DEFINITION 1
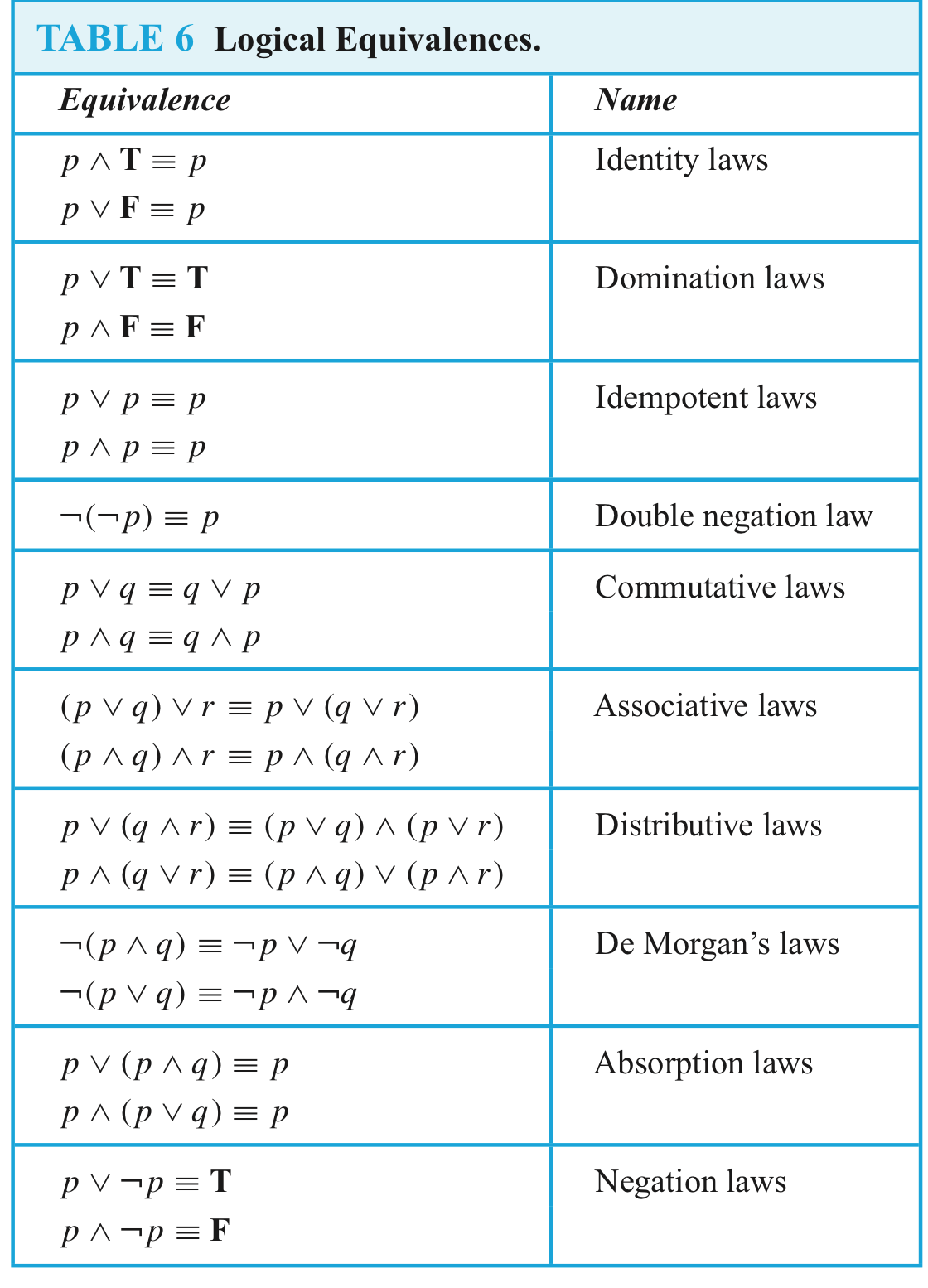
A compound proposition that is always true,no matter what the truth values of the proposi-tional variables that occur in it, is called atautology.
A compound proposition that is always false iscalled a contradiction.
A compound proposition that is neither a tautology nor a contradiction is called contingency.
Logical Equivalences
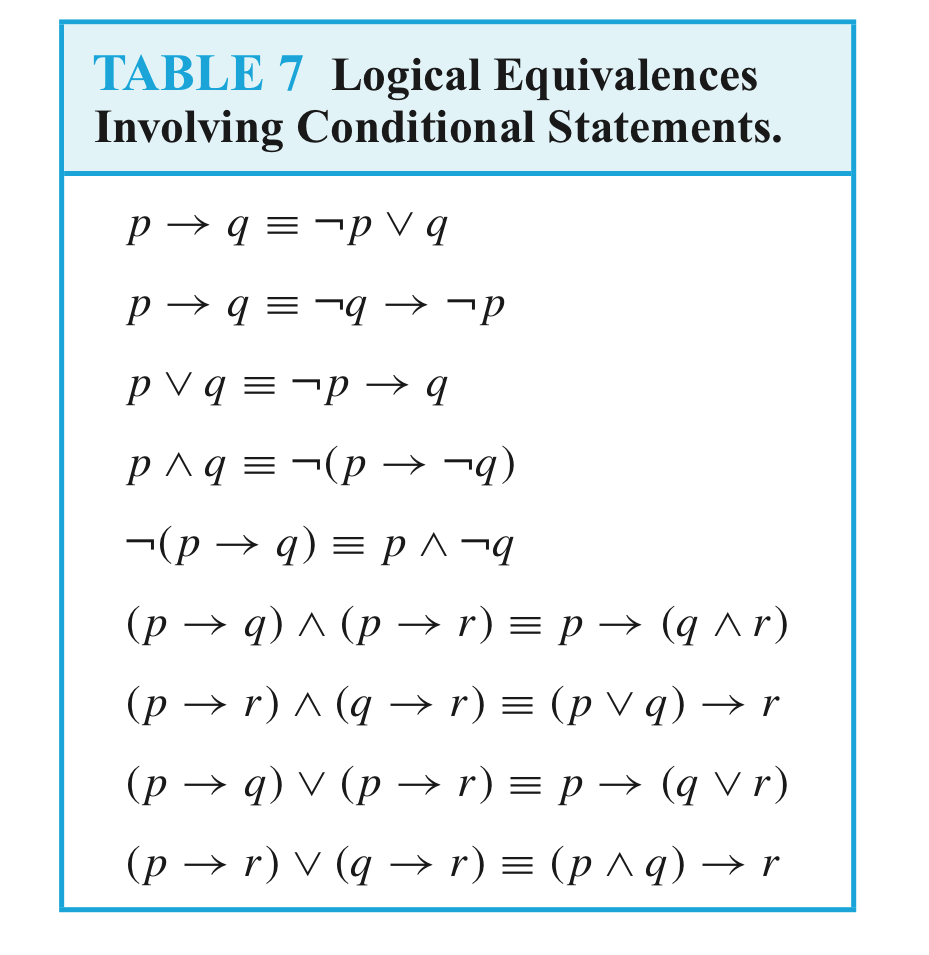
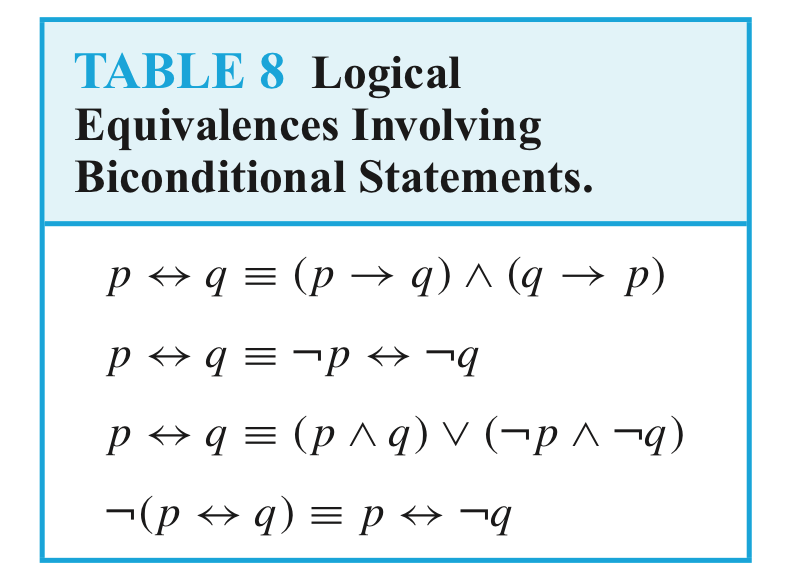
Compound propositions that have the same truth values in all possible cases are called logically equivalent.
DEFINITION 2
The compound propositions p and q are called logically equivalent if p ↔ q is a tautology.
The notation p ≡ q denotes that p and q are logically equivalent.
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
6128846 查看本文章


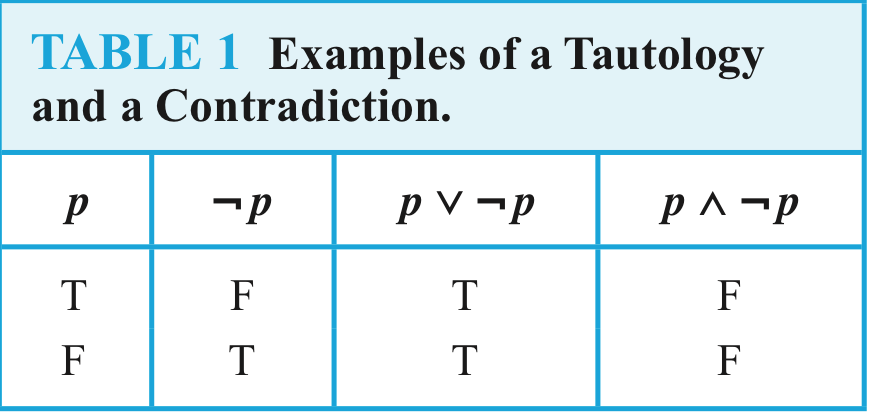
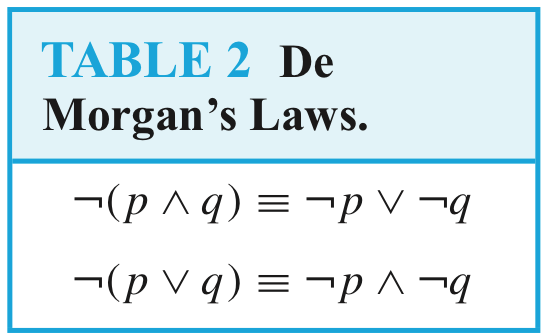
In general, 2**n rows are required if a compound proposition involves n propositional variables.