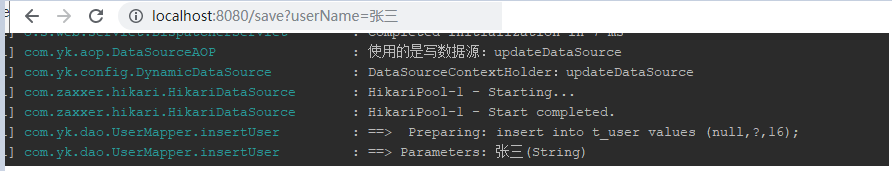
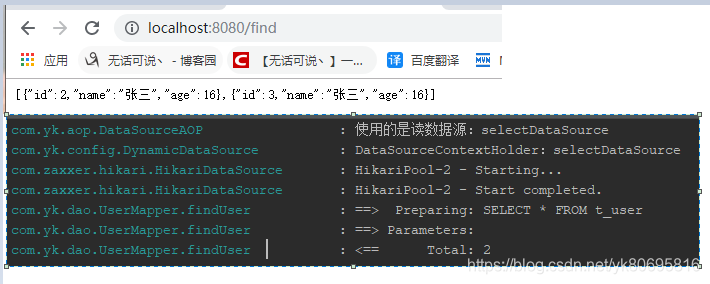
Mycat环境搭建
Mycat下载地址
Mycat文档
接着前篇已经搭建好的Mysql主从复制开始
# 解压
tar -zxvf Mycat-server-1.6.7.1-release-20190627191042-linux.tar.gz
#启动
./bin/mycat start
#关闭
./bin/mycat stop
#启动日志
tail -f logs/wrapper.log
#运行日志
tail -f logs/mycat.log查看,wrapper.log。出现下图就是启动成功了

然后进入conf目录下
配置schema.xml
<mycat:schema xmlns:mycat="http://io.mycat/">
<!-- test是mycat的逻辑库名称,链接需要用的 -->
<schema name="test" checkSQLschema="false" sqlMaxLimit="100" dataNode="noed-1"></schema>
<!-- database 是MySQL数据库的库名 -->
<dataNode name="noed-1" dataHost="dbHost1" database="test" />
<dataHost name="dbHost1" maxCon="1000" minCon="10" balance="3" writeType="0" dbType="mysql" dbDriver="native" switchType="1" slaveThreshold="100">
<heartbeat>select user()</heartbeat>
<!-- 可以配置多个主从 -->
<writeHost host="hostM1" url="192.168.100.131:3306" user="root" password="root">
<!-- 可以配置多个从库 -->
<readHost host="hostS2" url="192.168.100.132:3306" user="root" password="root" />
</writeHost>
</dataHost>
</mycat:schema>配置server.xml
<mycat:server xmlns:mycat="http://io.mycat/">
<!-- 读写都可用的用户 -->
<user name="root" defaultAccount="true">
<property name="password">root</property>
<property name="schemas">test</property>
</user>
<!-- 只读用户 -->
<user name="user">
<property name="password">user</property>
<property name="schemas">test</property>
<property name="readOnly">true</property>
</user>
</mycat:server>| 属性 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 客户端连接端口号 | 8066 |
| server. xmI | Mycat的配置文件,设置账号、参数等 |
| schema. xmI | Mycat对应的物理数据库和数据库表的配置 |
| rule. xmI | Mycat分片(分库分表)规则 |


在配置完这些的时候出现了一个问题,就是当逻辑库名与实际Mysql的库名不同时。连接Mycat中间件的时候就会找不到表,也无法创建表。后来查看Mycat.log看到了,到真实库中查询的时候也是携带了逻辑库的名称。也不清除是哪里配置不对。后来就把逻辑库和真实的Mysql库名改成一致了


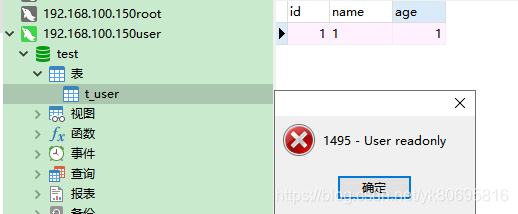
可以看到配置的读用户是无法写数据的。
Springboot实现读写分离
- 数据源连接配置
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
####写数据源
update:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.100.150:8066/test
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
###读数据源
select:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.100.150:8066/test
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: user
password: user
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource- 配置读写数据源
DataSourceConfig.java
/**
* 配置读写数据源
*/
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Bean(name = "selectDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.select")
public DataSource dataSource1() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "updateDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.update")
public DataSource dataSource2() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
}
- 保存本地数据源
DataSourceContextHolder.java
/**
* 保存本地多数据源
*/
@Component
@Lazy(false)
public class DataSourceContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
// 设置数据源类型
public static void setDbType(String dbType) {
contextHolder.set(dbType);
}
public static String getDbType() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
public static void clearDbType() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
}
- 配置动态切换数据源类
DynamicDataSource.java
/**
* 该类继承自 AbstractRoutingDataSource 类,在访问数据库时会调用该类的 determineCurrentLookupKey() 方法获取数据库实例的 key
*/
@Component
@Primary
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DynamicDataSource.class);
@Autowired
@Qualifier("selectDataSource")
private DataSource selectDataSource;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("updateDataSource")
private DataSource updateDataSource;
/**
* 返回生效的数据源名称
*/
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
logger.info("DataSourceContextHolder:{}", DataSourceContextHolder.getDbType());
return DataSourceContextHolder.getDbType();
}
/**
* 配置使用的数据源信息,如果不存在就使用默认的数据源
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
Map<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("selectDataSource", selectDataSource);
map.put("updateDataSource", updateDataSource);
//注册数据源
setTargetDataSources(map);
setDefaultTargetDataSource(updateDataSource);
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
- APO配置
DataSourceAOP.java
@Aspect
@Component
@Lazy(false)
// Order设定AOP执行顺序 使之在数据库事务上先执行
@Order(0)
public class DataSourceAOP {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DataSourceAOP.class);
//横切点
@Before("execution(* com.yk.service.*.*(..))")
public void process(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
if (methodName.startsWith("get") || methodName.startsWith("count") || methodName.startsWith("find")
|| methodName.startsWith("list") || methodName.startsWith("select") || methodName.startsWith("check")) {
DataSourceContextHolder.setDbType("selectDataSource");
logger.info("使用的是读数据源:selectDataSource");
} else {
DataSourceContextHolder.setDbType("updateDataSource");
logger.info("使用的是写数据源:updateDataSource");
}
}
}主要的配置完成,其他的都是dao,service,controller了。