一.什么是jsx
jsx是js的语法糖 它是js和html的组合使用
二.为什么用jsx语法
高效定义模版,编译后使用 不会带来性能问题
三.jsx语法转化为js语法
jsx语法通过babel转化为js语法 内部调用了createElement()方法
html标签
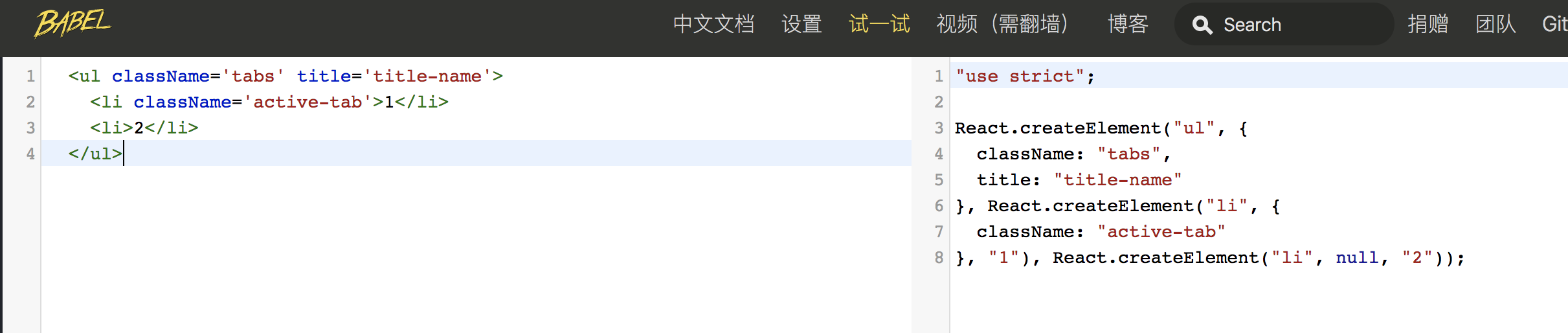
自定义组件

React.Fragment组件
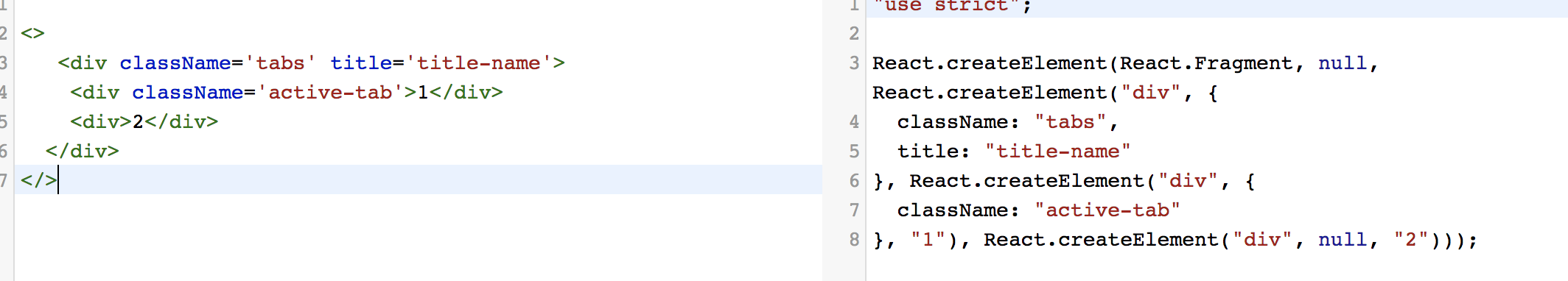
React.createElement(标签名type,属性对象config,子节点1,子节点2.....)
1.参数:标签名,属性对象,子节点 返回值:虚拟dom对象
2.标签名type类型:1.标签名字符串 2.组件(自定义组件:函数组件/class组件,react原生组件:React.Fragment等)
3.config对象:写在标签type上的属性集合
虚拟dom:
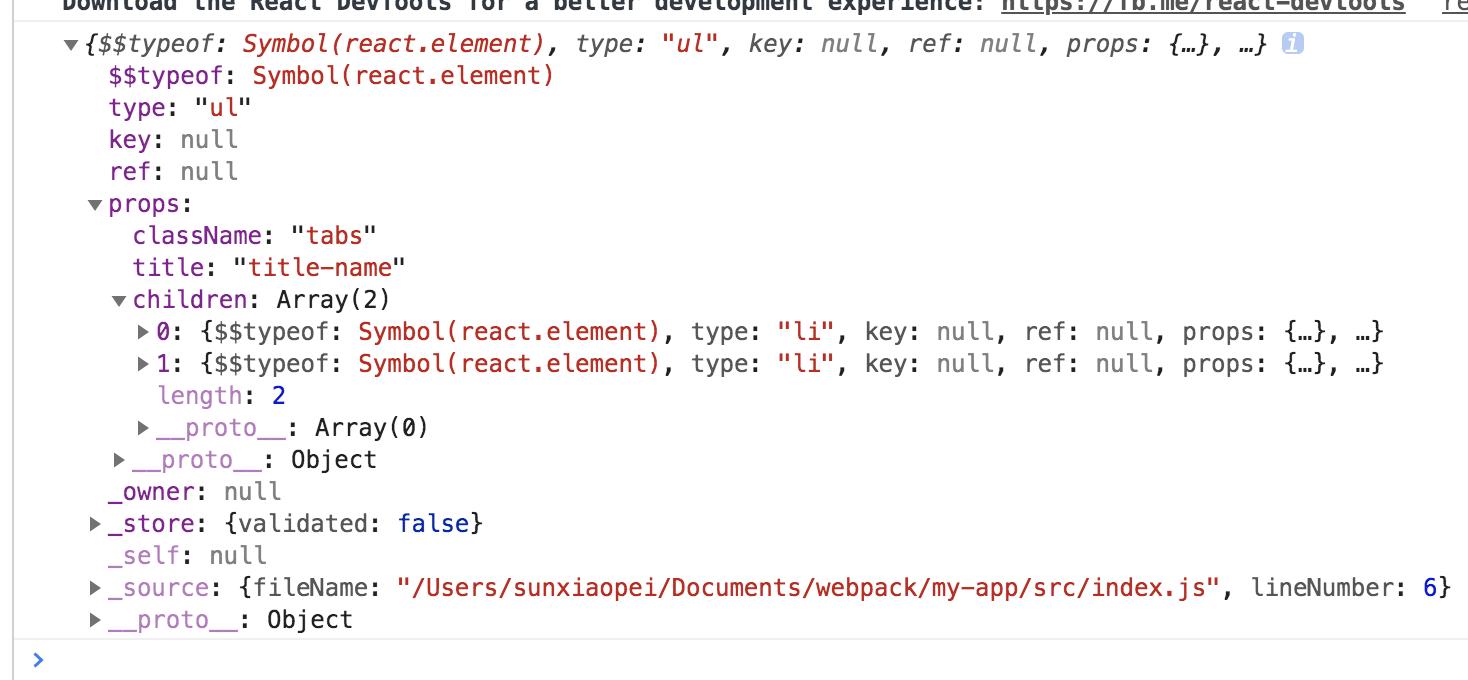
四,React.createElement(type,config,[...children])源码分析
作用:根据指定的第一个参数 创建一个react元素
源码解析:
function createElement(type, config, children) { var propName; //提取保留名称 var props = {}; var key = null; var ref = null; var self = null; var source = null; //标签的属性不为空时 说明标签有属性值 特殊处理:把key和ref赋值给单独的变量 if (config != null) { //有合理的ref if (hasValidRef(config)) { ref = config.ref; } //有合理的key if (hasValidKey(config)) { key = '' + config.key; } self = config.__self === undefined ? null : config.__self; source = config.__source === undefined ? null : config.__source; //config中剩余属性,且不是原生属性(RESERVED_PROPS对象的属性),则添加到新props对象中 for (propName in config) { if (hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) && !RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)) { props[propName] = config[propName]; } } } // Children can be more than one argument, and those are transferred onto // the newly allocated props object. //子元素数量(第三个参数以及之后参数都是子元素) var childrenLength = arguments.length - 2; if (childrenLength === 1) { props.children = children; } else if (childrenLength > 1) { var childArray = Array(childrenLength); //依次将children push到数组中 for (var i = 0; i < childrenLength; i++) { childArray[i] = arguments[i + 2]; } { //冻结array 返回原来的childArray且不能被修改 防止有人修改库的核心对象 冻结对象大大提高性能 if (Object.freeze) { Object.freeze(childArray); } } props.children = childArray; }
// Resolve default props (解决默认props) //如果defaultProps有值 则设置值 如果没有值取默认值 这个一般针对的是组件 而不是div这样的标签 if (type && type.defaultProps) { var defaultProps = type.defaultProps; for (propName in defaultProps) { if (props[propName] === undefined) { props[propName] = defaultProps[propName]; } } } { //一旦ref或者key存在 if (key || ref) { //如果type是组件的话 var displayName = typeof type === 'function' ? type.displayName || type.name || 'Unknown' : type; if (key) { defineKeyPropWarningGetter(props, displayName); } if (ref) { defineRefPropWarningGetter(props, displayName); } } } //props:1.config的属性值 2.children的属性(字符串/数组)3.default的属性值 return ReactElement(type, key, ref, self, source, ReactCurrentOwner.current, props); }
部分代码解析:
1.hasValidRef
作用:是否设置了ref属性
var hasOwnProperty = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty; function hasValidRef(config) { { if (hasOwnProperty.call(config, 'ref')) { //获取‘ref’属性的描述对象的取值器 var getter = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(config, 'ref').get; if (getter && getter.isReactWarning) { return false; } } } return config.ref !== undefined; }
(1) Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty()
//判断某一个属性是否在实例对象本身上,而不是在原型上 返回值:布尔值 let obj = { a: 1 }; obj.hasOwnProperty("a") //true obj.hasOwnProperty("toString")//false
(2) Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, props)
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj)
let obj = { foo: 123, get bar() { return '123' } }; //返回对象指定某一个属性的描述对象 Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, 'bar') //返回对象所有属性的描述对象 Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj)
返回值
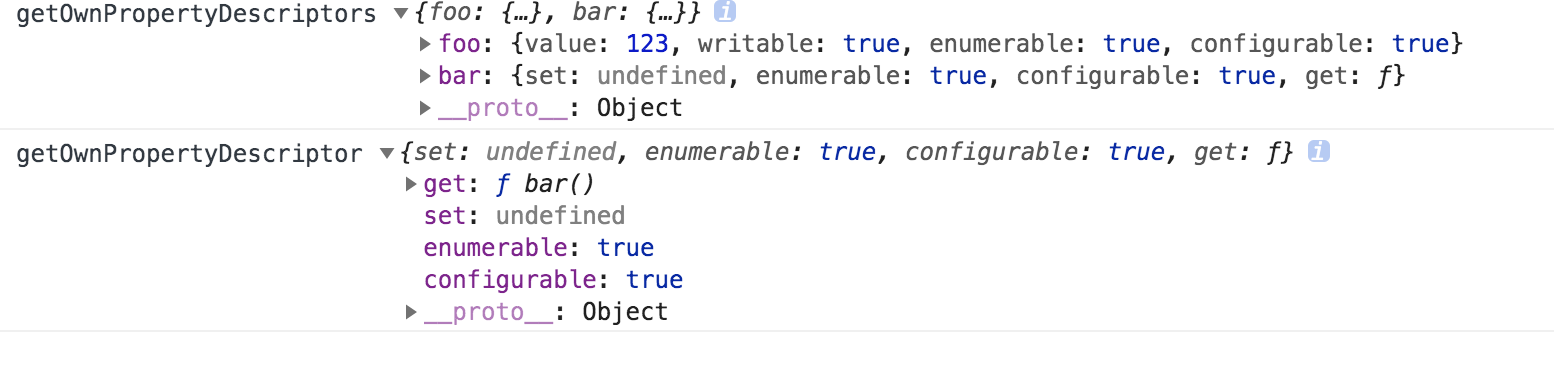
2.hasValidKey
作用:是否设置了key属性
function hasValidKey(config) { { if (hasOwnProperty.call(config, 'key')) { var getter = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(config, 'key').get; if (getter && getter.isReactWarning) { return false; } } } return config.key !== undefined; }
五,ReactElement源码分析
作用:返回一个虚拟dom对象
源码:
var ReactElement = function (type, key, ref, self, source, owner, props) { var element = { //因为react最终渲染dom时候,确保是react.createElement类型 需要判断$$typeof===REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE $$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE, // Built-in properties that belong on the element type: type, key: key, ref: ref, props: props, // Record the component responsible for creating this element. _owner: owner }; { // The validation flag is currently mutative. We put it on // an external backing store so that we can freeze the whole object. // This can be replaced with a WeakMap once they are implemented in // commonly used development environments. //WeakMap element._store = {}; // To make comparing ReactElements easier for testing purposes, we make // the validation flag non-enumerable (where possible, which should // include every environment we run tests in), so the test framework // ignores it. Object.defineProperty(element._store, 'validated', { configurable: false, enumerable: false, writable: true, value: false }); // self and source are DEV only properties. Object.defineProperty(element, '_self', { configurable: false, enumerable: false, writable: false, value: self }); // Two elements created in two different places should be considered // equal for testing purposes and therefore we hide it from enumeration. Object.defineProperty(element, '_source', { configurable: false, enumerable: false, writable: false, value: source }); if (Object.freeze) { //代码性能优化:将element的一些属性配置为不可配置 提高性能 Object.freeze(element.props); Object.freeze(element); } } return element;//返回虚拟dom对象 };