https://blog.csdn.net/chenhao0568/article/details/135296013?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
All tense formats in English and examples of the same sentence
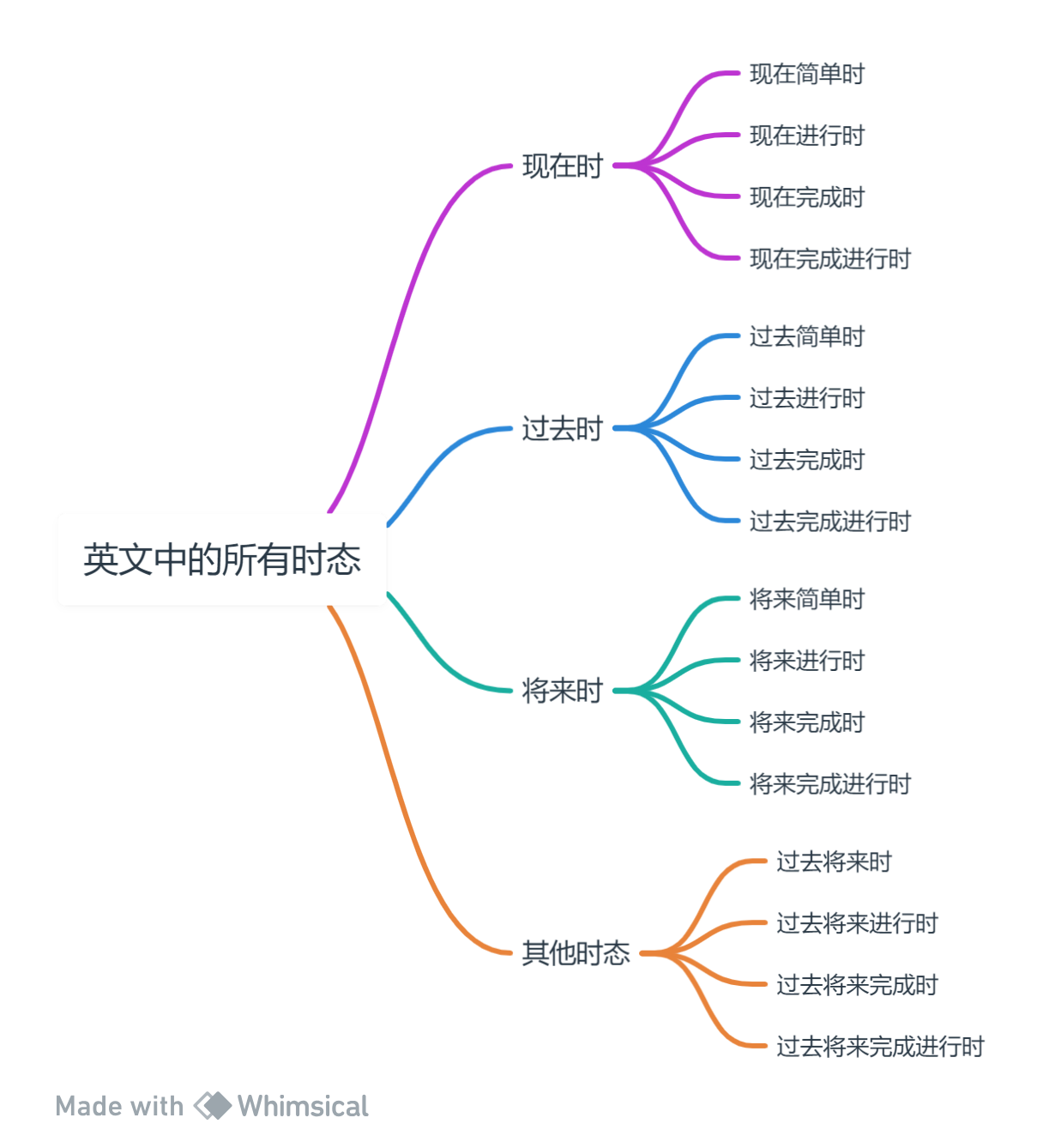
There are three main categories of tenses in English: past tense, present tense, and future tense. Each type of tense has four basic forms: simple (simple), progressive, perfect, and perfect progressive. There are 16 types in total (3*4 combinations + 4 types of past and future tenses). Below I will list the formats of these tenses and use the same sentence as an example to facilitate understanding.
-
present tense
- Simple present tense : [subject + verb base form (third person singular plus -s)] describes habitual actions, universal truths, states, or feelings.
- Example: She reads a book.
- Present continuous tense : [Subject + am/is/are + verb -ing] describes ongoing actions or temporary activities at the current stage.
- 示例:She is reading a book.
- Present perfect tense : [subject + has/have + past participle] describes actions that occurred in the past and have an impact on the present, or actions that started in the past and continue to the present.
- 示例:She has read a book.
- Present perfect continuous tense : [subject + has/have + been + verb -ing] emphasizes an action that started in the past and continues to the present, and may continue to happen.
- 示例:She has been reading a book.
- Simple present tense : [subject + verb base form (third person singular plus -s)] describes habitual actions, universal truths, states, or feelings.
-
past tense
- Simple past tense : [subject + past tense verb] describes an action or situation that occurred at a certain time in the past.
- Example: She read a book.
- Past continuous tense : [subject + was/were + verb -ing] describes an ongoing action at a specific time in the past.
- 示例:She was reading a book.
- Past perfect tense: [subject + had + past participle] indicates an action that was completed at a time in the past or before the action.
- 示例:She had read a book.
- Past perfect continuous tense: [Subject + had + been + verb -ing] emphasizes the action that was in progress until a certain point in the past.
- 示例:She had been reading a book.
- Simple past tense : [subject + past tense verb] describes an action or situation that occurred at a certain time in the past.
-
future tense
- Simple future tense: [subject + will/shall + verb base form] expresses actions or plans, plans, and predictions that will happen in the future.
- 示例:She will read a book.
- Future continuous tense: [Subject + will be + verb -ing] indicates an action that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future.
- 示例:She will be reading a book.
- Future perfect tense: [Subject + will have + past participle] expresses an action that has been completed before a certain point in the future.
- 示例:She will have read a book.
- Future perfect continuous tense : [Subject + will have been + verb -ing] emphasizes an action that will continue until a certain point in the future.
- 示例:She will have been reading a book.
- Simple future tense: [subject + will/shall + verb base form] expresses actions or plans, plans, and predictions that will happen in the future.
The use of these tenses depends on the time and duration of the action you want to express. For example, if you want to emphasize that an action is in progress, you can use the continuous tense; if you want to emphasize that an action has been completed, you can use the perfect tense.
-
Others
The past future tense is a slightly more complex tense used to express an action or state that was expected to occur before a certain point in the past. These tenses include past future tense, past future continuous tense, past future perfect tense, and past future perfect continuous tense. Here are the formats, uses, and examples of these tenses: -
Future-in-the-Past
- Format: [Subject + would/should + verb base form]
- Purpose: Used to express an action or state that is expected to occur at a certain point in time in the past.
- 示例:Yesterday, she said she would read a book.
-
Future Continuous in the Past
- Format: [Subject + would/should be + verb -ing]
- Purpose: Used to describe an action expected to be taking place at a specific time in the past.
- 示例:Yesterday, she said she would be reading a book.
-
Future Perfect in the Past
- Format: [Subject + would/should have + past participle]
- Purpose: Used to express an action that is expected to have been completed before a certain point in the past.
- 示例:Yesterday, she said she would have read a book.
-
Future Perfect Continuous in the Past
- Format: [Subject + would/should have been + verb -ing]
- Purpose: Used to describe actions that are expected to last for a period of time before a certain point in time in the past.
- 示例:Yesterday, she said she would have been reading a book.
These tenses are often used in indirect speech to express expectations or plans for the future at some point in the past. For example, "Yesterday, she said she would read a book" means that yesterday she said she planned to read a book (when she said this, reading was in the future).