OSPF virtual link with the principle of multi-regional
A generation, OSPF multipleregion
The reason: to improve the scalability of the network (multi-zone), fast convergence (control the number of domain router)
1. Three traffic
-
Exchanging packets constituting traffic between routers within a single area - traffic within
-
Inter-domain traffic - exchanging configuration data packet traffic between routers in different regions of
- Exchanging packets constituting traffic between the routers in the router of OSPF areas or another autonomous system external domain traffic --OSPF
Two, OSPF router type
Four kinds: DR | BDR | ABR | ASBR
OSPF area types
(1) the backbone
(2) non-backbone area - according to the type of routing to learn to distinguish
- Standard area
- Peripheral areas - no LSA4,5,7 notice
- Totally peripheral area - in addition to a route advertisement LSA3 nobody, without notice LSA3,4,5,7
- Non-stubby area
Peripheral areas and complete peripheral region
To meet the conditions
- Only as a default route to export their area;
- As the area can not cross the region virtual link;
- Stub area where no autonomous system border router ASBR;
- Not the backbone area Area 0
LSA4,5,7 tip region does not advertise; fully distal region, in addition to a default route advertised LSA3 no no-summary LSA3,4,5,7 advertisement make it a fully distal region - this is only added on an ABR command, because only ABR will summarize
Three, OSPF link state database members (seven LSA type)
Each router creates a database by each interface corresponding to adjacent nodes and interfaces consisting of speed
Each entry in the link-state database called LSA (Link State Advertisement), there are six common type of LSA
| Types of | description | use |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Router LSA | Issued by the router in the area |
| Type 2 | Network LSA | Issued by the DR region in |
| Type 3 | Network Summary LSA | ABR issued in other regions of the summary notice link |
| Type 4 | ASBR summary LSA | ABR issued for an ASBR information |
| Type 5 | AS external LSA | ASBR issued for external routes advertised |
| Type 7 | NSSA external LSA | ASBR in the NSSA issued for external routes advertised in the region of the connection |
Type 4 Type 5 and wherein simultaneous, 4 emitted from the ABR, ASBR for announcing location information issued by the ASBR 5, to advertise external route. If the region does not appear ASBR 4 and 5 do not.
Fourth, the router selects the route of entry
1, only the router is added to the optimum route to the routing table entries
based on 2, routing entry
(1) from the Management
(2) metric
V. Route Redistribution
1, a single IP routing protocol is the preferred embodiment the network management IP route
2, CiscoIOS can perform a plurality of routing protocols, each routing protocol and the routing protocols and services belong to the same autonomous system
3, CiscoIOS use routing retransmission distribution characteristics of different protocols to exchange routing information created (swap different protocols with different process IDs)
Redistributed into the OSPF domain route path type
- Type 1 is the external path (Type1 externalpath, E1)
- Type 2 external path (Type2 externalpath, E2)
NSSA area is OSPF RFC Addendum
Defines a special type of LSA 7
provide similar totally stubby area stub area and the characteristics
may be provided comprising ASBR
Six, OSPF among virtual link
In OSPF, link refers to the existence of a virtual connection to the backbone area through a non-backbone area links (virtual links to solve the problem it can not connect to other routers on the backbone of the regional area, but this requires a virtual link segment network is stable enough)
Virtual link object
- A region connected to the backbone through a region of non-backbone area
- A segment connected by a non-backbone area backbone region
Virtual link configuration rule and characteristics of
(1) must be arranged in a virtual link between two routers ABR
(2) is not a transfer region distal region
(3) virtual link stability depends on the stability of the region through which the
(4) by the virtual link help provide redundancy logic
VII given below configuration example of a virtual link
The first is the environment (simulation experiments Cisco equipment) in the GNS software version 1.3 win10 system, combined with the experimental configuration SecureCRT
(1) First, the topology is as shown in FIG.
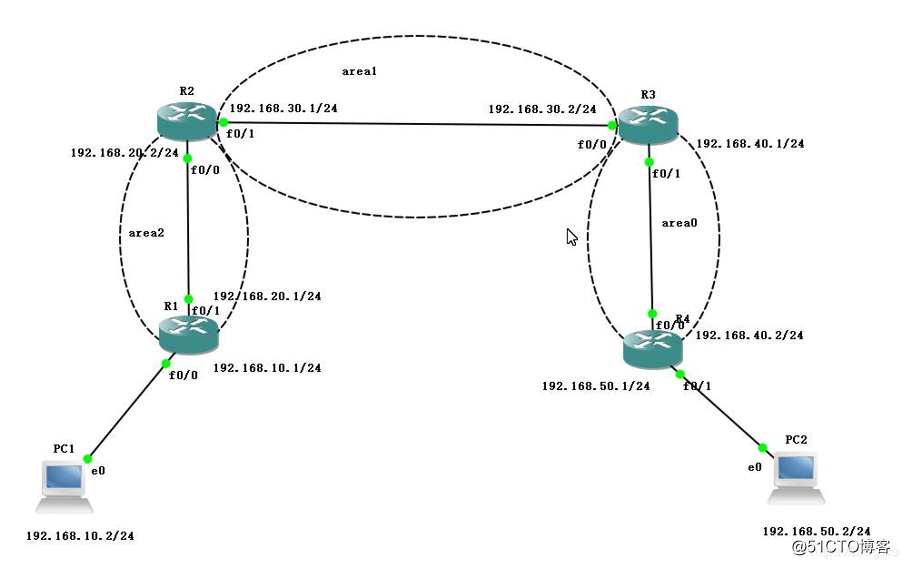
(2) configure the IP address of the routing
The OSPF protocol (3) configure the router
(4) an IP address configured VPC ping test package
(5) configure a virtual link operations
(6) Test of ping packets
The following is a list of all the configuration and operation of the specific experimental verification process and results
R1 configuration command list
conf t //进入全局模式
//配置R1路由器的ip地址
int f0/0
ip add 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
int f0/1
ip add 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0
no shut
ex //返回到全局模式(exit)
//进入环回接口配置固定ip地址
int loopback 0
ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
no shut
ex
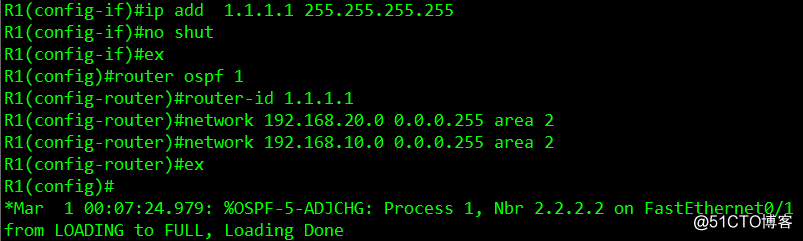
//配置OSPF协议
router ospf 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
network 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 2 //宣告自身网段信息
network 192.168.20.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
ex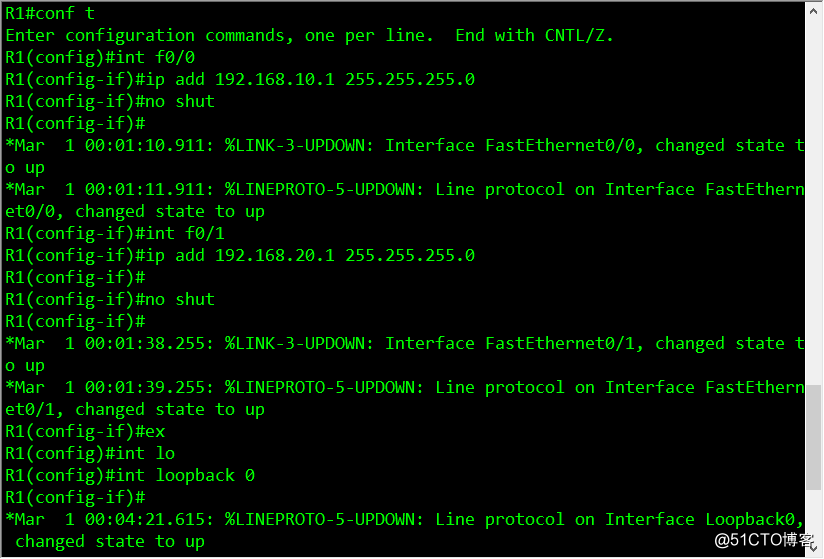
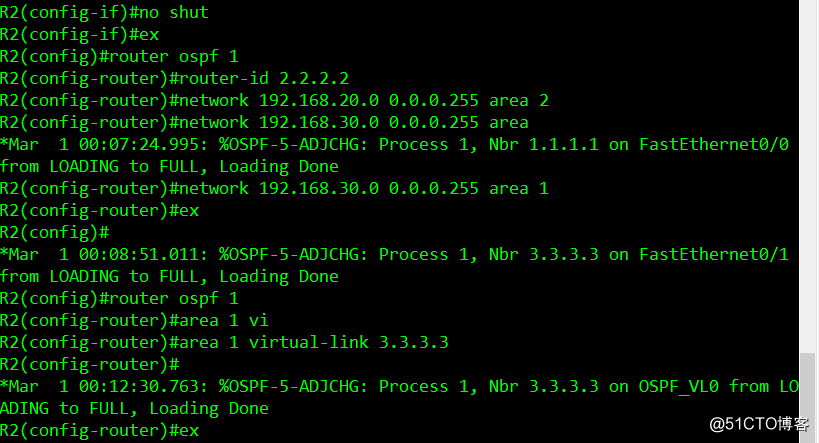
R2 configuration command list
conf t //进入全局模式
//配置R2路由器的ip地址
int f0/0
ip add 192.168.20.2 255.255.255.0
no shut
int f0/1
ip add 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
ex //返回到全局模式
//进入环回接口配置固定ip地址
int lo 0
ip add 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
no shut
ex
//配置OSPF协议
router ospf 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
network 192.168.20.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
network 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255 area 1 //宣告自身网段信息
ex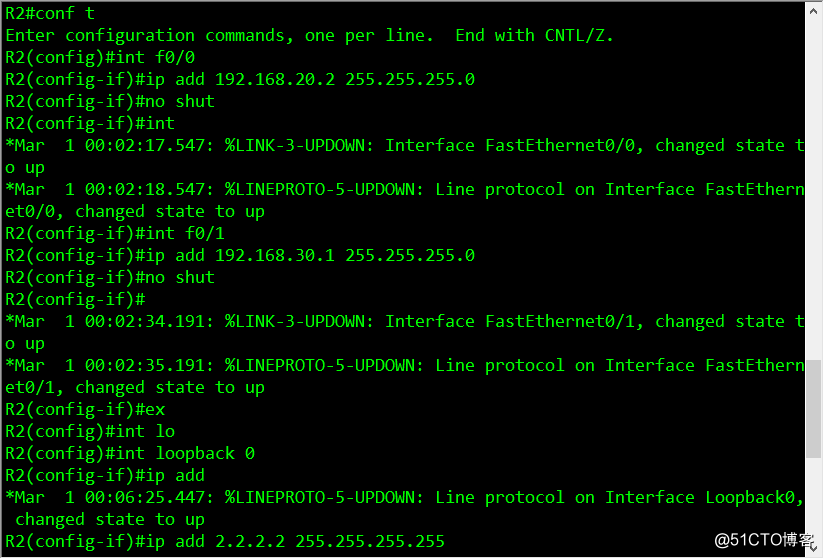
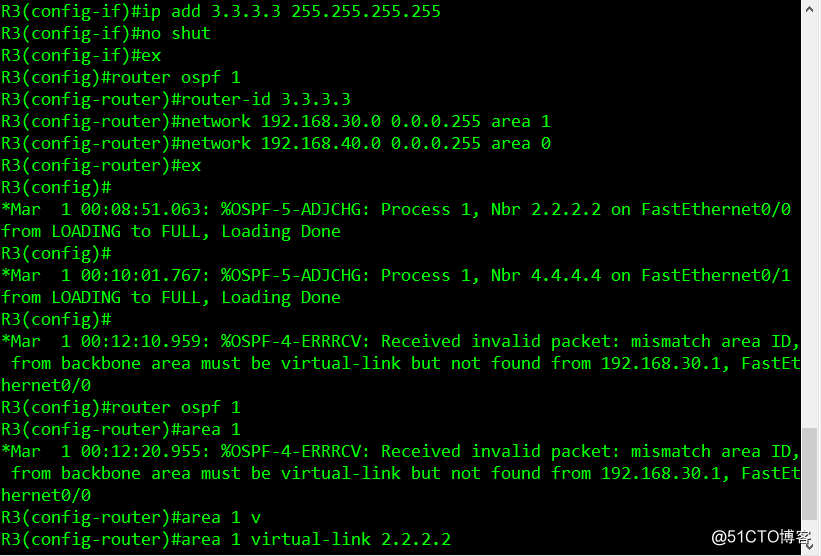
R3 configuration command list
conf t
int f0/0
ip add 192.168.30.2 255.255.255.0
no shut
ex
int f0/1
ip add 192.168.40.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
int lo 0
ip add 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
no shut
ex
router ospf 1
router-id 3.3.3.3
network 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
network 192.168.40.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
ex
router ospf 1
area 1 virtual-link 2.2.2.2
ex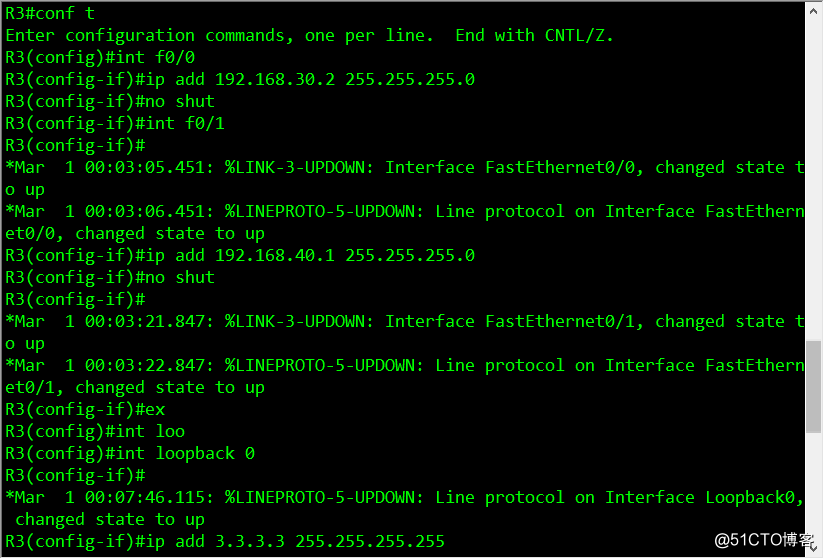
R4 configuration command list
conf t
int f0/0
ip add 192.168.40.2 255.255.255.0
no shut
int f0/1
ip add 192.168.50.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
ex
int lo 0
ip add 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
no shut
ex
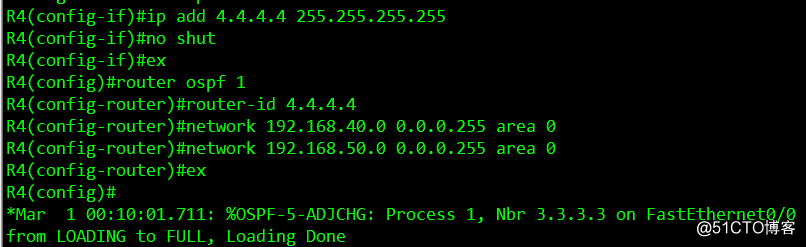
router ospf 1
router-id 4.4.4.4
network 192.168.40.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.50.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
ex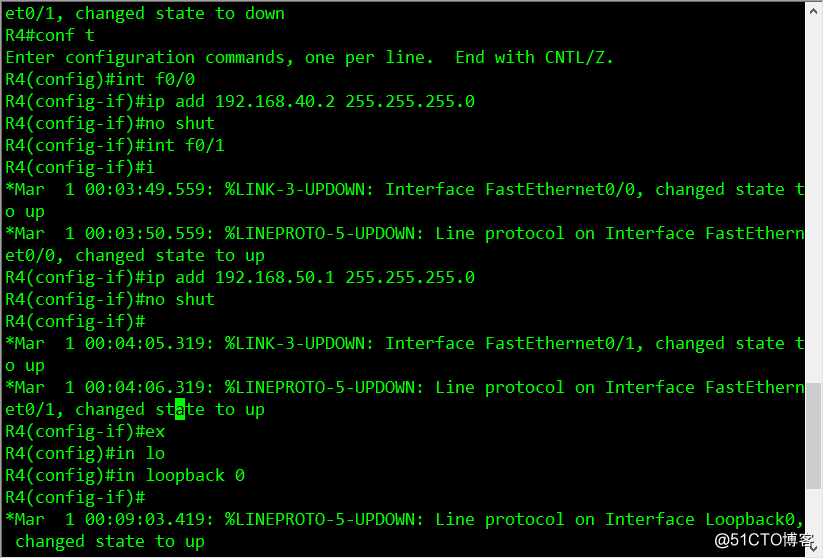
Host access results, not arranged in the virtual link when R2 and R3 are not communicating with each other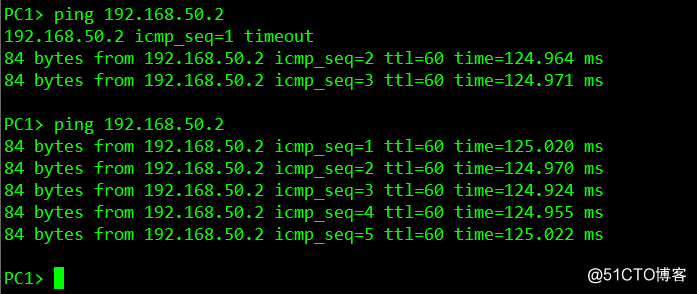
Eight, summary
For the first dynamic and static routes have a clear understanding, according to the article introduces the basic principles and understand the contents of a few pieces of the OSPF protocol, especially the establishment of related concepts DR, BDR router, regional backbone and regional standards and OSPF adjacencies (state 7), distributed appreciated that re-routing, virtual link two structures embodiment theories, including a simpler configuration experimental virtual link.
Theory can refer to the article! https://blog.51cto.com/14557673/2446363
configure OSPF protocol specific reference to the following experiments article! Thank you!