本篇内容有:如何根据坐标有目的的选择(where)、如何根据坐标有目的的更新(scatter_nd)、如何生成一个坐标系()
1.where
where针对的tensor是一个bool类型的tensor,即元素都由True或False组成,where(tensor)返回元素为True的位置
# 随机生成符合正态分布的[3,3]的tensor a = tf.random.normal([3,3]) print(a) # 将其对应的bool矩阵赋值给mask mask = a>0 print(mask) # 通过mask取到true对应的a的元素值 print(tf.boolean_mask(a,mask)) # 通过where获取true的位置 indices = tf.where(mask) print(indices) # 通过indices从a中取元素 print(tf.gather_nd(a,indices))
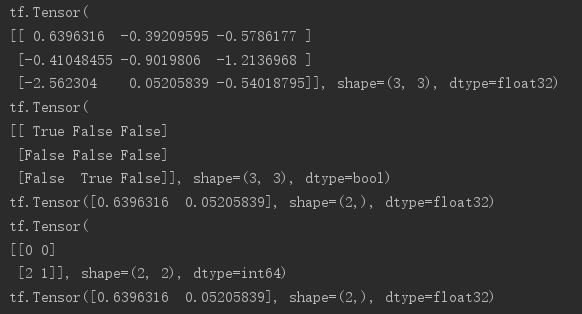
print(mask) # 定义A tensor元素全为1 A = tf.ones([3,3]) # 定义B tensor元素全为0 B = tf.zeros([3,3]) # 采样时取A上的true B上的false print(tf.where(mask,A,B))

2.scatter_nd
# 指定更新值的index indices = tf.constant([[4],[3],[1],[7]]) # 指定更新元素 updates = tf.constant([9,10,11,12]) # 指定底板shape shape = tf.constant([8]) print(tf.scatter_nd(indices,updates,shape))

# 指定更新元素的索引 indices = tf.constant([[0],[2]]) # 指定更新元素的值 updates = tf.constant([ [[5,5,5,5],[6,6,6,6],[7,7,7,7],[8,8,8,8]], [[5,5,5,5],[6,6,6,6],[7,7,7,7],[8,8,8,8]] ]) print(updates.shape) # 指定底板shape shape = tf.constant([4,4,4]) print(tf.scatter_nd(indices,updates,shape))
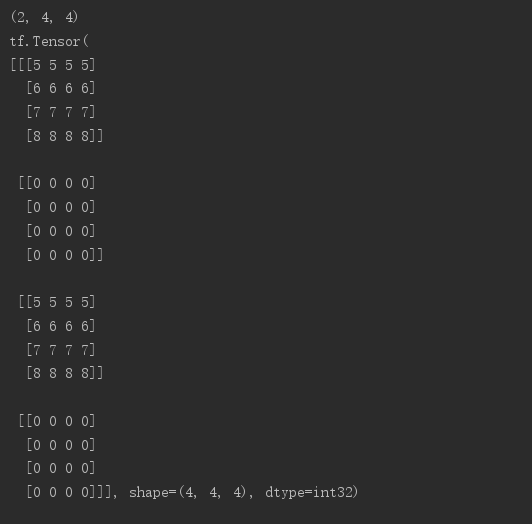
3.meshgrid
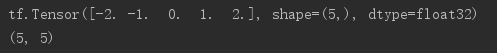
# 生成y轴,范围-2,2,元素个数5个 y = tf.linspace(-2,2,5) print(y) # 按照相同方式生成x轴 x = tf.linspace(-2,2,5) # 生成坐标系 points_x,points_y = tf.meshgrid(x,y) print(points_x.shape)
然后通过tf.stack方法,即可实现x和y的合并,从而生成点的坐标