假设有两个高斯分布:
高斯分布相乘
计算这两个高斯分布的乘积:
高斯分布的乘积还是高斯分布,且根据这篇博客 直观理解高斯相乘可以计算出 的均值 和方差 。
接下来分析一下 和
首先是均值
当 时:
所以,
当 时:
所以,
当 时:
所以,
可以看出 是位于 和 之间。
接下来是方差
所以 的方差比 和 的方差都要小。
代码验证高斯分布相乘
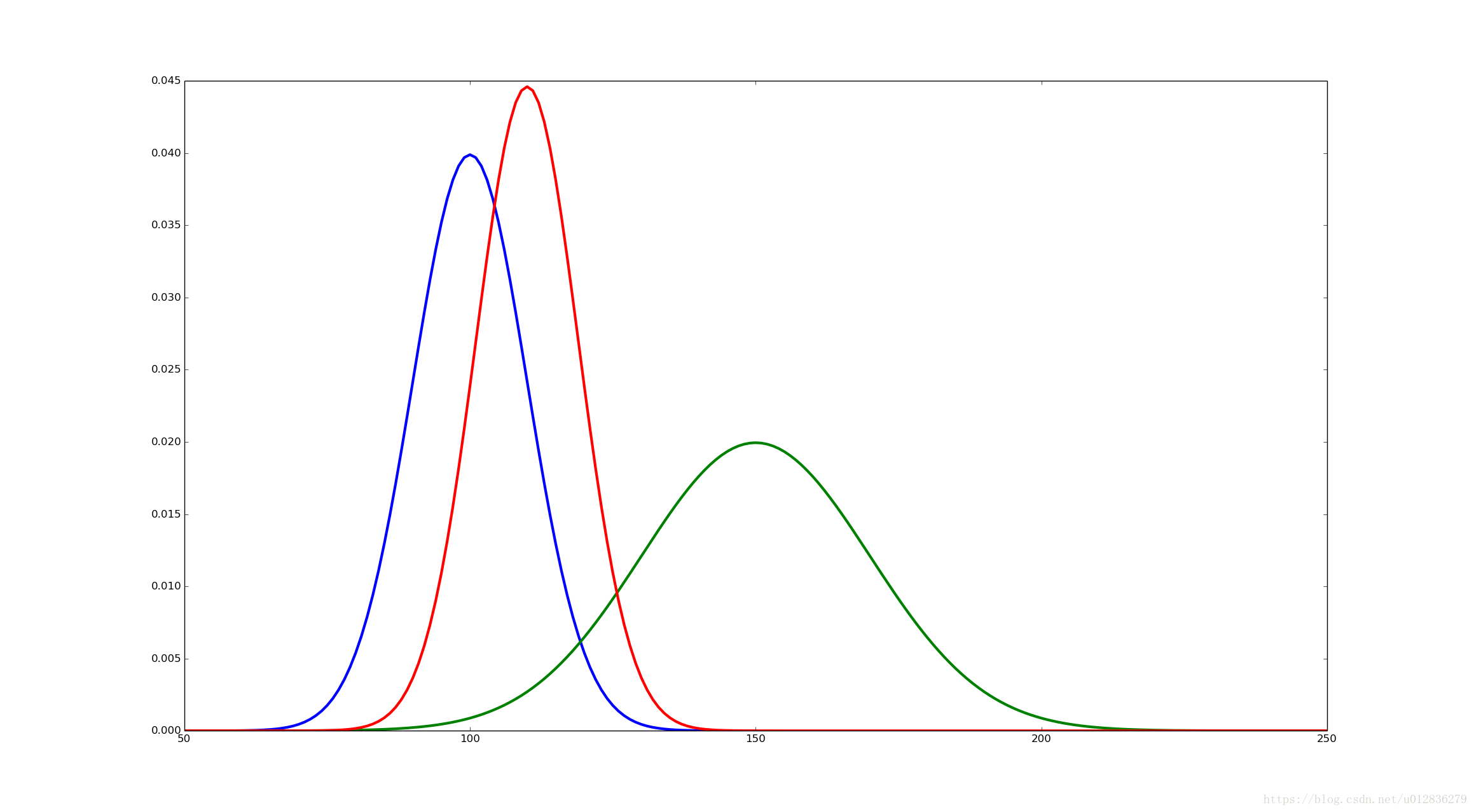
紧接着,通过python代码验证这个结果:
其中,红色的曲线表示高斯分布的乘积,其详细的代码如下所示:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from math import *
class Distribution:
def __init__(self,mu,sigma,x,values,start,end):
self.mu = mu
self.sigma = sigma
self.values = values
self.x = x
self.start = start
self.end =end
def normalize(self):
s = float(sum(self.values))
if s != 0.0:
self.values = [i/s for i in self.values]
def value(self, index):
index -= self.start
if index<0 or index >= len(self.values):
return 0.0
else:
return self.values[index]
@staticmethod
def gaussian(mu,sigma,cut = 5.0):
sigma2 = sigma*sigma
extent = int(ceil(cut*sigma))
values = []
x_lim=[]
for x in xrange(mu-extent,mu+extent+1):
x_lim.append(x)
values.append(exp((-0.5*(x-mu)*(x-mu))/sigma2))
p1=Distribution(mu,sigma,x_lim,values,mu-extent,mu-extent+len(values))
p1.normalize()
return p1
if __name__=='__main__':
p1 = Distribution.gaussian(100,10)
plt.plot(p1.x,p1.values,"b-",linewidth=3)
p2 = Distribution.gaussian(150,20)
plt.plot(p2.x,p2.values,"g-",linewidth=3)
start = min(p1.start,p2.start)
end = max(p1.end,p2.end)
mul_dist = []
x_lim = []
for index in range(start,end):
x_lim.append(index)
mul_dist.append(p1.value(index)*p2.value(index))
#normalize the distribution
s= float(sum(mul_dist))
if s!=0.0:
mul_dist=[i/s for i in mul_dist]
plt.plot(x_lim,mul_dist,"r-",linewidth=3)
plt.show()