






def picread(filelist):
'''
读取狗的图片并转换成张量
'''
#1.构造文件队列
file_queue=tf.train.string_input_producer(filelist)
#2.构造阅读器去读取图片内容(默认读取一张图片)
value=reader.read(file_queue)
print(value)
#还是会报错的,对于读取的图片时间,一定要解码
#3.对于读取的图片数据进行解码
image=tf.image.decode_jpeg(value)
print(image)
#要多做一步,因为你的原图片大小不一样
image_resize=tf.image.resize_images(image,[200,200])
print(image_resize)
#注意:一定要把样本的形状固定 [200,200,3] 3是彩色的 不然不知道读多少个
image_resize.set_shape([200,200,3])
#4.进行批次处理
tf.train.batch([image_resize],batch_size=20,num_threads=1,capacity=20)
#20大小一样就行了 或者比他大
print(image_batch)
return image_batch
if __name__=="__main__":
#1.找到文件,放入列表
file_name=os.listdir("./data/dog/")
filelist=[os.path,join("./data/dog/",file) for file in file_name]
#print(file_name)
image_resize=picread(filelist)
#开启会话运行结果
with tf.Session as sess:
#定义一个线程协调器
coord=tf.train.Coordinator()
#开启读取文件的线程
threads=tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess,coord=coord)
#打印读取的内容
print(sess.run([image_resize]))
#回收子线程
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)

这个网站可以看一下



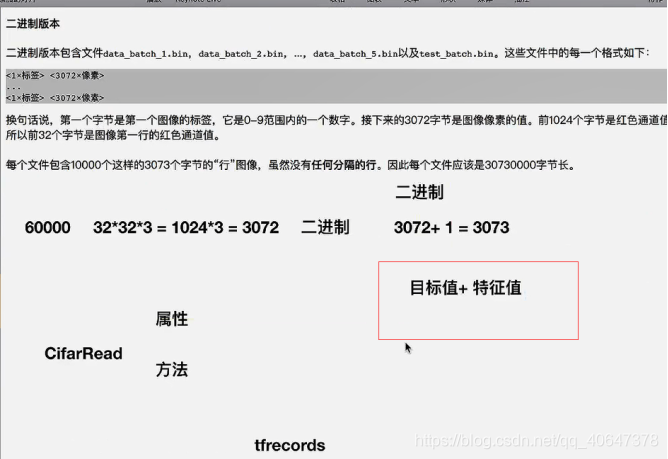
#知识点补充
1.TensorFlow 中 tf.app.flags.FLAGS 的用法介绍
https://blog.csdn.net/rosefun96/article/details/78923140
感觉说得很零碎,总结起来的话,tf.app.flags.DEFINE_xxx()就是添加命令行的optional argument(可选参数),而tf.app.flags.FLAGS可以从对应的命令行参数取出参数。 固定格式,记住就行了
2.uint8,表示变量是无符号整数,范围是0到255.
uint8是指0~2^8-1 = 255数据类型,一般在图像处理中很常见。
def picread(filelist):
#1.构造文件队列
file_queue=tf.train.string_input_producer(filelist)
#2.构造阅读器去读取图片内容,默认读取一张图片
value=reader.read(file_queue)
print(value)
#还是会报错的,一定要解码
#3.解码
image=tf.image.decode_jpeg(value)
print(image)
#要多一步处理图片的大小,统一大小
image_resize=tf.image.resize_images(image,[200,200])
print(image_resize)
image_resize.set_shape([200,200,3])
#4.进行批处理
tf.train.batch([image_resize],batch_szie=20,num_threads=1,capacity=20)
print(image_batch)
return image_batch
#定义cifar的数据等命令行参数
FLAGS=tf.app.flags.FLAGS
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string("cifar_dir","./data/cifar10/cifar-10-batches-bin","文件的目录")
class CifarRead(object):
#完成读取二进制文件,写进tfrecords,读取tfrecords
def_init_(self,filelist):
#文件列表
self.file_list=filelist
#定义读取的图片的一些属性
self.height=32
self.width=32
self.channel=3
#二进制文件每张图片的字节
self.label_bytes=1
self.image_bytes=self.height*self.width*self.channel
def read_and_decode(self):
#1.构造文件队列
file_queue=tf.train.string_input_producer(self.file_list)
#2.二进制文件读取器,这个图片选取的是二进制的内容
reader=tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(self.bytes)
key,value=reader.read(file_queue)
#3.解码内容,这个是二进制内容的解码了
label_image=tf.decode_raw(value,tf.unit8)
print(label_image)
#这个时候的他的输出的特征值是后面的目标值
#4.分割出图片和标签数据,特征值和目标值
#这个时候数据类型是 unit8,但是计算必须是unit类型
#[self.label.bytes]这个前面定义了是1
label=tf.cast(tf.slice(label_image,[0],[self.label.bytes],tf.int32))
#labelimage切的范围[0],[self.label_bytes]
image=tf.slice(label_image,[self.label_bytes],[self.image_bytes])
#告诉他第一个在哪里停止
#5.可以对图片的特征数据进行改变
image_reshape=tf.reshape(image,[self.height,self.width,self.channel])
print(label,image_reshape)
#6.批量处理数据
image_batch,label_batch=tr.train.batch([image_reshape,label],batch_size=10,num_threads=1,capacity=10)
print(image_batch,label_batch)
return image_batch,label_batch
if __name="__main__":
#1.找到文件,放入列表
file_name=os.listdir(FLAGS.cifar_dir)
#下面是只要bin结尾的数据
file_list=[os.path,join(FLAGS.cifar_dir,file) for file in file_name if file[-3:]="bin"]
#print(file_name)
cf=CifarRead(filelist)
#别忘了调用这个
image_batch,label_batch=cf.read_and_decode()
#开启会话运行结果
with tf.Session as sess:
#定义一个线程协调器
coord=tf.train.Coordinator()
#开启读文件的线程
threads=tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess,coord=coord)
#打印读取的内容
print(sess.run([image_batch,label_batch]))
#回收子线程
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)


比如二维码识别 电脑上的图片 与你识别出来的结果 存成类字典的格式



#批量处理数据
def write_to_tfrecords(self,image_batch,label_batch):
'''
将图片的特征值和目标值存进tfrecords
:param image_batch:10张照片的特征值
:param label_batch:10张照片的目标值
:return:None
'''
#1.构造一个TFRecord存储器
writer=tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(FLAGS.cifar_tfrecords)
#2.循环将所有样本都写入文件,每张图片样本都要构造example协议
for i in range(10):
#取出第i个图片数据的特征值和目标值
#image=image_batch[i] 这个获取的是一个类型,我们如果想要获得值
#再转换成字符串
image=image_batch[i].eval().tostring()
label=int(label_batch[i].eval()[0])
#构造一个样本的example
example=tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
"image":tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[image])),
"label":tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[label])),
}))
#写入单独的样本
writer.write(example.SerializeToString)
#关闭
writer.close()
return None
#因为是二进制,所以要解析,int就不用了
def read_from_tfrecords(self):
#1.构造文件队列
tf.train.string_input_producer([])
#2.构造文件阅读器,读取文件的内容
reader=tf.TFRecordReader()
key,value=reader.read(file_queue)
#3.解析 example
features=tf.parse_single_example(value,features={
#"image":tf.FixedLenFeature(shape,dtype)
#shape 我们一般指定为空 只有float32,int64,string
"image":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.string),
"label":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64),
})
#print(features["image"],features["label"])
#4.解码内容,如果读取的内容格式是string需要解码,如果是int64,float32不需要
image=tf.decode_raw(features["image"],tf.unit8)
#固定图片形状,方便批处理
image_reshape=tf.reshape(image,[self.height,self.width,self.channel])
label=tf.cast(features["label"],tf.int32)
print(image_reshape,label)
#进行批处理
image_batch,label_batch=tf.train.batch([image_reshape,label],batch_size=10,num_threads=1,capacity=10)
return(image_batch,label_batch)
#加上这个解析,后面的二进制读取和存储都不用了,有的前面加了#都是因为上一步
# 由于有一个eval 所以它一定要写进session
if __name__=="__main__":
#1.找到文件,放入列表 路径+名字 ---->列表当中
file_name=os.listdir(FLAGS.cifar_dir)
filelist=[os.path,join(FLAGS.cifar _dir,file) for file in file_name if file[-3:]="bin"]
#上面是只要bin结尾的数据
#print(file_name)
cf=CifarRead(filelist)
#别忘了调用这个
#image_batch,label_batch=cf.read_and_decode()
image_batch,label_batch=cf.read_from_tfrecords()
#开启会话运行结果
with tf.Session() as sess:
#定义一个线程协调器
coord=tf.train.Coordinator()
#开启读文件的线程
threads=tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess,coord=coord)
#存进tfrecords文件
#print("开始存储")
#cf.write_to_tfrecords(image_batch,label_batch)
#print("结束存储")
#打印读取的内容
print(sess.run([image_batch,label_batch]))
#回收子线程
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
