蒙特卡洛树搜索及实现三子棋游戏
预备知识
双人有限零和顺序游戏
MCTS运行所在的框架/环境是一个游戏,它本身是一个非常抽象和宽泛的概念,因此这里我们只关注一种游戏类型:双人有限零和顺序游戏。这个名词一开始听起来会有些复杂,但是实际上非常简单,现在来让我们将它分解一下:
游戏:意味着我们在一种需要交互的情境中,交互通常会涉及一个或多个角色
有限:表明在任意时间点,角色之间存在的交互方式都是有限的
双人:游戏中只有两个角色
顺序:玩家依次交替进行他们的动作
零和:参与游戏的两方有完全相反的目标,换句话说就是,游戏的任意结束状态双方的收益之和等于零
我们可以很轻松的验证,围棋、国际象棋和井字棋都是双人有限零和顺序游戏:有两位玩家参与,玩家能进行的动作总是有限的,双方的游戏目标是完全相反的(所有游戏的结果之和等于0)原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_16137569/article/details/83543641
游戏树
游戏树是一种常见的数据结构,其中每一个节点代表游戏的一个确定状态,从一个节点到该节点的一个子节点(如果存在)是一个移动。节点的子节点数目称为分支因子。游戏树的根节点代表游戏的初始状态。游戏树的终端节点是没有子节点的节点,至此游戏结束,无法再进行移动。终端节点的状态也就是游戏的结果(输/赢/平局)。
下面以井字棋游戏为例,形象地来看下什么是游戏树。
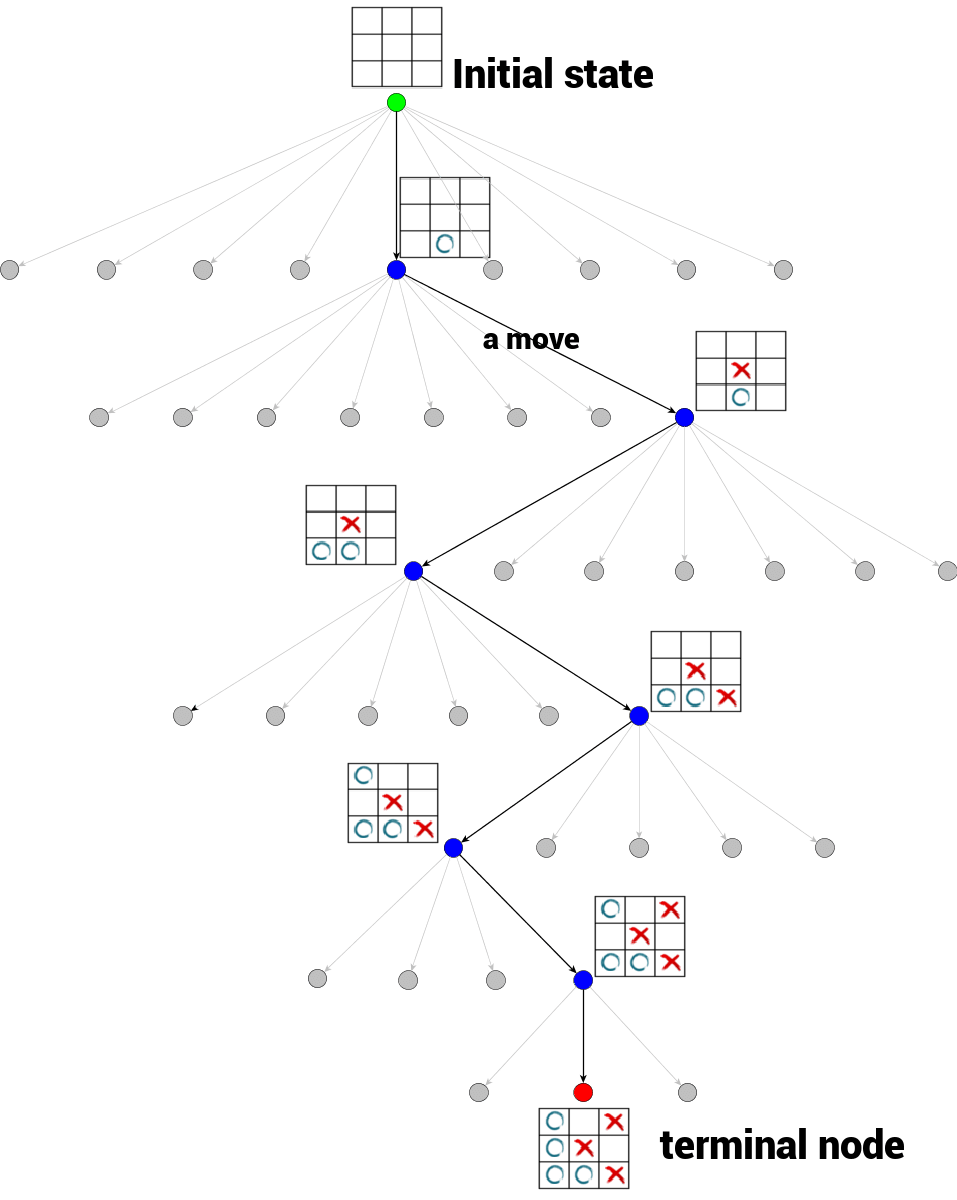
每个父节点的子节点数量对应着本次可以执行的Action的数量
蒙特卡洛树搜索
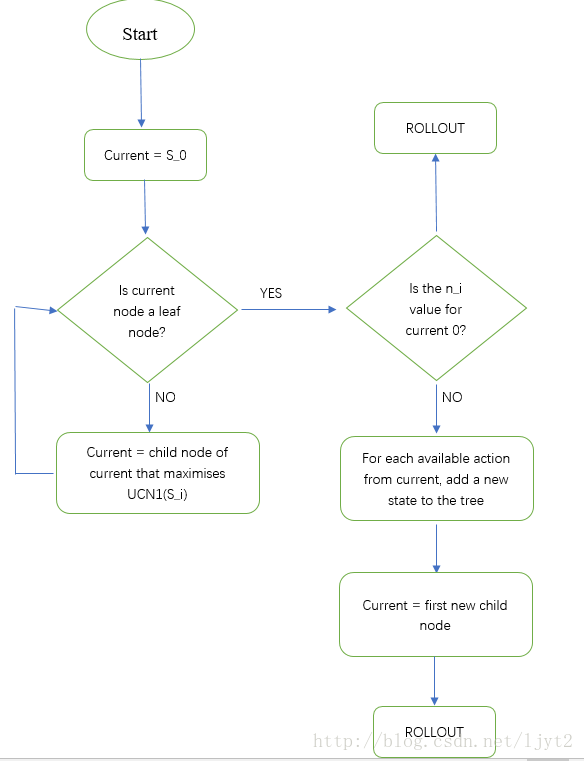
搜索流程图
搜索步骤
-
选择
从根节点开始,我们选择采用UCB计算得到的最大的值的孩子节点,如此向下搜索,直到我们来到树的底部的叶子节点(没有孩子节点的节点),若果该节点没有子节点,就会去执行扩展 -
扩展
到达叶子节点后,如果还没有到达终止状态,那么我们就要对这个节点进行扩展(这里是一个迭代过程),扩展出一个或多个节点。可以扩展一个节点也可以扩展多个节点. -
模拟
我们基于目前的这个状态,根据某一种策略(例如random policy)进行模拟,直到游戏结束为止,产生结果,比如胜利或者失败。此处的模拟可以指定模拟多少轮也可以指定模拟多少时间.所以模拟的本质还是用频率去逼近概率 -
反向传播
根据模拟的结果,我们要自底向上,反向更新所有节点的信息.一般需要更新的值有该节点被访问的次数和该节点的奖励值.若模拟结果为胜利,则奖励为正,模拟结果为失败,则奖励为负.奖励函数也可以设计的很复杂
每次搜索步骤需要N次的模拟,但只对应了一次下棋,每次下棋后都会更新状态,并从新状态开始(人也下完了棋),进行下一次的搜索.(下一步棋)
具体案例可以看博客
节点状态
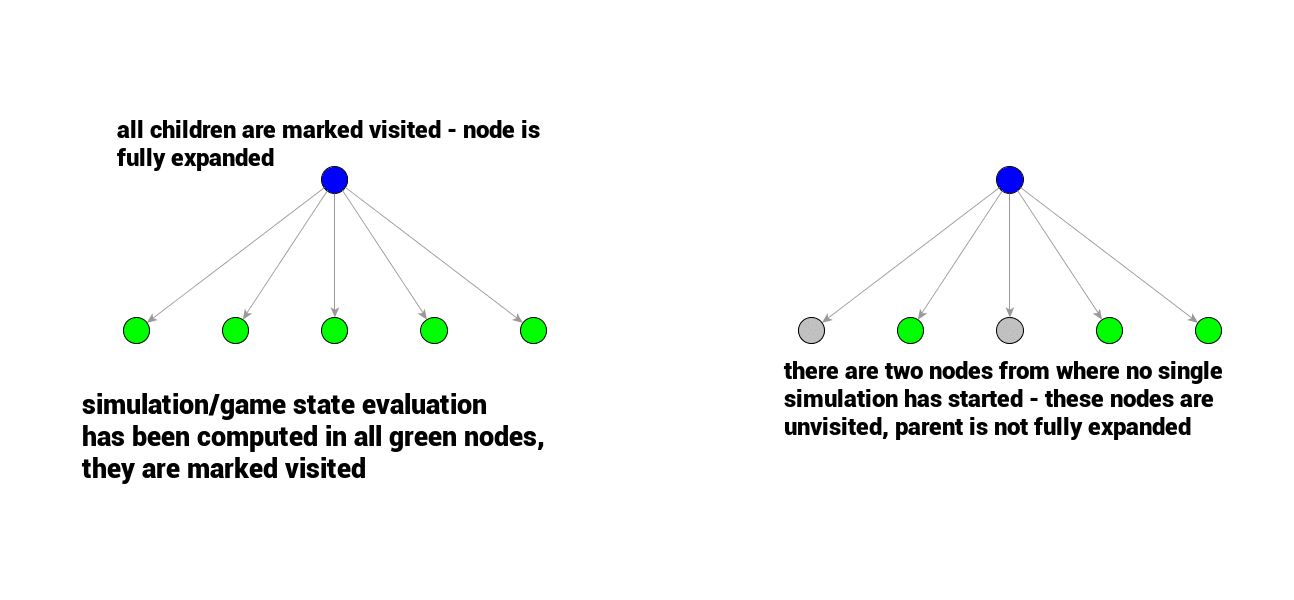
某个节点的所有子节点全都被访问过,则该节点称作完全扩展,否则就是未完全扩展.
图中灰色的节点表示被扩展出来但是还没有被访问过
UCT计算
( 是节点被访问的次数,而 则是其父节点已经被访问的总次数)
UCT的第一部分是(总收益/总次数=平均每次的收益),即优先选择收益大的.但只有这一项是不够的,那些未被选中的节点之后就再也无法选到了,
UCT的第二部分是倾向于那些未被探索的节点,(子节点被探索的越少则分母越小,)
c是一个常数,用于平衡两部分的值
何时停止
原则上,模拟的次数越多则结果越好,但在实际中往往会指定一个时间限制或是模拟次数限制,防止运行时间过长(比如跟你对战的ai迟迟不下棋).在模拟结束后,最佳的移动通常是访问次数最多的那个节点.
代码实现
实现一个三子棋程序
其中蒙特卡洛树代码来自git
蒙特卡洛核心类
-
mcts类:
search方法对应模拟方法
executeRound方法定义了一次模拟流程
selectNode对应节点选择,
- 该节点若有子节点,则使用getBestChild方法获得UCT值最大的节点
- 若无子节点,则使用expand方法扩展子节点
rollout方法将在选择的节点上随机执行一种Action
backpropogate方法对应反向传播
getBestChild,在n次executeRound执行完后,选择子节点中最优的
getAction方法是从子节点中获取其动作(下到哪里)
-
treeNode类,用于构建树形结构,存储当前节点的状态
-
randomPolicy方法:规定了rollout时使用哪种方式,一般使用随机选择的方式
from __future__ import division
import time
import math
import random
def randomPolicy(state):
while not state.isTerminal():
try:
action = random.choice(state.getPossibleActions())
except IndexError:
raise Exception("Non-terminal state has no possible actions: " + str(state))
state = state.takeAction(action)
return state.getReward()
class treeNode():
def __init__(self, state, parent):
self.state = state
self.isTerminal = state.isTerminal()
self.isFullyExpanded = self.isTerminal
self.parent = parent
self.numVisits = 0
self.totalReward = 0
self.children = {}
class mcts():
def __init__(self, timeLimit=None, iterationLimit=None, explorationConstant=1 / math.sqrt(2),
rolloutPolicy=randomPolicy):
if timeLimit != None:
if iterationLimit != None:
raise ValueError("Cannot have both a time limit and an iteration limit")
# time taken for each MCTS search in milliseconds
self.timeLimit = timeLimit
self.limitType = 'time'
else:
if iterationLimit == None:
raise ValueError("Must have either a time limit or an iteration limit")
# number of iterations of the search
if iterationLimit < 1:
raise ValueError("Iteration limit must be greater than one")
self.searchLimit = iterationLimit
self.limitType = 'iterations'
self.explorationConstant = explorationConstant
self.rollout = rolloutPolicy
def search(self, initialState):
self.root = treeNode(initialState, None)
if self.limitType == 'time': # 时间限制
timeLimit = time.time() + self.timeLimit / 1000
while time.time() < timeLimit:
self.executeRound()
else: # 次数限制
for i in range(self.searchLimit):
self.executeRound()
# executeRound执行完后,其叶子节点就存放了他们的信息
bestChild = self.getBestChild(self.root, 0)
return self.getAction(self.root, bestChild)
def executeRound(self):
node = self.selectNode(self.root)
reward = self.rollout(node.state)
self.backpropogate(node, reward)
def selectNode(self, node):
while not node.isTerminal: # 这里会一直找到游戏结束,即最后一个节点
if node.isFullyExpanded:
node = self.getBestChild(node, self.explorationConstant)
else:
return self.expand(node) # 每次把所有的孩子都扩展出来
return node
def expand(self, node):
actions = node.state.getPossibleActions()
for action in actions:
if action not in node.children:
newNode = treeNode(node.state.takeAction(action), node)
node.children[action] = newNode
if len(actions) == len(node.children):
node.isFullyExpanded = True
return newNode
raise Exception("Should never reach here")
def backpropogate(self, node, reward):
while node is not None:
node.numVisits += 1
node.totalReward += reward
node = node.parent
def getBestChild(self, node, explorationValue):
bestValue = float("-inf")
bestNodes = []
for child in node.children.values():
nodeValue = child.totalReward / child.numVisits + explorationValue * math.sqrt(
2 * math.log(node.numVisits) / child.numVisits)
if nodeValue > bestValue:
bestValue = nodeValue
bestNodes = [child]
elif nodeValue == bestValue:
bestNodes.append(child)
return random.choice(bestNodes)
def getAction(self, root, bestChild):
for action, node in root.children.items():
if node is bestChild:
return action
状态类
- Action类是动作类,封装了执行的动作,比如下棋到哪个位置
- NaughtsAndCrossesState类是状态类,要提供以下方法
- 维护玩家状态: currentPlayer
- 维护棋盘状态: board
- 提供一个获得所有可行状态的方法getPossibleActions
- 提供一个执行Action的方法takeAction,并且要更新自己的状态
- 提供一个isTerminal函数,用于判断游戏是否结束
- 提供一个getReward方法,用于计算奖励
from __future__ import division
from copy import deepcopy
from mcts import mcts
from functools import reduce
import operator
class NaughtsAndCrossesState(object):
def __init__(self):
self.target_num = 3 # 最终目标
self.board_width = 3
self.board = [[0] * self.board_width for _ in range(self.board_width)]
self.currentPlayer = 1
def getPossibleActions(self):
possibleActions = []
for i in range(len(self.board)):
for j in range(len(self.board[i])):
if self.board[i][j] == 0:
possibleActions.append(Action(player=self.currentPlayer, x=i, y=j))
return possibleActions
def takeAction(self, action):
newState = deepcopy(self)
newState.board[action.x][action.y] = action.player
newState.currentPlayer = self.currentPlayer * -1
return newState
def isTerminal(self):
for row in self.board:
if abs(sum(row)) == self.target_num:
return True
for column in list(map(list, zip(*self.board))):
if abs(sum(column)) == self.target_num:
return True
for diagonal in [[self.board[i][i] for i in range(len(self.board))],
[self.board[i][len(self.board) - i - 1] for i in range(len(self.board))]]:
if abs(sum(diagonal)) == self.target_num:
return True
return reduce(operator.mul, sum(self.board, []), 1)
def getReward(self):
for row in self.board:
if abs(sum(row)) == self.target_num:
return sum(row) / self.target_num
for column in list(map(list, zip(*self.board))):
if abs(sum(column)) == self.target_num:
return sum(column) / self.target_num
for diagonal in [[self.board[i][i] for i in range(len(self.board))],
[self.board[i][len(self.board) - i - 1] for i in range(len(self.board))]]:
if abs(sum(diagonal)) == self.target_num:
return sum(diagonal) / self.target_num
return False
class Action():
def __init__(self, player, x, y):
self.player = player
self.x = x
self.y = y
def __str__(self):
return str((self.x, self.y))
def __repr__(self):
return str(self)
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.__class__ == other.__class__ and self.x == other.x and self.y == other.y and self.player == other.player
def __hash__(self):
return hash((self.x, self.y, self.player))
if __name__ == '__main__':
import numpy as np
s = NaughtsAndCrossesState()
tree = mcts(timeLimit=1000)
while True:
# 机器下棋
action = tree.search(initialState=s)
s = s.takeAction(action)
print("ai:", action)
print(np.array(s.board))
if s.isTerminal():
print("ai win")
break
# 人下棋
x, y = list(map(int, input().split()))
action = Action(-1, x, y)
s = s.takeAction(action)
print("人:", action)
print(np.array(s.board))
print(s.isTerminal())
if s.isTerminal():
print("human win")
break
我们在实际使用中,只需定义一个合适的State和Action类并实现其方法,就可以应用到mcts中.不要将State和Action耦合在MCTS中,这样就没有扩展性了