网格搜索
简单说,就是将所有可调的参数,组成一个网格表,训练过程会自动选出最优模型参数:
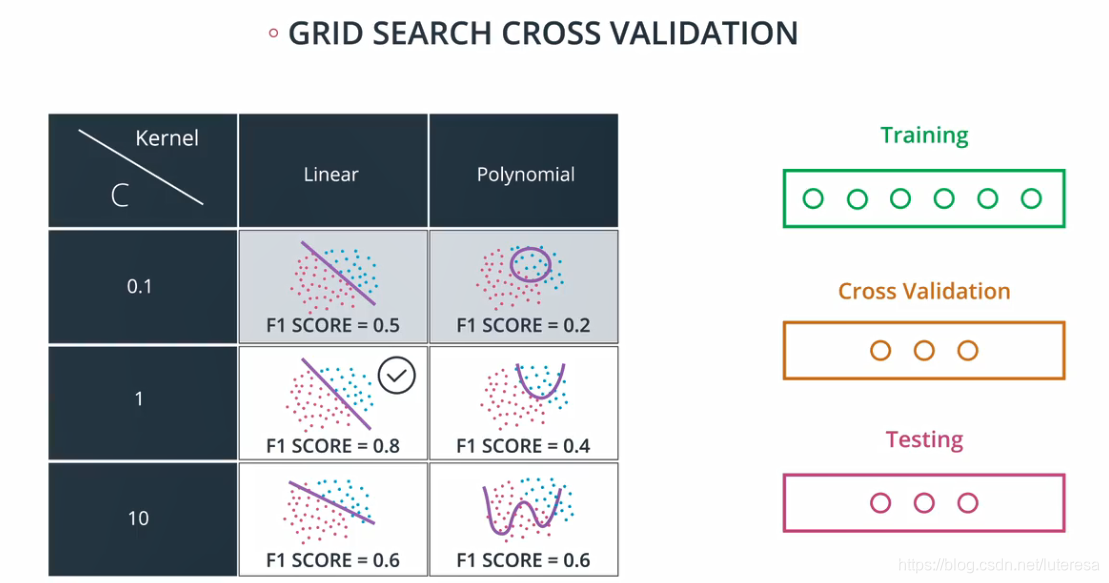
以决策树模型为例,拟合样本数据。
这个初始模型会过拟合。 然后,我们将使用网格搜索为这个模型找到更好的参数,以减少过拟合。
首先,导入:
%matplotlib inline
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
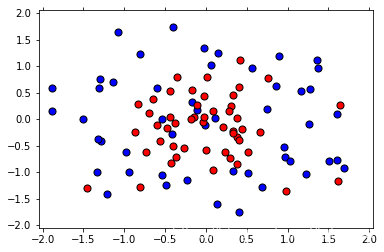
1.阅读并绘制数据
现在,这个函数将帮助我们读取 csv 文件并绘制数据。
def load_pts(csv_name):
data = np.asarray(pd.read_csv(csv_name, header=None))
X = data[:,0:2]
y = data[:,2]
plt.scatter(X[np.argwhere(y==0).flatten(),0], X[np.argwhere(y==0).flatten(),1],s = 50, color = 'blue', edgecolor = 'k')
plt.scatter(X[np.argwhere(y==1).flatten(),0], X[np.argwhere(y==1).flatten(),1],s = 50, color = 'red', edgecolor = 'k')
plt.xlim(-2.05,2.05)
plt.ylim(-2.05,2.05)
plt.grid(False)
plt.tick_params(
axis='x',
which='both',
bottom='off',
top='off')
return X,y
X, y = load_pts('data.csv')
plt.show()
2. 将我们的数据分为训练和测试集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, make_scorer
#Fixing a random seed
import random
random.seed(42)
# Split the data into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
3. 拟合一个决策树模型
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
# Define the model (with default hyperparameters)
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)
# Fit the model
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Make predictions
train_predictions = clf.predict(X_train)
test_predictions = clf.predict(X_test)
现在我们来绘制模型,并找到测试 f1_score
以下函数将帮助我们绘制模型。
def plot_model(X, y, clf):
plt.scatter(X[np.argwhere(y==0).flatten(),0],X[np.argwhere(y==0).flatten(),1],s = 50, color = 'blue', edgecolor = 'k')
plt.scatter(X[np.argwhere(y==1).flatten(),0],X[np.argwhere(y==1).flatten(),1],s = 50, color = 'red', edgecolor = 'k')
plt.xlim(-2.05,2.05)
plt.ylim(-2.05,2.05)
plt.grid(False)
plt.tick_params(
axis='x',
which='both',
bottom='off',
top='off')
r = np.linspace(-2.1,2.1,300)
s,t = np.meshgrid(r,r)
s = np.reshape(s,(np.size(s),1))
t = np.reshape(t,(np.size(t),1))
h = np.concatenate((s,t),1)
z = clf.predict(h)
s = s.reshape((np.size(r),np.size(r)))
t = t.reshape((np.size(r),np.size(r)))
z = z.reshape((np.size(r),np.size(r)))
plt.contourf(s,t,z,colors = ['blue','red'],alpha = 0.2,levels = range(-1,2))
if len(np.unique(z)) > 1:
plt.contour(s,t,z,colors = 'k', linewidths = 2)
plt.show()
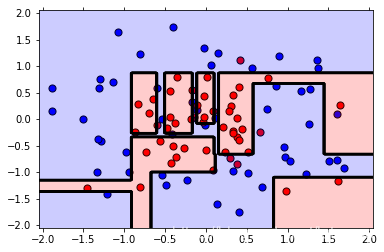
plot_model(X, y, clf)
print('The Training F1 Score is', f1_score(train_predictions, y_train))
print('The Testing F1 Score is', f1_score(test_predictions, y_test))
The Training F1 Score is 1.0
The Testing F1 Score is 0.7000000000000001
The Training F1 Score is 1.0
The Testing F1 Score is 0.7
由上图知,现在的模型明显是过拟合的。 我们不仅仅是看图表,还需要看看高训练分(1.0)和低测试分(0.7)之间的差异。思考一下,我们是否可以找到更好的超参数来让这个模型做得更好? 接下来我们将使用网格搜索。
4.使用网格搜索来完善模型
现在,我们将执行以下步骤:
1.首先,定义一些参数来执行网格搜索。 我们建议使用max_depth, min_samples_leaf, 和 min_samples_split。
2.使用f1_score,为模型制作记分器。
3.使用参数和记分器,在分类器上执行网格搜索。
4.将数据拟合到新的分类器中。
5.绘制模型并找到 f1_score。
6.如果模型不太好,请尝试更改参数的范围并再次拟合。
from sklearn.metrics import make_scorer
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)
# TODO: Create the parameters list you wish to tune.
parameters = {'max_depth':[2,4,6,8,10],'min_samples_leaf':[2,4,6,8,10], 'min_samples_split':[2,4,6,8,10]}
# TODO: Make an fbeta_score scoring object.
scorer = make_scorer(f1_score)
# TODO: Perform grid search on the classifier using 'scorer' as the scoring method.
grid_obj = GridSearchCV(clf, parameters, scoring=scorer)
# TODO: Fit the grid search object to the training data and find the optimal parameters.
grid_fit = grid_obj.fit(X_train, y_train)
获得最佳估算模型,用最佳估算器重新拟合参数,并统计参数得分;
# TODO: Get the estimator.
best_clf = grid_fit.best_estimator_
# Fit the new model.
best_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Make predictions using the new model.
best_train_predictions = best_clf.predict(X_train)
best_test_predictions = best_clf.predict(X_test)
# Calculate the f1_score of the new model.
print('The training F1 Score is', f1_score(best_train_predictions, y_train))
print('The testing F1 Score is', f1_score(best_test_predictions, y_test))
# Plot the new model.
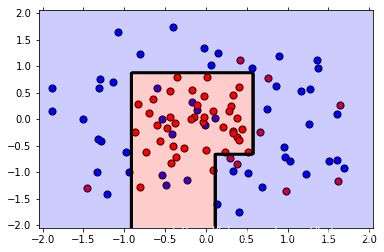
plot_model(X, y, best_clf)
# Let's also explore what parameters ended up being used in the new model.
best_clf
The training F1 Score is 0.8148148148148148
The testing F1 Score is 0.8
DecisionTreeClassifier(ccp_alpha=0.0, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=4, max_features=None, max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=4, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort='deprecated',
random_state=42, splitter='best')
- 总结
注意,通过使用网格搜索,我们将 F1 分数从 0.7 提高到 0.8(同时我们失去了一些训练分数,但这没问题)。 另外,如果你看绘制的图,第二个模型的边界更为简单,这意味着它不太可能过拟合。
