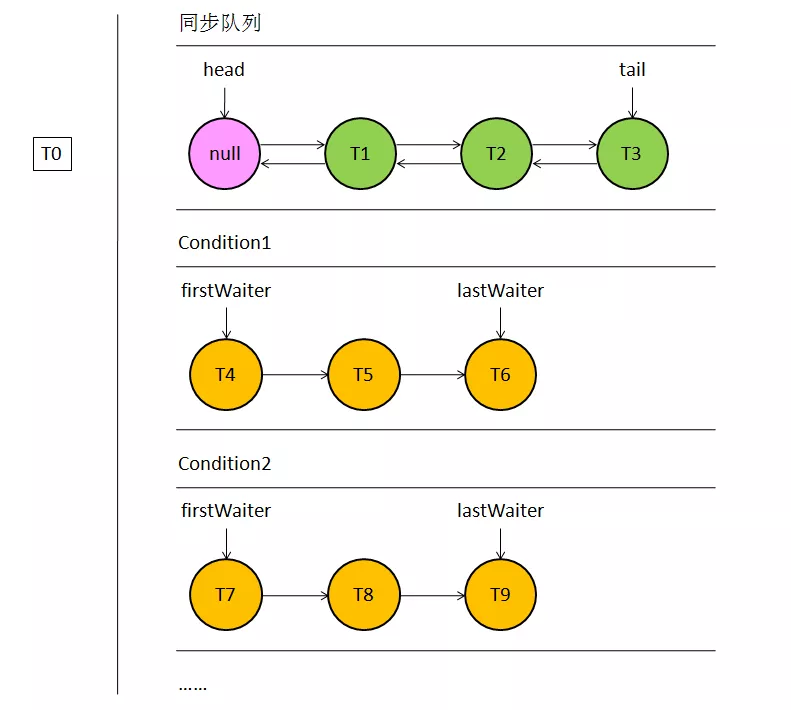
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer内部其实有两个排队区,一个是同步队列,一个是条件队列。从上图可以看出,同步队列只有一条,而条件队列可以有多条。同步队列的结点分别持有前后结点的引用,而条件队列的结点只有一个指向后继结点的引用。
图中T表示线程,每个结点包含一个线程,线程在获取锁失败后首先进入同步队列排队,而想要进入条件队列该线程必须持有锁才行。接下来我们看看队列中每个结点的结构。
static final class Node { //表示当前线程以共享模式持有锁 static final Node SHARED = new Node(); //表示当前线程以独占模式持有锁 static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null; /** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled */ //表示当前结点已经取消获取锁 static final int CANCELLED = 1; /** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */ //表示后继结点的线程需要运行 static final int SIGNAL = -1; /** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */ //表示当前结点在条件队列中排队 static final int CONDITION = -2; /** * waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should * unconditionally propagate */ //表示后继结点可以直接获取锁 static final int PROPAGATE = -3; //表示当前结点的等待状态 volatile int waitStatus; //表示同步队列中的前继结点 volatile Node prev; //当前结点持有的线程引用 volatile Thread thread; //表示条件队列中的后继结点 Node nextWaiter; /** * Returns true if node is waiting in shared mode. */ //当前结点状态是否是共享模式 final boolean isShared() { return nextWaiter == SHARED; } //返回当前结点的前继结点 final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException { Node p = prev; if (p == null) throw new NullPointerException(); else return p; } //构造器1 Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker } //构造器2, 默认用这个构造器 Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter //注意持有模式是赋值给nextWaiter this.nextWaiter = mode; this.thread = thread; } //构造器3, 只在条件队列中用到 Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition this.waitStatus = waitStatus; this.thread = thread; } }
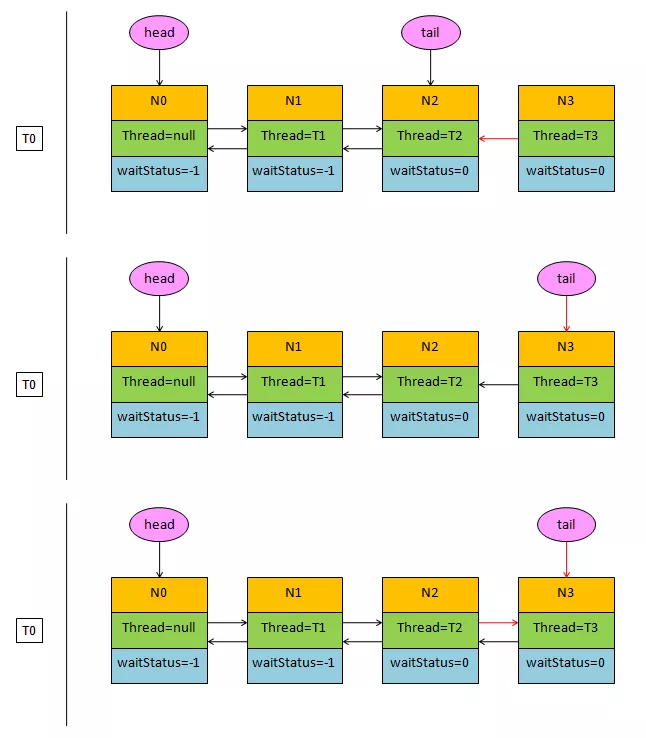
结点进入同步队列时会进行哪些操作?
/** * Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above. * @param node the node to insert * @return node's predecessor * 结点入队操作, 返回前一个结点 * 注意,入队操作使用一个死循环,只有成功将结点添加到同步队列尾部才会返回,返回结果是同步队列原先的尾结点。 * 读者需要注意添加尾结点的顺序,分为三步:指向尾结点,CAS更改尾结点,将旧尾结点的后继指向当前结点。 * 在并发环境中这三步操作不一定能保证完成,所以在清空同步队列所有已取消的结点这一操作中,为了寻找非取消状态的结点, * 不是从前向后遍历而是从后向前遍历的。还有就是每个结点进入队列中时它的等待状态是为0,只有后继结点的线程需要挂起时才会将前面结点的等待状态改为SIGNAL。 */ private Node enq(final Node node) { for (;;) { //获取同步队列尾结点引用 Node t = tail; //如果尾结点为空说明同步队列还没有初始化 if (t == null) { // Must initialize //初始化同步队列 if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) tail = head; } else { //1.指向当前尾结点 node.prev = t; //2.CAS更改尾结点 if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { //3.将旧尾结点的后继指向当前结点 t.next = node; //for循环唯一的出口 return t; } } } }
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI4Njc5NjM1NQ==&mid=2247485225&idx=1&sn=21641556bc68b8edf1bade0ff4c625f9&chksm=ebd63805dca1b1131c8ea1c13c662fc406df0f261f51c6df9aa254802c4cd6353a0f221949c1&scene=21#wechat_redirect