版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
1. Binary Classification
logistic regression is an algorithm to implement binary classification.
2. The saving mode of image
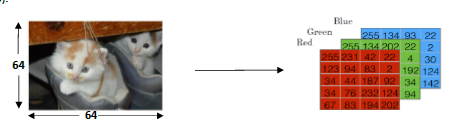
A RGB image is saved as a three-dimension array(64*64*3) in the computer. We reshape the array into a new vector X(64*64*64*3, 1), which is the input of the neural network. We define the height of X as . The goal of Binary Classification is to learn a classifier. This is a process from 'x' to 'y'. 'y' is 0 or 1.
3. Notation
(1) (x,y) : a single training example.
(2) x: -dimensional feature vector.
(3) y: The label of x. (0 or 1 represents if it is the object we want to detect.)
(4) m training example:.
(5) m_train: (
)
(6) m_test: (
)