Organizational Strategy and Informatization
- The relationship between organizational strategy and information strategy:
- In the face of a changing environment (the new economy or the challenge of global economic integration), enterprises must specify the correct organizational strategy
- Informatization strategy is an important part of organizational strategy and a guideline for organizational informatization
- The informatization strategy must obey the core idea of the organizational strategy and be formulated under the framework of the organizational strategy
- Organizational Strategy: The organization's comprehensive plan for achieving its goals and fulfilling its mission
- Organizational Strategic Structure:
- General strategy: the general direction of the organization
- Business strategy: the competition and cooperation strategy of a certain product or business unit to enhance the competitiveness in a specific field
- Functional strategy: Strategies formulated by functional departments such as marketing, manufacturing, R&D, and information technology, to help the organization and its subordinate business units achieve strategic goals through the optimization of overall capabilities
The overall strategy can be understood as the general direction, the business strategy can be understood as inter-departmental, and the functional strategy can be understood as the internal direction of a single department.
- Organizational strategy development process:
- Environmental analysis: starting from the internal and external advantages and disadvantages of the organization, through evaluating opportunities and risks, forming an organization's judgment on the environment
- Strategic decision-making: On the basis of environmental analysis, various information is synthesized to reach a strategic plan; the strategic decision-making plan of the organization includes:
- Clarify the mission of the organization; the mission refers to the nature and development direction of the organization (who and what to do)
- Determine achievable goals; goals are the results of actions (what tasks to accomplish in what time, what to do)
- Form an organization's strategic guidelines
- Formation and perfection of strategic planning: fine-tuning the formed strategic decisions for implementation
- Organizational strategy planning methods:
-
SWOT matrix method (Boston matrix)
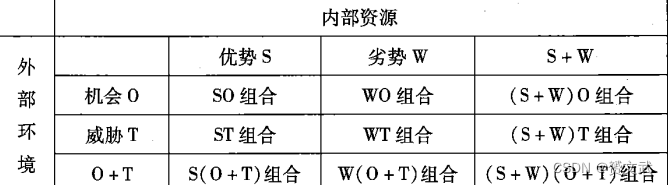
- Combination analysis: SO—use advantages to win external development opportunities, ST—use advantages to deal with external environmental threats, WO—create conditions, seize opportunities and reduce disadvantages, WT—avoid four combinations as much as possible
- Comprehensive analysis: a trade-off approach to deal with actual complex situations; reflected in the S+W column in the above figure
-
Porter's five forces model (five forces competition model)
-
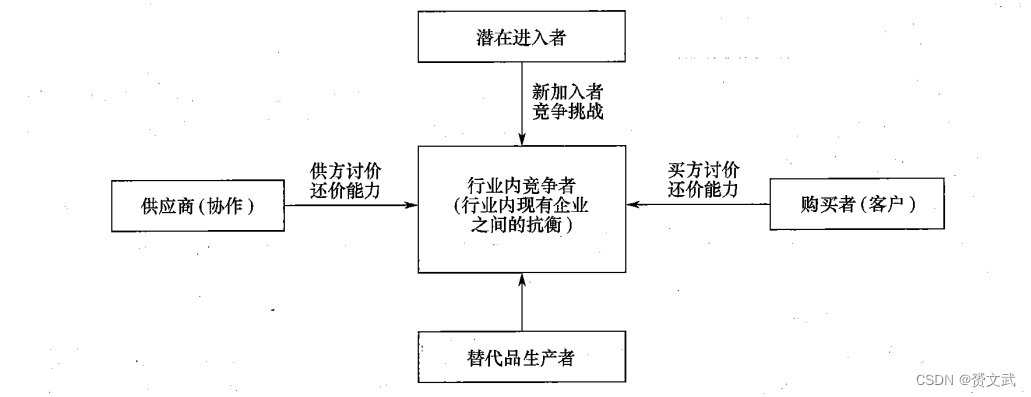
- Five kinds of competitiveness: Competitors in the same industry (existing competitors), potential competitors (potential entrants), bidding power of suppliers, bidding power of customers (buyers), substitute products (substitute producers)
- Porter's five forces model is suitable for strategic analysis of enterprises to develop new businesses
-
Value Chain Analysis
- Value chain: a dynamic process of creating value composed of all the different but interrelated production and operation activities of an enterprise
- Classification of value creation activities:
- Basic activities: substantive activities of production and operation; supply of raw materials, production and processing, storage and transportation of finished products, marketing and after-sales service, etc.
- Ancillary activities: Activities that provide services to primary activities; procurement management of enterprise inputs, technology development, human resource management, enterprise infrastructure
- The value chain analysis method is suitable for business process reorganization or strategic analysis
-
- The relationship between organizational strategy and informatization
- The purpose of organizational informatization is to support the realization of organizational strategy, which is the inevitable result of the development of organizational informatization to a certain stage. Informatization is a tool for organizational strategy formulation
- The effectiveness or efficiency of informatization has become an important factor affecting the formulation and realization of organizational strategies
- The implementation of organizational strategy requires the comprehensive support of information technology, and informatization is an important guarantee for the realization of organizational strategy
Information planning
Overview of information planning
- Problems in the development of information technology:
- Information island: a phenomenon in which data and information units are stored separately, cannot automatically realize information sharing and exchange, and need to rely on manual contact with the outside world; the lack of overall planning of the organization's informationization process results
- IT black hole: the phenomenon of no return on IT investment or a very low rate of return; lack of effective planning for organizational information work
- IT project quagmire: the implementation of the ERP system either exceeds the scheduled time or exceeds the budget; the lack of an effective plan for the implementation of information technology causes
- Informatization planning: the forward-looking overall arrangement of informatization work, which is the overall planning of the construction key points, steps, personnel technology and other elements in the process of informatization construction
- Embodying the Strategic Goals of the Informatization Strategy
- Business fit: IT investment matches the organization's vision and strategic goals
- Competitive advantage: through creating a new strategic business information system, to improve the competitive advantage of the survival and development of rental
- Resource Management: Optimizing the Allocation of Organizational Information Resources
- Technical architecture: clearly outline the information technology architecture that is compatible with organizational strategy, organizational structure, and business processes
- The role of information planning
- Effectively manage the organization's information assets, make overall arrangements for the organization's information resources, share resources, and avoid the emergence of "information islands" to the greatest extent
- Reduce the overall risk and investment cost of informatization construction
- Align information technology with organizational strategy to enhance organizational competitiveness
- Improve the communication and cooperation between the business department and the information department, so that the information work can be carried out in an orderly manner
- American scholar Nolan proposed the Nolan model (organizational IT application development is divided into six stages of initiation, expansion, control, integration, data management, and maturity)
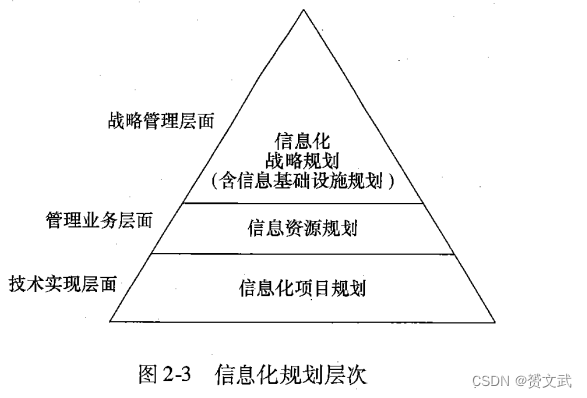
- Ways to carry out information planning
- Bottom-up; suitable for organizations with relatively stable business
- From top to bottom; suitable for organizations with a clear development strategy
- From the outside in; starting from factors external to the organization
- Blossom in the middle; start from the middle (management) of the organization
Informatization strategic planning
Strategies that describe the direction, focus, steps and measures of organizational informatization construction are called informatization strategies
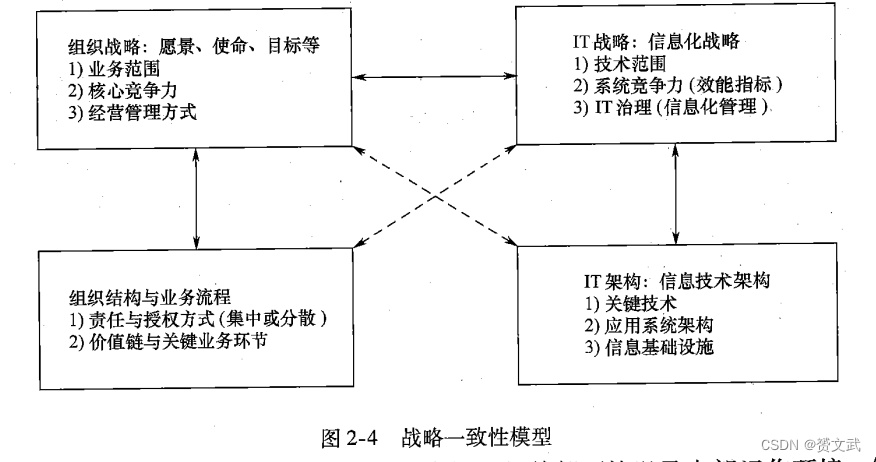
- Informatization strategy content
- Vision and structure of informatization construction
-
Identification of organizational strategy and core competitiveness
-
The direction of management improvement and business improvement
-
Function point and vision analysis of informatization
-
Analyze the status quo of informatization and evaluate the capabilities of informatization; systematically analyze the status quo of enterprise informatization from three aspects: people, process and technology
-
Analyze gaps and explore ideas for improvement
-
Business needs adjustment
-
Analyze information system architecture
-
- Project proposal selection and organization
- Project solution selection; combined with the informatization system architecture, clarify the overall timetable for informatization, the timing table for the construction of each subsystem, the category and scale of each subsystem, and clarify the selection procedures and standards for the hardware and software of each subsystem, Determine the IT project
- Project organization of informatization construction; relationship between enterprises and external service consultants, selection of internal personnel, selection of service consultants, formation of multi-level joint teams, and clarification of responsibilities around the key points of problems
- Informatization project planning
- Phase planning of informatization construction; clarify the scope, objectives, methods, dependencies, time and resource requirements of each construction phase
- Risk management quality monitoring strategy; analysis of possible psychological reactions in various stages and aspects; clear project quality monitoring, risk prevention and transformation methods
- The main implementation plan and training plan; comprehensively form the main implementation plan and the first-stage plan of the specific informatization project, and formulate the training plan on the basis of considering the training purpose, time, objects, and methods
- Vision and structure of informatization construction
- Informatization strategic planning steps
- Basic information research
- Research on informatization restrictions and development trends; the first is the status and trend of national economy and social informatization, the impact and impact of the development of information technology on the economy, and the second is to investigate the status and trends of industry informatization
- Organizational informatization demand research;; inside and outside the organization
- Research on basic conditions for informatization construction; favorable and unfavorable conditions for internal informatization construction
- Status assessment and problem analysis; analysis of challenges faced by informatization, problems to be solved by informatization, requirements of organizational development for informatization, etc.
- Design and formulate informatization strategic goals; determine the long-term goals, value, scale, and steps of informatization strategies, and form organizational informatization strategies
- Basic information research
- How to make an IT plan
- Strategic target set conversion method SST; proposed by William King, the steps include: identifying the strategic set of the organization (with or without a strategic plan), transforming the organizational strategic set into an organizational information strategy, and submitting the selection plan for review; advantages: it reflects the requirements of various groups , gives a structured method for transforming into information system goals, disadvantages: the focus is not prominent
- Value chain analysis; sees the organization as a collection of input, transformation, and output activities, each of which adds value to the final service or product
- Key success factor method CSF; advantages: intuitively guide senior managers to look at the relationship between the entire enterprise and information technology; main steps: understand enterprise goals, identify key success factors, identify performance indicators and standards, and identify data to measure performance
- Contents of IT strategy plan
- Environmental analysis; Informatization strategic planning basis
- Informatization strategy; organizational informatization guidelines
- Informatization system architecture design; organization informatization overall program
- Information technology standards; standards to be followed for specific technologies, products, methods and technical processes adopted in informatization
- Project assignment and management; clarify the functional modules at each level and the priority of the corresponding information tasks of each part, and make overall plans
Information Resource Planning
- The Emergence and Connotation of Information Resource Planning
- In the 1970s and 1980s, American scholar James Martin (J.Martin) proposed strategic data planning and pointed out that four data environments need to be identified and managed
- Data files; decentralized design by system analysts and programmers, formatted and non-standard data files accompanied by various fees for application design; simple implementation, high modification and maintenance costs
- Application database: Relatively independent normative text, with low degree of sharing
- Main database: After strict system analysis, the data model is established, the storage structure and processing program are relatively independent, the sharing is highly correlated, and the maintenance cost is low
- information retrieval system
- The root cause of the data processing crisis is that the system lacks comprehensive and effective high-level (strategic) data planning
- Martin et al. also emphasized the standardized management of data, that is, the establishment of an overall consistent data standard—consistent specifications for data naming, data attributes, data design, and data use.
- Information resource planning (IRP)——Comprehensive planning of the information needed for organizational management or business activities, from generation, acquisition to processing, storage, transmission and utilization
- In the 1970s and 1980s, American scholar James Martin (J.Martin) proposed strategic data planning and pointed out that four data environments need to be identified and managed
- Steps in Information Resource Planning
- Establish a working group responsible for information resource planning
- Analyze the functional domain and its business; the functional domain is also called the functional scope and the business scope, which refers to the main management activity areas. Enterprises or organizations of different industries and sizes have different functional domains.
- Standardize functional domain data
- Key Work of Information Resource Planning
- Business Analysis; Functional Areas - Business Processes - Business Activities
- Thematic database and data standardization; thematic database is an intensive database environment, which constitutes a data resource that is independent of specific applications
- Requires all source information to enter the system one at a time
- The stability of the theme database is guaranteed by the basic table. The basic table has three characteristics: atomicity (the data items are all data elements), normative (the data structure reaches three paradigms), and deductiveness (the data in the table can generate all output data. )
- A data element is the smallest indivisible unit of data
Informatization project planning
Informatization project planning: under the constraints of specific time, quality, funds, etc., a series of activities aimed at applying information technology; scientific informatization project specification refers to using project management methods and tools to Make a comprehensive plan for the scope, progress, cost, quality, etc.
- Scope plan; a description of the final deliverables and scope of work for the IT project. WBS - work structure breakdown tool
- Schedule; usually intelligence-intensive, labor-intensive projects, highly dependent on human resources. Gantt chart
- Cost planning: the management activity of estimating the costs incurred during project implementation under the premise of ensuring that the contract requirements such as project quality and construction period are met.
- Quality plan; developing quality plan considerations:
- Constraints on quality in the contract
- The quality policy of the enterprise; such as the quality of purchased raw materials and equipment; the quality assurance of project products; the guarantee of environment, monitoring and safety
- Quality inspection standards; various indicators of the final deliverables of the project. Such as the number of software defects, response time, maximum number of user visits, etc. (most important)
- Quality inspection process; what means or methods are used to check or prove whether a certain link of the project meets the established quality standards
- Management plan for quality inspection structure; release of quality inspection results, preservation of quality inspection documents, tracking plan for quality deviation rectification
Information organization
There are two key points in the work of informatization organization: 1. Establish a corresponding informatization organization structure in combination with the actual situation of the organization; 2. Establish the core soul of informatization organization work—the CIO mechanism
Information organization
- Definition of information organization: in a broad sense - the entire organization, in a narrow sense - the organization responsible for information management in the organization, also known as the information department IT
- Types of IT organizations
- Information department under the business unit
- Information department at the same level as the business department
- Department of Information under the direct leadership of the CEO
- Information department directly led by the Information Management Committee
- The functions of the information organization
- Informatization strategy formulation and management organization
- Information system development and management
- Information system operation maintenance and management
- Information resource management and service
- Job setting of information organization
- System R&D and Management Department; the most basic, main positions: system analysts and designers, programmers and testers
- System operation maintenance and management department; console operators, equipment administrators, data entry personnel, operation training teachers, data keeper, support personnel, etc.
- Information resource management and service department; the main positions include resource administrator, information officer, information service and technical support personnel
CIO mechanism
CIO is translated into Chinese as chief information officer, usually also known as information director, that is, a manager who is responsible for the construction, implementation and operation of organizational information technology, and is usually a member of the decision-making level of the organization
-
The background of CIO generation - the arrival of the information integration stage, and the enterprise enters the period of strategic information management
-
CIO Mechanism Composition An information management system
with the CIO as the core, the information technology department as the support, and the business department as the main body of informatization implementation- CIO; core, main responsibilities: participate in strategic decision-making and deploy specific work
- Informatization Management Committee; also known as the Informatization Leading Group, whose main responsibility is to be responsible for the planning of the entire informatization strategy of the enterprise
- Information department; information technology support center, enterprise information management center, main responsibilities: responsible for the collection, sorting, and statistics of information resources, providing relevant data information to decision-makers, construction, management and maintenance of information systems, and personnel training , provide emergency technical support services, etc.
- Information personnel in the business department; the main body of informatization implementation
-
Functions of CIOs
- Strategic adviser; does not decide the corporate strategy but can introduce the informatization results of the industry and competitors to the CEO and other senior managers of the company in an easy-to-understand form
- Strategic executor; from procurement to sales, from production to inventory, realize system integration in all aspects
- Intermediary of information dissemination; enables communication between many stakeholders inside and outside the enterprise
-
CIO capabilities
- Technical knowledge; implement corporate strategic ideas and intentions with best IT practices
- Management knowledge; it is beneficial to fundamentally grasp the essence of informatization construction, scientifically formulate informatization planning and carry out project management
- Communication skills
- Coordination
- project management ability