LeNet-5
LeNet-5 可以进行MNIST手写数字识别
-
网络基本结构
input (1) conv1 (6) pool1 (6) conv2 (16) pool2 (16) fc3 fc4 fc5 softmax
括号内的数字代表该层的通道数
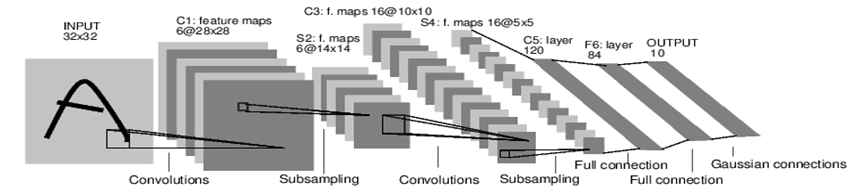
-
特点
- 卷积层-池化层被认为能够提取输入图像的平移不变特征
-
损失函数的曲线图如下:
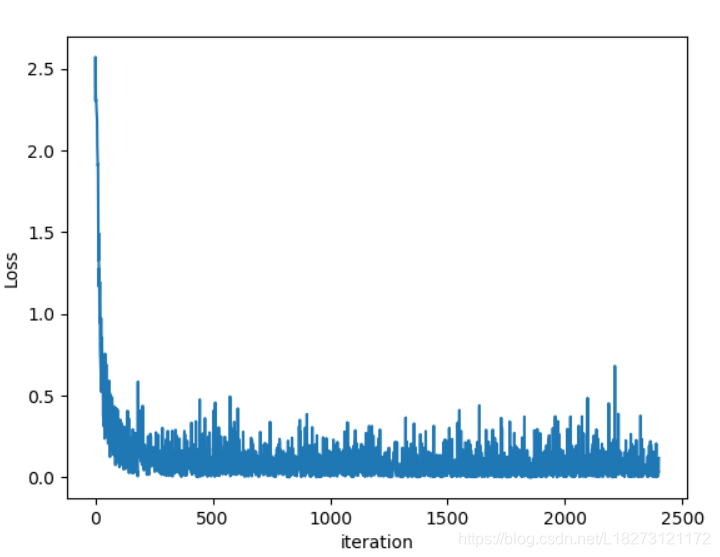
上代码
#CNN进行MNIST手写数字集的识别
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.data as data
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#Hyper parameters
LR = 0.01
EPOCH = 2
BATCH_SIZE = 50
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False
transforms = transforms.ToTensor()
#准备训练集和测试集
train_set = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./data/MNIST',
train=True,
transform=transforms,
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST
)
train_loader = data.DataLoader(
dataset=train_set,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle=True
)
#测试集只取2000个数据
test_set = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root = './data/MNIST',
train=False,
transform=transforms,
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST)
test_loader = data.DataLoader(
dataset=test_set,
batch_size= 2000,
shuffle=True
)
test_loader = iter(test_loader).next()
#搭建网络
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( #input shape: (1,28,28) (C,H,W)
nn.Conv2d(1,16,5,1,2), # ->(16,28,28)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2,2) # ->(16,14,14)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(16,32,5,1,2), # ->(32,14,14)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2,2) # ->(32,7,7)
)
# self.fc1 = nn.Linear(32*7*7,400) # ->(1,400)
# self.fc2 = nn.Linear(400,120) # ->(1,120)
# self.fc3 = nn.Linear(120,10) # ->(1,10)
self.fc = nn.Linear(32*7*7,10)
def forward(self,x):
# x = self.conv1(x)
# x = self.conv2(x)
# x = x.view(-1,32*7*7)
# x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
# x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
# x = self.fc3(x)
# return x
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(-1,32*7*7)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
net = Net()
#定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(),lr=LR,betas=(0.9,0.99))
#训练网络
loss_his = []
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for i,(inputs,labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
#inputs: 图像 Tensor(50,1,28,28)
#labels: 标签 Tensor(50)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs) #Tensor(50,10)
#loss是一个批次内所有样本loss的平均值
#loss是一个值(1维的Tensor)
loss = criterion(outputs,labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
loss_his.append(loss)
if (i % 50) == 0:
#每50批次计算一次loss和accuracy并输出
inputs,labels = test_loader
outputs = net(inputs)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs,1)
accuracy = (predicted == labels).sum().item()/labels.size(0)*100
print('Epoch: ',epoch,'|loss: %.3f'%(loss.data.numpy()),'|Accuracy: %.2f%%'%(accuracy))
print('Training Finished !')
#显示预测示例
images,labels = test_loader
images = images[:10]
labels = labels[:10]
outputs = net(images)
_,predicted = torch.max(outputs,1)
print('GroundTruth:\n',labels.numpy())
print('Predicted Types:\n',predicted.numpy())
plt.plot(loss_his)
plt.xlabel('iteration')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.show()
输出结果:
Epoch: 0 |loss: 2.310 |Accuracy: 9.55%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.372 |Accuracy: 87.20%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.260 |Accuracy: 94.40%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.037 |Accuracy: 95.90%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.077 |Accuracy: 96.75%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.072 |Accuracy: 95.80%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.049 |Accuracy: 96.75%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.087 |Accuracy: 96.25%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.104 |Accuracy: 97.10%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.197 |Accuracy: 96.65%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.033 |Accuracy: 97.20%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.196 |Accuracy: 97.10%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.015 |Accuracy: 96.95%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.047 |Accuracy: 96.95%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.119 |Accuracy: 97.30%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.075 |Accuracy: 96.60%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.081 |Accuracy: 97.35%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.048 |Accuracy: 96.50%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.025 |Accuracy: 97.20%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.024 |Accuracy: 96.65%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.004 |Accuracy: 97.30%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.023 |Accuracy: 97.25%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.004 |Accuracy: 97.50%
Epoch: 0 |loss: 0.170 |Accuracy: 97.90%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.024 |Accuracy: 96.95%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.181 |Accuracy: 96.95%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.036 |Accuracy: 97.65%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.082 |Accuracy: 97.75%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.026 |Accuracy: 97.30%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.127 |Accuracy: 97.75%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.220 |Accuracy: 96.80%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.412 |Accuracy: 97.55%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.166 |Accuracy: 97.70%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.022 |Accuracy: 97.40%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.047 |Accuracy: 97.75%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.002 |Accuracy: 97.55%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.023 |Accuracy: 97.45%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.046 |Accuracy: 97.80%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.084 |Accuracy: 97.35%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.090 |Accuracy: 97.75%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.005 |Accuracy: 97.85%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.188 |Accuracy: 97.40%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.068 |Accuracy: 97.80%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.023 |Accuracy: 97.40%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.114 |Accuracy: 97.45%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.040 |Accuracy: 97.80%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.072 |Accuracy: 97.40%
Epoch: 1 |loss: 0.004 |Accuracy: 98.05%
Training Finished !
GroundTruth:
[0 4 1 0 5 9 3 8 5 6]
Predicted Types:
[0 4 1 0 5 9 3 8 5 6]
AlexNet
-
网络基本结构:
input (3,224,224) conv1 (96,55,55) pool1 (96,27,27) conv2 (256,27,27) pool2 (256,13,13) conv3 (384,13,13) conv4 (384,13,13) conv5(256,13,13) pool (256,6,6) dropout fc6 (4096) dropout fc7 (4096) fc8 (1000) softmax
括号中表示每层激活值的shape,即(C, H, W)

-
特点
(1) 使用ReLU激活函数,解决梯度消失的问题
(2) 使用Dropout层来进行正则化,防止网络的过拟合
(3) 采用两个GPU进行并行运算
(4) 采用Local Response Normalization (LRN) 局部响应归一化层
上代码
#AlexNet网络结构
import torch
import torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as tranforms
import numpy as np
#搭建网络
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,num_classes):
super(Net,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # -> (224,224,3)
nn.Conv2d(3,96,11,4), # -> (55,55,96)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3,2) # -> (27,27,96)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(96,256,5,1,2), # -> (27,27,256)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3,2) # -> (13,13,256)
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256,384,3,1,1), # -> (13,13,384)
nn.ReLU()
)
self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(384,384,3,1,1), # -> (13,13,384)
nn.ReLU()
)
self.conv5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(384,256,3,1,1), # -> (13,13,256)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3,2), # -> (6,6,256)
nn.Dropout()
)
self.fc6 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(256*6*6,4096), # -> (4096)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout()
)
self.fc7 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(4096,4096), # -> (4096)
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc8 = nn.Linear(4096,num_classes)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
x = self.conv5#ssss(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0),6*6*256)
x = self.fc6(x)
x = self.fc7(x)
x = self.fc8(x)
return x
net = Net(1000)
print(net)
VGG-16
- 网络基本结构


2.特点
(1)卷积核采用小卷积核:3 x 3 卷积 2 x 2 池化
(2)卷积层都是same convolution,不改变图片的高和宽,只将通道数进行成倍增加
(3)池化层的参数设置: f = 2 ,s = 2,p = 0,所以图片经过池化后高和宽都减半
(4)参数量大:138milion 个参数,大部分集中在全连接层
GoogleNet
GoogleNet又叫InceptionNet,网络主要由Inception 模块组成
Inception 模块: 由若干个不同尺寸的过滤器组成,运用这些过滤器对输入进行卷积和池化,然后将输出结果按照深度拼接在一起形成输出层
-
网络基本结构
如下图


-
特点
(1)采用多个过滤器: 有1x1、3x3、5x5三种尺寸的卷积和3x3的池化,不需要人为的去设计过滤器的尺寸,相当于让网络自己去学习过滤器的种类和尺寸
(2)采用1x1卷积: 1x1卷积在不改变图片高和宽的前提下,可以压缩通道的数目,从而达到减少参数的数量和计算过程中的乘法次数

上代码
#GoogleNet网络结构
# GoogleNet也叫InceptionNet,整个网络有多个Inception 模块组成
#这里只搭建Inception模块
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class InceptionNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels):
super(InceptionNet,self).__init__()
self.branch1x1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,64,1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64,eps = 0.001),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.branch3x3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,96,1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(96, eps = 0.001),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(96, 128, 3, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128, eps=0.001),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.branch5x5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,16,1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(16, eps = 0.001),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(16,32,5,1,2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32, eps=0.001),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.branch_pool = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(3,1,1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels, eps=0.001),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,32,1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32, eps=0.001),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self,x):
branch_1x1 = self.branch1x1(x)
branch_3x3 = self.branch3x3(x)
branch_5x5 = self.branch5x5(x)
branch_pool= self.branch_pool(x)
branch = [branch_1x1,branch_3x3,branch_5x5,branch_pool]
x = torch.cat(branch,1)
return x
net = InceptionNet(3)
print(net)
ResNet
ResNet 提出 残差模块(Residual Block), 解决网络加深后训练难度增大的现象,有效缓解反向传播时由于深度过深导致的梯度消失现象,这使得网络加深之后性能不会变差。
-
基本结构
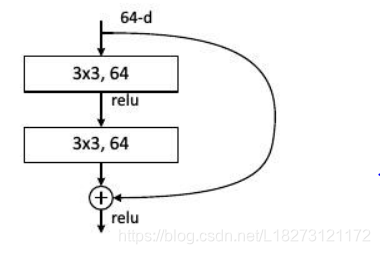
-
特点
(1)Residual Block: 随着深度的增加,模型在训练集上的正确率不会下降,而误差会一直减小,从而使得可以训练更深层的神经网络
(2)大量使用批处理化: Batch Normalization -
准确率
使用ResNet去进行CIFAR10数据集的图片分类
- 训练集上的accuracy:90.00 %
- 测试集上的accuracy:78.68 %
上代码
ResNet.py
#ResNet网络
#接口:ResNet(layers, num_classes)
# layers: 每个残差层中残差模块的数目
# num_classes:分类的类别数
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
#先搭建残差模块
class ResModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels,out_channels,stride = 1):
super(ResModule,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,3,stride,1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels, eps = 0.001),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(out_channels,out_channels,3,1,1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels, eps = 0.001)
)
#对residual进行卷积,保证residual和x 在各个维度上的值相等
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 3, stride, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels, eps=0.001)
)
def forward(self,x):
residual = x
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
if (x.size(1) != residual.size(1)) or (x.size(2) != residual.size(2)):
# x的在各个维度上的值发生变化时
residual = self.downsample(residual)
x = F.relu(x+residual)
return x
#再搭建残差网络
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,layers,num_classes):
#block: 残差模块类
# layers: 每个残差层中残差模块的数目
# num_classes:分类的类别数
super(ResNet,self).__init__()
self.in_channels = 16
self.conv = nn.Sequential( # -> (3,32,32)
nn.Conv2d(3,self.in_channels,3,1,1), # -> (16,32,32)
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channels, eps = 0.001),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.resLayer1 = self.make_layer(ResModule,layers[0],32,1) # -> (32,32,32)
self.resLayer2 = self.make_layer(ResModule, layers[1], 64,2) # -> (64,16,16)
self.resLayer3 = self.make_layer(ResModule, layers[2], 128,2) # -> (128,8,8)
self.maxPool = nn.MaxPool2d(2,2) # -> (128,4,4)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(128*4*4,500) # -> (500)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(500,120) # -> (120)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(120,num_classes) # -> (num_classes)
def make_layer(self,block,num_modules,out_channels,stride = 1):
#block: 残差模块类
#num_modules: 需要搭建的残差模块的数目
resLayer = []
resLayer.append(
block(self.in_channels,out_channels,stride)
)
for i in range(num_modules):
resLayer.append(
block(out_channels,out_channels)
)
self.in_channels = out_channels
return nn.Sequential(
*resLayer
)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.resLayer1(x)
x = self.resLayer2(x)
x = self.resLayer3(x)
x = self.maxPool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0),-1)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
classification_CIFAR10.py
#使用残差结构来图像分类
#数据集:CIFAR10
import ResNet
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.functional as F
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch.utils.data as data
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#超参数
EPOCH = 20
LR = 0.01
BATCH_SIZE = 60
DOWNLOAD = False
#准备数据集CIFAR10
def get_data():
#数据转换器
train_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5,0.5,0.5],[0.5,0.5,0.5])
# transforms.Scale(4),
# transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
# transforms.RandomCrop(32)
]
)
test_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5,0.5,0.5],[0.5,0.5,0.5])]
)
train_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root='./data/CIFAR10',
train = True,
download=DOWNLOAD,
transform = train_transform
)
train_loader = data.DataLoader(
dataset=train_set,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle=True
)
test_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root='./data/CIFAR10',
train = False,
download=DOWNLOAD,
transform = test_transform
)
test_loader = data.DataLoader(
dataset=test_set,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle=True
)
return train_loader,test_loader
#搭建网络
net = ResNet.ResNet([3,4,5],10)
net = net.cuda()
#定义优化器和损失函数
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
criterion = criterion.cuda()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr = LR, betas=(0.9,0.99))
train_loader,test_loader = get_data()
# #训练网络
# print('开始训练网络...\n')
# print('网络是否在cuda上训练:\n')
# print(next(net.parameters()).is_cuda)
# losses_his = []
# for epoch in range(EPOCH):
# for i, (images,labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
# images = images.cuda()
# labels = labels.cuda()
# optimizer.zero_grad()
# outputs = net(images)
# loss = criterion(outputs,labels)
# loss.backward()
# optimizer.step()
#
# losses_his.append(loss.item())
#
# if (i+1) % 50 == 0:
# #每隔50批次输出一次loss和accuracy
# _, predicted = torch.max(outputs,1)
# correct = (predicted == labels).sum().item()
# trian_accuracy = correct/labels.size(0)*100
#
# print('Epoch: %d | Batch: [%d,%d] | Loss: %.4f | Accuracy: %.2f %% '%(epoch,i+1,1000,loss.data.item(),trian_accuracy) )
# torch.save(net.state_dict(),'./models/ResNet_CIFAR10.pkl')
net.load_state_dict(torch.load('./models/ResNet_CIFAR10.pkl'))
#测试网络
num_correct = 0
total_test = 0
net.eval()
print('开始测试网络...')
with torch.no_grad():
for (images,labels) in test_loader:
images = images.cuda()
labels = labels.cuda()
outputs = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs,1)
num_correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
total_test += labels.size(0)
test_accuracy = num_correct/ total_test*100
print('Test set: Accuracy: %.2f %%'%(test_accuracy))
#输出部分测试用例
classes = ('plane','car','bird','cat','deer','dog','frog','horse','ship','truch')
num_show = 10 #展示的测试用例个数
#test_loader是个可迭代数据对象,每个元素包含两个张量。
# 一个是图像张量,其维度为:(60,3,32,32);一个是标签张量,其维度是:(60)
data = iter(test_loader).next()
images,labels = data #images是图片张量,维度:(60,3,32,32) labels是标签张量,维度:(60)
images = images[:num_show]
labels = labels[:num_show]
images = images.cuda()
labels = labels.cuda()
outputs = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs,1)
print('Ground Truth:')
print(' '.join('%5s'% classes[labels[i]] for i in range(num_show)))
print('Predicted Types:')
print(' '.join('%5s'% classes[predicted[i]] for i in range(num_show)))
#可视化
plt.plot(losses_his)
plt.title('Loss Function Curve')
plt.xlabel('iteration')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.show()
输出
Test set: Accuracy: 78.68 %
Ground Truth:
cat plane dog plane car deer dog truch car dog
Predicted Types:
cat plane dog plane car deer dog truch car cat
其他
#使用CNN进行图像分类
#数据集:CIFAR-10
import torch
import torch.nn as nn #构建网络的常用包
import torchvision #包含常用数据集包
import torchvision.transforms as transforms #数据格式转化包
#加载和标准化CIFAR10训练集和测试集
#先定义转换器
transforms = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.5,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0.5,0.5))])
#准备训练集和测试集
trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data/CIFAR_10', train = True,transform = transforms,download = False)
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset,batch_size = 4,shuffle = True)
print(trainset.data.size())
testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data/CIFAR_10', train = False,transform = transforms,download = False)
testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset,batch_size = 4,shuffle = True)
#共有10中类别的图片
classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat',
'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')
#预先展示一些训练图像
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #数据可视化
import numpy as np
#展示图像
def imshow(img):
img = img * 0.5 + 0.5 #逆标准化
np_img = img.numpy() #转numpy()对象
plt.imshow(np.transpose(np_img,(1,2,0))) #维度转换
#搭建网络
import torch.nn.functional as F
class cnnNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
#定义各个层,相当于一些处理函数
super(cnnNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3,6,5)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2,2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6,16,5)
self.L1 = nn.Linear(16*5*5,120)
self.L2 = nn.Linear(120,84)
self.L3 = nn.Linear(84,10)
def forward(self,x):
#定义前馈函数,反向传播函数被自动通过autograd定义
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(-1,16*5*5)
x = F.relu(self.L1(x))
x = F.relu(self.L2(x))
x = self.L3(x)
return x
net = cnnNet()
# 定义Loss函数和优化器
import torch.optim as optim
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() #Loss函数
opt_Momentum = optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr = 0.001,momentum=0.9)
# #训练网络
# for epoch in range(2):
# running_loss = 0.0
# for i, data in enumerate(trainloader,0):
# inputs, labels = data
# #开始迭代
# opt_Momentum.zero_grad()
# outputs = net(inputs)
# loss = criterion(outputs,labels)
# loss.backward()
# opt_Momentum.step()
#
# #显示每次训练结果
# running_loss += loss.item()
# if i % 1000 == 999:
# running_loss = running_loss/1000
# print('[%d, %d] loss: %.3f'%(epoch+1, i+1,running_loss))
# running_loss = 0.0
#
##print('网络模型训练完成')
# torch.save(net.state_dict(),'CNN.pkl')
#导入已经训练好的网络
net.load_state_dict(torch.load('./model/CNN.pkl'))
#在测试数据上测试网络
#Step 1: 个例测试,每组4张图片
dataIter = iter(testloader)
images ,labels = dataIter.next()
print('images的维度:\n',images.size())
print(labels)
imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(images))
print('测试用例:')
print('GroundTruth: ')
print(' '.join('%5s' % classes[labels[j]] for j in range(4)))
plt.show()
outputs = net(images)
_,predicted = torch.max(outputs.data,1)
print('Predicted Types: ')
print(' '.join('%5s' % classes[predicted[j]] for j in range(4)))
#STEP 2: 计算正确率
#总体的正确率
total = 0 #总样本数
correct = 0 #统计预测正确的个数
with torch.no_grad():
for data in testloader:
images, labels = data
outputs = net(images)
_,predicted = torch.max(outputs,1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (labels == predicted).sum().item()
accuracy = correct/total *100
print('Total accuracy: ')
print('Accuracy of CNN on the %s test images: %s'%(total,accuracy))
#每类图片的预测的正确率
class_total = list(0.for i in range(10))
class_correct = list(0. for i in range(10))
with torch.no_grad():
for data in testloader:
images, labels = data
outputs = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs,1)
c = (labels == predicted)
for i in range(4):
class_total[labels[i]] += 1
if c[i].item() == 1:
class_correct[labels[i]] += 1
print('Class accuracy: ')
for i in range(10):
print('Accuracy of %5s on the %5s test images: %s'%(classes[i],class_total[i],100*class_correct[i]/class_total[i]))
参考链接
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/94694563
