原文链接:http://tecdat.cn/?p=12187
金融分析师通常关心检测市场何时“发生变化”:几个月或至几年内市场的典型行为可以立即转变为非常不同的行为。投资者希望及时发现这些变化,以便可以相应地调整其策略,但是这样做可能很困难。
RHmm从CRAN不再可用,因此我想使用其他软件包复制功能实现马尔科夫机制转换(Markov regime switching)模型从而对典型的市场行为进行预测,并且增加模型中对参数的线性约束功能。
library(SIT)
load.packages('quantmod')
# find regimes
load.packages('RHmm', repos ='http://R-Forge.R-project.org')
y=returns
ResFit = HMMFit(y, nStates=2)
VitPath = viterbi(ResFit, y)DimObs = 1
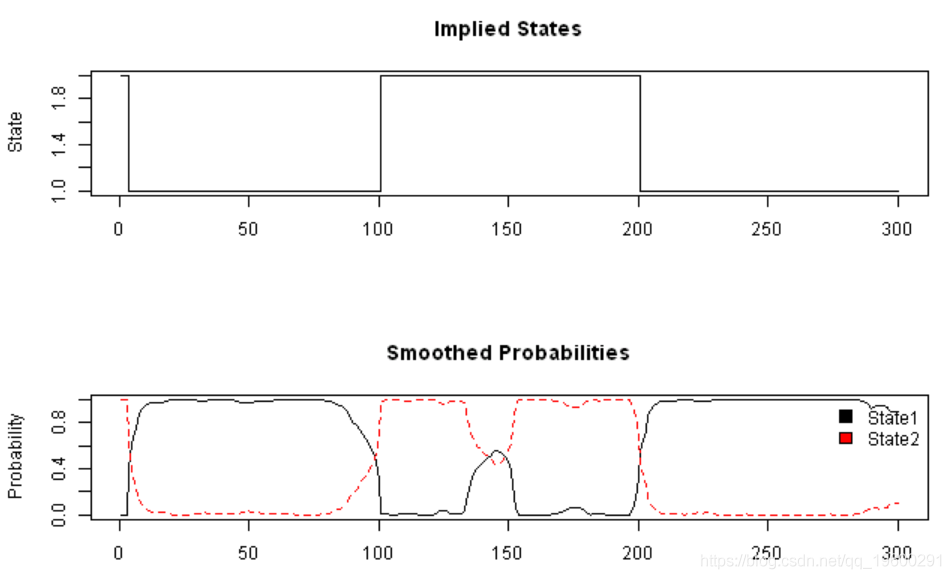
matplot(fb$Gamma, type='l', main='Smoothed Probabilities', ylab='Probability')
legend(x='topright', c('State1','State2'), fill=1:2, bty='n')
fm2 = fit(mod, verbose = FALSE)使用logLik在迭代69处收敛:125.6168
probs = posterior(fm2)
layout(1:2)
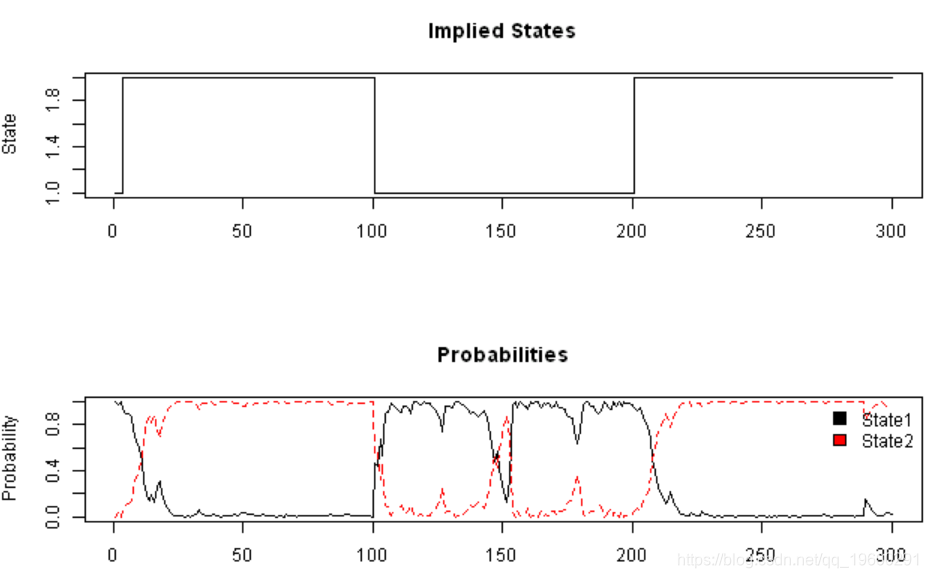
plot(probs$state, type='s', main='Implied States', xlab='', ylab='State')
matplot(probs[,-1], type='l', main='Probabilities', ylab='Probability')
legend(x='topright', c('State1','State2'), fill=1:2, bty='n')
#*****************************************************************
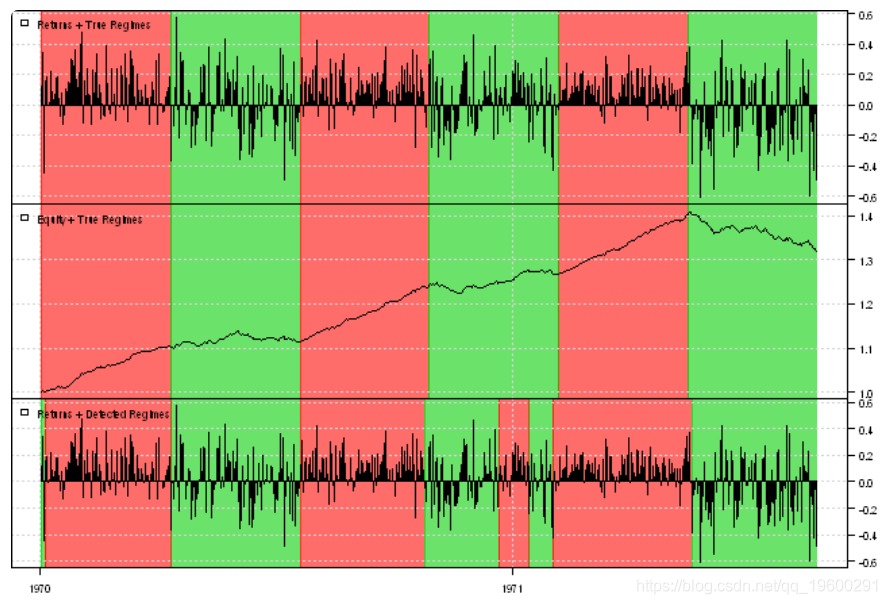
# Add some data and see if the model is able to identify the regimes
#******************************************************************
bear2 = rnorm( 100, -0.01, 0.20 )
bull3 = rnorm( 100, 0.10, 0.10 )
bear3 = rnorm( 100, -0.01, 0.25 )
true.states = c(true.states, rep(2,100),rep(1,100),rep(2,100))
y = c( bull1, bear, bull2, bear2, bull3, bear3 )
DimObs = 1
plota(data, type='h', x.highlight=T)
plota.legend('Returns + Detected Regimes')
#*****************************************************************
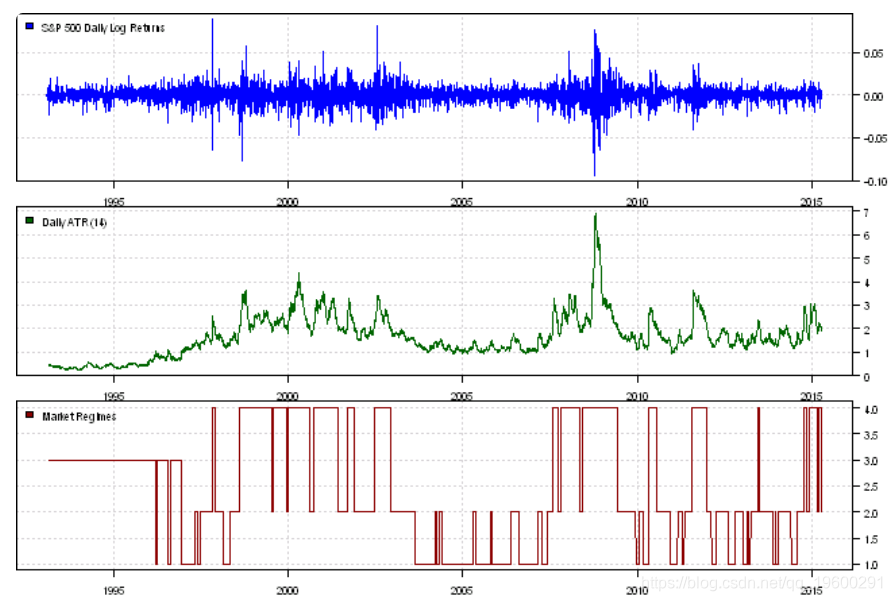
# Load historical prices
#******************************************************************
data = env()
getSymbols('SPY', src = 'yahoo', from = '1970-01-01', env = data, auto.assign = T)
price = Cl(data$SPY)
open = Op(data$SPY)
ret = diff(log(price))
ret = log(price) - log(open)
atr = ATR(HLC(data$SPY))[,'atr']
fm2 = fit(mod, verbose = FALSE)使用logLik在迭代30处收敛:18358.98
probs = posterior(fm2)
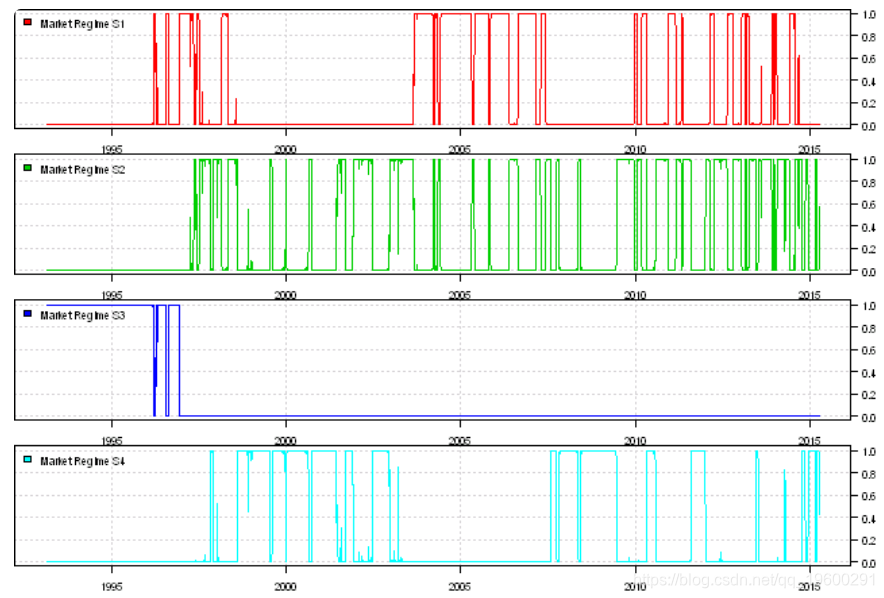
print(head(probs))layout(1:3)
plota(temp, type='l', col='darkred')
plota.legend('Market Regimes', 'darkred')
layout(1:4)