首先要感谢下面博主: mark 一下
https://www.cnblogs.com/s-b-b/p/6208565.html
说的很清楚,代码也能直接用,只是做了一点点小改进:1,将冲突的hash值存放到了链尾.2.增加了remove函数,方便删除不要的节点.此方法中,一个key至只对应一个value.
lookup函数:
//定义一个查找根据key查找结点的方法,首先是用Hash函数计算头地址,然后根据头地址向下一个个去查找结点,如果结点的key和查找的key值相同,则匹配成功,lookup即为查找key
install 函数:
//定义一个插入结点的方法,首先是查看该key值的结点是否存在,如果存在则更改value值就好,如果不存在,则插入新结点。
HashList3.h的代码如下
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
#define HASHSIZE 10
typedef unsigned int uint;
//节点定义,key,value,与next指针
typedef struct Node{
const char* key;
const char* value;
Node *next;
}Node;
//one key to one value
class HashTable{
private:
Node* node[HASHSIZE];//定义节点数
public:
HashTable();//构造函数
uint hash(const char* key);//hash函数
uint BKDRHash(const char* key);//BKDRHash函数
Node* lookup(const char* key,uint &pos);//find 函数
bool install(const char* key,const char* value);//insert节点
bool remove(const char* key);//删除节点
const char* get(const char* key);
void display();
};
HashTable::HashTable(){
// for (int i = 0; i < HASHSIZE; ++i)
// {
// node[i] = NULL;
// }
}
//BKDR hash 算法
uint HashTable::BKDRHash(const char* key)
{
uint seed = 131;
/* 31 131 1313 13131 131313 etc.. */
uint hash = 0;
for (; *key; ++key)
{
hash = (hash * seed) + (*key);
}
return hash%HASHSIZE;
}
uint HashTable::hash(const char* key){
uint hash=0;
for (; *key; ++key)
{
hash=hash*33+*key;
}
return hash%HASHSIZE;
}
Node* HashTable::lookup(const char* key,uint &pos){
Node *np;
uint index;
index = BKDRHash(key);
uint ipos = 0;
for(np=node[index];np;np=np->next,ipos++)
{
if(!strcmp(key,np->key))//equel return 0
{
pos = ipos;
return np;
}
}
return NULL;
}
bool HashTable::install(const char* key,const char* value){
uint index,pos;
Node *np,*tail;
if(!(np=lookup(key,pos)))
{
index = BKDRHash(key);
np = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(!np) return false;
np->key=key;
if (!(node[index]))
{
node[index] = np;
}
else
{
tail=node[index];
while(tail->next)
{
tail=tail->next;
}
tail->next = np;
}
// np->next = node[index];
// node[index] = np;
}
np->value=value;
return true;
}
bool HashTable::remove(const char* key)
{
Node *np,*pre;
uint pos;
uint index = BKDRHash(key);
if((np=lookup(key,pos)))
{
if (pos == 0)
{
node[index] = np->next;
}
else
{
pre = node[index];
for (int i = 1; i < pos; ++i)
{
pre = pre->next;
}
pre->next = pre->next->next;
}
free(np);
return true;
}
return false;
}
void HashTable::display(){
Node* temp;
for (int i = 0; i < HASHSIZE; ++i)
{
if(!node[i])
{
printf("[]\n");
}
else
{
printf("[");
for (temp=node[i]; temp; temp=temp->next)
{
printf("[%s : %s] -> ",temp->key,temp->value );
}
printf("]\n");
}
}
}
测试代码(HashList3.cpp)如下
#include "HashList3.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
HashTable *ht = new HashTable();
const char* key[]={"a","b","k","u","9"};
const char* value[]={"value1","value2","value3","nihao","shide"};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
ht->install(key[i],value[i]);
}
printf("-------------------------\n");
ht->display();
printf("-------------------------\n\n");
ht->remove("u");
ht->display();
printf("-------------------------\n\n");
ht->remove("a");
ht->display();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
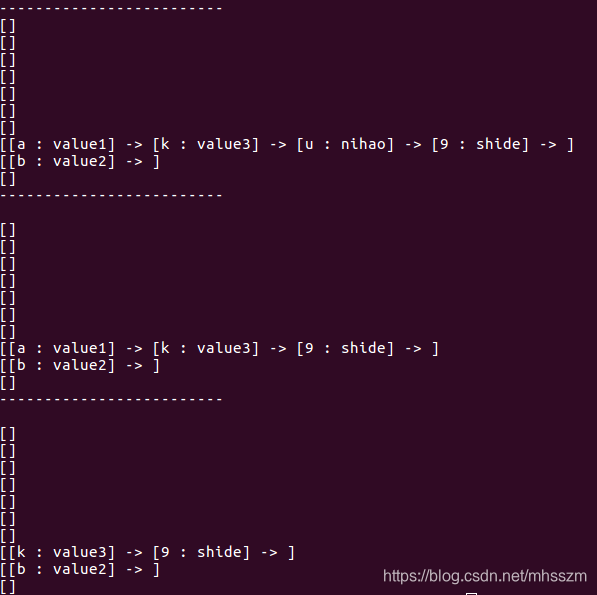
原文是将后加入的节点放在链表的最前端,这里将后加入的节点放置链表最末端.hash算法有更该.当然少量数据看不到区别,大量数据才有对比性.