题目下载【传送门】
第1题
简述:支持向量机的实现
(1)线性的情况:
第1步:读取数据文件,可视化数据:
% Load from ex6data1:
% You will have X, y in your environment
load('ex6data1.mat');
% Plot training data
plotData(X, y);
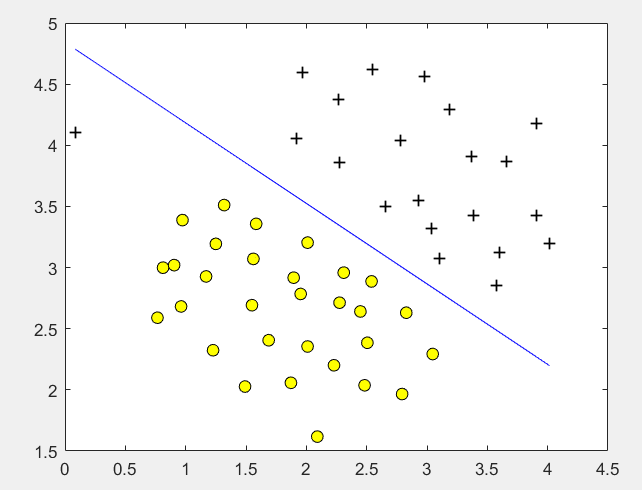
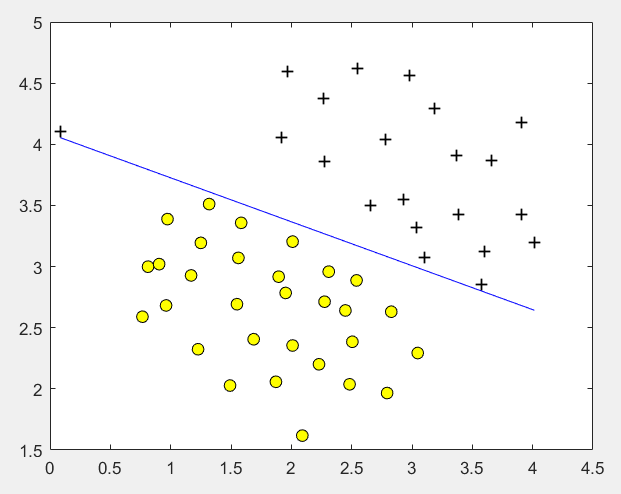
第2步:设定不同的C,使用线性核函数训练SVM,并画出决策边界:
C = 1; model = svmTrain(X, y, C, @linearKernel, 1e-3, 20); visualizeBoundaryLinear(X, y, model);
运行结果:
C = 1时:
C = 1000时:
其中线性核函数linearKernel:
function sim = linearKernel(x1, x2) % Ensure that x1 and x2 are column vectors x1 = x1(:); x2 = x2(:); % Compute the kernel sim = x1' * x2; % dot product end
高斯核函数gaussianKernel实现:
function sim = gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma) % Ensure that x1 and x2 are column vectors x1 = x1(:); x2 = x2(:); % You need to return the following variables correctly. sim = 0; sim = exp(-norm(x1 - x2) ^ 2 / (2 * (sigma ^ 2))); end
训练模型svmTrain函数(实现较为复杂,直接调用):
function [model] = svmTrain(X, Y, C, kernelFunction, ...
tol, max_passes)
%SVMTRAIN Trains an SVM classifier using a simplified version of the SMO
%algorithm.
% [model] = SVMTRAIN(X, Y, C, kernelFunction, tol, max_passes) trains an
% SVM classifier and returns trained model. X is the matrix of training
% examples. Each row is a training example, and the jth column holds the
% jth feature. Y is a column matrix containing 1 for positive examples
% and 0 for negative examples. C is the standard SVM regularization
% parameter. tol is a tolerance value used for determining equality of
% floating point numbers. max_passes controls the number of iterations
% over the dataset (without changes to alpha) before the algorithm quits.
%
% Note: This is a simplified version of the SMO algorithm for training
% SVMs. In practice, if you want to train an SVM classifier, we
% recommend using an optimized package such as:
%
% LIBSVM (http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/)
% SVMLight (http://svmlight.joachims.org/)
%
%
if ~exist('tol', 'var') || isempty(tol)
tol = 1e-3;
end
if ~exist('max_passes', 'var') || isempty(max_passes)
max_passes = 5;
end
% Data parameters
m = size(X, 1);
n = size(X, 2);
% Map 0 to -1
Y(Y==0) = -1;
% Variables
alphas = zeros(m, 1);
b = 0;
E = zeros(m, 1);
passes = 0;
eta = 0;
L = 0;
H = 0;
% Pre-compute the Kernel Matrix since our dataset is small
% (in practice, optimized SVM packages that handle large datasets
% gracefully will _not_ do this)
%
% We have implemented optimized vectorized version of the Kernels here so
% that the svm training will run faster.
if strcmp(func2str(kernelFunction), 'linearKernel')
% Vectorized computation for the Linear Kernel
% This is equivalent to computing the kernel on every pair of examples
K = X*X';
elseif strfind(func2str(kernelFunction), 'gaussianKernel')
% Vectorized RBF Kernel
% This is equivalent to computing the kernel on every pair of examples
X2 = sum(X.^2, 2);
K = bsxfun(@plus, X2, bsxfun(@plus, X2', - 2 * (X * X')));
K = kernelFunction(1, 0) .^ K;
else
% Pre-compute the Kernel Matrix
% The following can be slow due to the lack of vectorization
K = zeros(m);
for i = 1:m
for j = i:m
K(i,j) = kernelFunction(X(i,:)', X(j,:)');
K(j,i) = K(i,j); %the matrix is symmetric
end
end
end
% Train
fprintf('\nTraining ...');
dots = 12;
while passes < max_passes,
num_changed_alphas = 0;
for i = 1:m,
% Calculate Ei = f(x(i)) - y(i) using (2).
% E(i) = b + sum (X(i, :) * (repmat(alphas.*Y,1,n).*X)') - Y(i);
E(i) = b + sum (alphas.*Y.*K(:,i)) - Y(i);
if ((Y(i)*E(i) < -tol && alphas(i) < C) || (Y(i)*E(i) > tol && alphas(i) > 0)),
% In practice, there are many heuristics one can use to select
% the i and j. In this simplified code, we select them randomly.
j = ceil(m * rand());
while j == i, % Make sure i \neq j
j = ceil(m * rand());
end
% Calculate Ej = f(x(j)) - y(j) using (2).
E(j) = b + sum (alphas.*Y.*K(:,j)) - Y(j);
% Save old alphas
alpha_i_old = alphas(i);
alpha_j_old = alphas(j);
% Compute L and H by (10) or (11).
if (Y(i) == Y(j)),
L = max(0, alphas(j) + alphas(i) - C);
H = min(C, alphas(j) + alphas(i));
else
L = max(0, alphas(j) - alphas(i));
H = min(C, C + alphas(j) - alphas(i));
end
if (L == H),
% continue to next i.
continue;
end
% Compute eta by (14).
eta = 2 * K(i,j) - K(i,i) - K(j,j);
if (eta >= 0),
% continue to next i.
continue;
end
% Compute and clip new value for alpha j using (12) and (15).
alphas(j) = alphas(j) - (Y(j) * (E(i) - E(j))) / eta;
% Clip
alphas(j) = min (H, alphas(j));
alphas(j) = max (L, alphas(j));
% Check if change in alpha is significant
if (abs(alphas(j) - alpha_j_old) < tol),
% continue to next i.
% replace anyway
alphas(j) = alpha_j_old;
continue;
end
% Determine value for alpha i using (16).
alphas(i) = alphas(i) + Y(i)*Y(j)*(alpha_j_old - alphas(j));
% Compute b1 and b2 using (17) and (18) respectively.
b1 = b - E(i) ...
- Y(i) * (alphas(i) - alpha_i_old) * K(i,j)' ...
- Y(j) * (alphas(j) - alpha_j_old) * K(i,j)';
b2 = b - E(j) ...
- Y(i) * (alphas(i) - alpha_i_old) * K(i,j)' ...
- Y(j) * (alphas(j) - alpha_j_old) * K(j,j)';
% Compute b by (19).
if (0 < alphas(i) && alphas(i) < C),
b = b1;
elseif (0 < alphas(j) && alphas(j) < C),
b = b2;
else
b = (b1+b2)/2;
end
num_changed_alphas = num_changed_alphas + 1;
end
end
if (num_changed_alphas == 0),
passes = passes + 1;
else
passes = 0;
end
fprintf('.');
dots = dots + 1;
if dots > 78
dots = 0;
fprintf('\n');
end
if exist('OCTAVE_VERSION')
fflush(stdout);
end
end
fprintf(' Done! \n\n');
% Save the model
idx = alphas > 0;
model.X= X(idx,:);
model.y= Y(idx);
model.kernelFunction = kernelFunction;
model.b= b;
model.alphas= alphas(idx);
model.w = ((alphas.*Y)'*X)';
end
(2)非线性的情况:
第1步:读取数据文件,并可视化数据:
% Load from ex6data2:
% You will have X, y in your environment
load('ex6data2.mat');
% Plot training data
plotData(X, y);
第2步:使用高斯核函数进行训练:
% SVM Parameters C = 1; sigma = 0.1; % We set the tolerance and max_passes lower here so that the code will run % faster. However, in practice, you will want to run the training to % convergence. model= svmTrain(X, y, C, @(x1, x2) gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma)); visualizeBoundary(X, y, model);
运行结果:
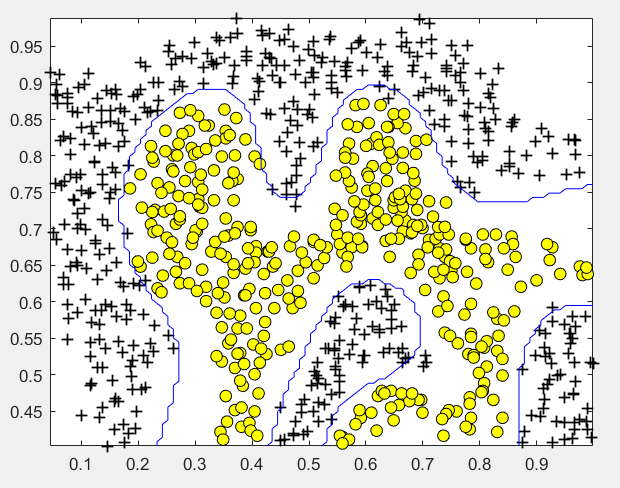
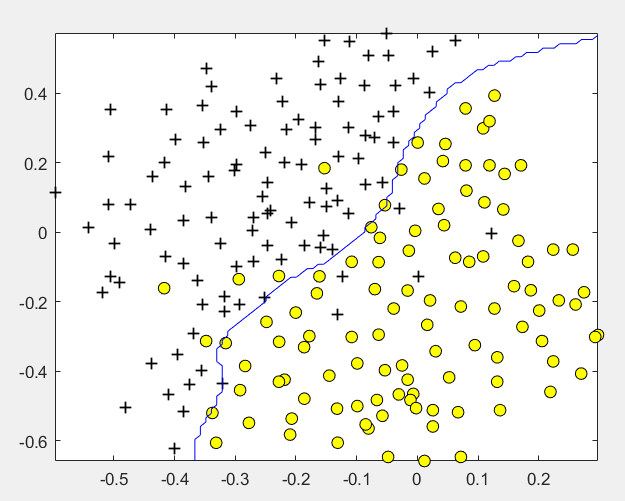
(3)非线性情况2:
第1步:读取数据文件,并可视化数据:
% Load from ex6data3:
% You will have X, y in your environment
load('ex6data3.mat');
% Plot training data
plotData(X, y);
第2步:尝试不同的参数,选取准确率最高的:
% Try different SVM Parameters here [C, sigma] = dataset3Params(X, y, Xval, yval); % Train the SVM model= svmTrain(X, y, C, @(x1, x2) gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma)); visualizeBoundary(X, y, model);
其中datasetParams函数:
function [C, sigma] = dataset3Params(X, y, Xval, yval)
% You need to return the following variables correctly.
C = 1;
sigma = 0.3;
C_vec = [0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, 30];
sigma_vec = [0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, 30];
m = size(C_vec, 2);
error_val = 1;
for i = 1:m
for j = 1:m
model= svmTrain(X, y, C_vec(i), @(x1, x2) gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma_vec(j)));
pred = svmPredict(model, Xval);
error_temp = mean(double(pred ~= yval));
if error_temp < error_val
C = C_vec(i);
sigma = sigma_vec(j);
error_val = error_temp;
end
end
end
end
其中svmPredict函数:
function pred = svmPredict(model, X)
% Check if we are getting a column vector, if so, then assume that we only
% need to do prediction for a single example
if (size(X, 2) == 1)
% Examples should be in rows
X = X';
end
% Dataset
m = size(X, 1);
p = zeros(m, 1);
pred = zeros(m, 1);
if strcmp(func2str(model.kernelFunction), 'linearKernel')
% We can use the weights and bias directly if working with the
% linear kernel
p = X * model.w + model.b;
elseif strfind(func2str(model.kernelFunction), 'gaussianKernel')
% Vectorized RBF Kernel
% This is equivalent to computing the kernel on every pair of examples
X1 = sum(X.^2, 2);
X2 = sum(model.X.^2, 2)';
K = bsxfun(@plus, X1, bsxfun(@plus, X2, - 2 * X * model.X'));
K = model.kernelFunction(1, 0) .^ K;
K = bsxfun(@times, model.y', K);
K = bsxfun(@times, model.alphas', K);
p = sum(K, 2);
else
% Other Non-linear kernel
for i = 1:m
prediction = 0;
for j = 1:size(model.X, 1)
prediction = prediction + ...
model.alphas(j) * model.y(j) * ...
model.kernelFunction(X(i,:)', model.X(j,:)');
end
p(i) = prediction + model.b;
end
end
% Convert predictions into 0 / 1
pred(p >= 0) = 1;
pred(p < 0) = 0;
end
运行结果:
第2题
概述:实现垃圾邮件的识别
第1步:读取数据文件,对单词进行处理:
% Extract Features
file_contents = readFile('emailSample1.txt');
word_indices = processEmail(file_contents);
% Print Stats
fprintf('Word Indices: \n');
fprintf(' %d', word_indices);
fprintf('\n\n');
单词处理过程:
去除符号、空格、换行等;
识别出邮箱、价格、超链接、数字,替换为特定单词;
在关键词列表中找出出现的关键词,并标记为出单词编号.
function word_indices = processEmail(email_contents)
% Load Vocabulary
vocabList = getVocabList();
% Init return value
word_indices = [];
% ========================== Preprocess Email ===========================
% Find the Headers ( \n\n and remove )
% Uncomment the following lines if you are working with raw emails with the
% full headers
% hdrstart = strfind(email_contents, ([char(10) char(10)]));
% email_contents = email_contents(hdrstart(1):end);
% Lower case
email_contents = lower(email_contents);
% Strip all HTML
% Looks for any expression that starts with < and ends with > and replace
% and does not have any < or > in the tag it with a space
email_contents = regexprep(email_contents, '<[^<>]+>', ' ');
% Handle Numbers
% Look for one or more characters between 0-9
email_contents = regexprep(email_contents, '[0-9]+', 'number');
% Handle URLS
% Look for strings starting with http:// or https://
email_contents = regexprep(email_contents, ...
'(http|https)://[^\s]*', 'httpaddr');
% Handle Email Addresses
% Look for strings with @ in the middle
email_contents = regexprep(email_contents, '[^\s]+@[^\s]+', 'emailaddr');
% Handle $ sign
email_contents = regexprep(email_contents, '[$]+', 'dollar');
% ========================== Tokenize Email ===========================
% Output the email to screen as well
fprintf('\n==== Processed Email ====\n\n');
% Process file
l = 0;
while ~isempty(email_contents)
% Tokenize and also get rid of any punctuation
[str, email_contents] = ...
strtok(email_contents, ...
[' @$/#.-:&*+=[]?!(){},''">_<;%' char(10) char(13)]);
% Remove any non alphanumeric characters
str = regexprep(str, '[^a-zA-Z0-9]', '');
% Stem the word
% (the porterStemmer sometimes has issues, so we use a try catch block)
try str = porterStemmer(strtrim(str));
catch str = ''; continue;
end;
% Skip the word if it is too short
if length(str) < 1
continue;
end
for i = 1:size(vocabList),
if strcmp(str, vocabList(i)),
word_indices = [word_indices i];
end
end
% Print to screen, ensuring that the output lines are not too long
if (l + length(str) + 1) > 78
fprintf('\n');
l = 0;
end
fprintf('%s ', str);
l = l + length(str) + 1;
end
% Print footer
fprintf('\n\n=========================\n');
end
其中读取关键字列表函数:
function vocabList = getVocabList()
%% Read the fixed vocabulary list
fid = fopen('vocab.txt');
% Store all dictionary words in cell array vocab{}
n = 1899; % Total number of words in the dictionary
% For ease of implementation, we use a struct to map the strings => integers
% In practice, you'll want to use some form of hashmap
vocabList = cell(n, 1);
for i = 1:n
% Word Index (can ignore since it will be = i)
fscanf(fid, '%d', 1);
% Actual Word
vocabList{i} = fscanf(fid, '%s', 1);
end
fclose(fid);
end
第3步:对关键字进行特征值标记,出现的关键词标记为1:
% Extract Features
features = emailFeatures(word_indices);
% Print Stats
fprintf('Length of feature vector: %d\n', length(features));
fprintf('Number of non-zero entries: %d\n', sum(features > 0));
其中emailFeatures函数为:
function x = emailFeatures(word_indices)
% Total number of words in the dictionary
n = 1899;
% You need to return the following variables correctly.
x = zeros(n, 1);
for i = 1:size(word_indices),
x(word_indices(i)) = 1;
end
end
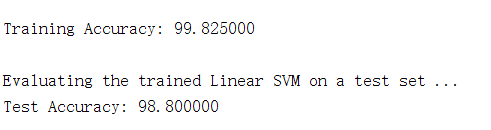
第4步:使用线性核函数进行训练,并分别计算训练集准确率和测试集准确率:
% Load the Spam Email dataset
% You will have X, y in your environment
load('spamTrain.mat');
fprintf('\nTraining Linear SVM (Spam Classification)\n')
fprintf('(this may take 1 to 2 minutes) ...\n')
C = 0.1;
model = svmTrain(X, y, C, @linearKernel);
p = svmPredict(model, X);
fprintf('Training Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
% Load the test dataset
% You will have Xtest, ytest in your environment
load('spamTest.mat');
fprintf('\nEvaluating the trained Linear SVM on a test set ...\n')
p = svmPredict(model, Xtest);
fprintf('Test Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == ytest)) * 100);
运行结果:
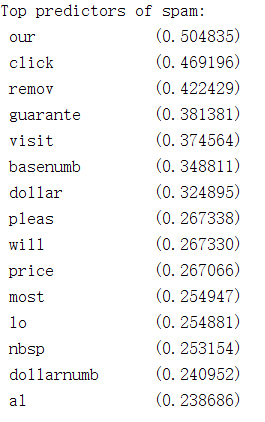
第5步:找出最高权重的关键词:
% Sort the weights and obtin the vocabulary list
[weight, idx] = sort(model.w, 'descend');
vocabList = getVocabList();
fprintf('\nTop predictors of spam: \n');
for i = 1:15
fprintf(' %-15s (%f) \n', vocabList{idx(i)}, weight(i));
end
fprintf('\n\n');
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
运行结果: