问题描述:3个人玩斗地主,一共54张牌,编写代码完成洗牌、发牌、看牌。
问题分析:1.准备牌:一共有54张牌,2张牌特殊(大王、小王),剩下52张牌是数字1-9和♥、♦、♠、♣的两两组合。
用一个list来存放花色,另一个list来存放数字,两两组合得到52个值,加上大王和小王,一共54个值,放在HashMap的value中,牌的索引为key。
2.洗牌:将索引按顺序放在一个list中,用集合Collections中的shuffle(list)方法,将索引的顺序打乱,索引对应的value也被打乱。
3.发牌:一人一张轮流发牌,一共3个人,用集合索引%3,发给3个人,最后剩下的3张牌是庭牌。
4.排序:用Collections的sort(list)方法,给每个玩家的牌和庭牌排序。
5.看牌:遍历玩家和庭牌的list,获取到Map的key值,通过key找到value。
代码编写:
package cn.itcast.cases2; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; public class DouDiZhu { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.准备牌 //创建一个Map集合,装牌的索引和对应的值 HashMap<Integer,String> poker=new HashMap<>(); //创建一个list,装有序的牌的索引 ArrayList<Integer> pokerIndex=new ArrayList<>(); //如果集合内容不再改变,可以使用List.of(Element e...)直接定义 //创建一个list,装牌的花色 List<String> colors=List.of("♥","♦","♠","♣"); //创建一个list,装牌的数字 List<String> numbers=List.of("2","A","K","Q","J","10","9","8","7","6","5","4","3"); //把大王和小王放进poker集合中,注意index也要放进对应的集合中 int index=0; poker.put(index,"大王"); pokerIndex.add(index); index++; poker.put(index,"小王"); pokerIndex.add(index); index++; //循环嵌套遍历两个集合,将组成的值一个一个放进poker的value中 for(String color:colors){ for(String num:numbers){ String val=num+ color; poker.put(index,val); pokerIndex.add(index); index++; } } //2.洗牌 Collections.shuffle(pokerIndex); //3.发牌 //定义4个集合,存储玩家牌和庭牌的索引 ArrayList<Integer> player1=new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Integer> player2=new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Integer> player3=new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Integer> tingpai=new ArrayList<>(); //用取余法发牌 for (int i = 0; i < pokerIndex.size(); i++) { Integer in=pokerIndex.get(i); if(i>=51){ //给庭牌发牌 tingpai.add(in); } else if(i%3==0){ //给1号玩家发牌 player1.add(in); } else if(i%3==1){ //给2号玩家发牌 player2.add(in); } else{ //给3号玩家发牌 player3.add(in); } } //4.排序,sort方法默认为升序排序 Collections.sort(player1); Collections.sort(player2); Collections.sort(player3); Collections.sort(tingpai); //5.看牌 //调用看牌的方法: lookPoker("双双",poker,player1); lookPoker("盛杭",poker,player2); lookPoker("阿竹",poker,player3); lookPoker("庭牌",poker,tingpai); } //定义一个看牌的方法,提高代码的复用性 //方法的参数为name:看牌者的名字,poker:扑克牌,list:牌的索引的集合 public static void lookPoker(String name,HashMap<Integer,String> poker,ArrayList<Integer> list){ //输出玩家名字,不换行 System.out.print(name+": "); //取出牌的索引 for(Integer key:list){ String val=poker.get(key); System.out.print(val+" "); } //输出所有值后换行 System.out.println(); } }
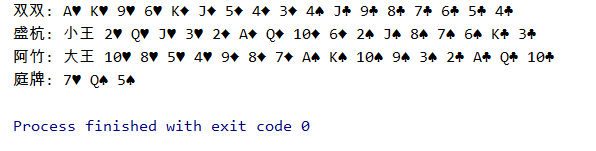
结果展示: