end of,by the end of,to the end,in the end.
at the end of…:即可表时间也可表地点,常用过去时
by the end of…: 表时间,常用完成时。
in the end/at last:基本等义,表 终于,最后,常用过去时
to the end:到。。。的终点为止
[By the end of] last term we had learned 16 units of Book III.
[At] the end of] the road you can find a big white house with brown windows.
8 for a moment,for the moment,in a moment,at the moment
for a moment:一会儿,片刻(= for a while) ,常与持续性动词连用
for the moment:暂时、目前,常用现在时。
in a moment:一会儿,立即马上(=soon;in a few minutes),用将来时
at the moment:此刻,眼下(= now),用现在进行时。
Please wait [for a moment].
Let’s leave things as they are [for the moment].
I’ll come back [in a moment].
I am very busy [at the moment];
9 in front of 与 in the front of
in front of :在。。。前面
in the front of:在。。。前部
A cat was parking [in front of] the hall
[In the front of ] the hall stood a big desk.
10 except与besides
except:除了,表不包含
besides:除了,表包含
Everyone went to the Palace Museum except Tome.//Tom 没有去
Besides Chinese he also studied many other subjects.//汉语也是学的功课之一
2.9 倒装结构
(一)全部倒装:只是将句中谓语动词全部置于主语之前
1 表方式或方位的副词或介词短语放在句首,要倒装
here,there,now,then,up,down,in ,awy,off,in the room,on the wall等。
[Here] is your letter.
[South of] the river lies a small factory.
[Out] rushed the children.
[Ahead] sat an old woman.
(二)部分倒装:指将谓语的一部分如助动词或情态动词放置在主语之前(英语中绝大多是部分倒装)
如果句子中没有助动词或情态动词,则需要添加助动词do,does,did,并将其放在主语之前。
1 only 放在句首时
[Only] in this way [can you] learn English well.
[Only] after being asked three times [did he ] come to the meeting.
[Only] when he is seriously ill [does he] ever stay in bed.
2 句首为否定意义的单词
如no,not ,never,seldom,little,hardly,at not time,in no way,not until…等
[Never] have I seen such a preformance.
[Nowhere] will you find the answer to his question.
[Not until] the child feel asleep did the mother leave the room.
3 so,neither,nor放于句首部分倒装
Tom can speak French.So can Jack.
If you wonit go,neither will I.
4 so…that中的so位于句首时,需倒装(so that所以,so…that为了)
[So frighteded was he] that he did not dare to move an inch.
5 在虚拟语气中条件句中从句谓语动词有were,had,should等词,可将if省略,把were,had,should 移到主语之前,采取部分倒装
[Were I you(If I were you)],I would try it again.
(三)补充:强调句
it+be +被强调部分+that/who
强调句子中某一个成分(通常是主语、宾语或状语)
I met Sam at the railway station yesterday.
It was I that met Sam at the railway station yesterday.//强调主语
It was Sam that I met at the railway station yesterday.//强调宾语
It was at the railway station that I met Sam yesterday.//强调地点状语
It was yesterday that I met Sam at the railway station.//强调时间状语
注意1 在强调主语时,that后的谓语动词要与被强调者保持人称和数的一致
It is [I] who/that [am] a teacher.
注意2 即使被强调的主语是复数,主句中谓语动词也用单数
It [is] [they] who often help me with my lessons.
注意3 在强调时间、地点、原因或方式状语时,不能用when,where,why或how,而用that
It was because her mother was ill that she didn’t go with us.
It was the house that the murder happened.
注意4 it is/was not until …that…
not … until 要变成 not until,that 从句中的位于动词要用肯定式
My father [didn’t] come home until 12:00 last night.
It [was not until] 12:00 last night [that] my father came home.
注意5 原句的谓语动词如果是现在或将来的各种时态用:it is …that/who…
原句的谓语动词是过去各种时态用:it was …that/who…
注意6 辨别 it is/was +名词+that 的名词性从句
强调句型结构的it is/was…that/who去掉,被强调部分归位后,能够形成一个完整的句子。
名词性从句中不可去掉,去掉原句不再成立。
注意7 用助动词do,does,did来强调句中谓语动词,加强陈述句和祈使句的语气,译为“的确,确实”等
He [did] send you a letter last week.
