This is a simplified version of the task Toy Train. These two versions differ only in the constraints. Hacks for this version are disabled.
Alice received a set of Toy Train™ from Bob. It consists of one train and a connected railway network of nn stations, enumerated from 11through nn. The train occupies one station at a time and travels around the network of stations in a circular manner. More precisely, the immediate station that the train will visit after station ii is station i+1i+1 if 1≤i<n1≤i<n or station 11 if i=ni=n. It takes the train 11 second to travel to its next station as described.
Bob gave Alice a fun task before he left: to deliver mm candies that are initially at some stations to their independent destinations using the train. The candies are enumerated from 11 through mm. Candy ii (1≤i≤m1≤i≤m), now at station aiai, should be delivered to station bibi (ai≠biai≠bi).
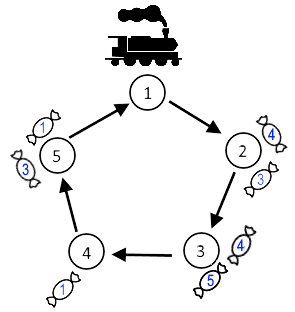 The blue numbers on the candies correspond to bibi values. The image corresponds to the 11-st example.
The blue numbers on the candies correspond to bibi values. The image corresponds to the 11-st example.
The train has infinite capacity, and it is possible to load off any number of candies at a station. However, only at most one candy can be loaded from a station onto the train before it leaves the station. You can choose any candy at this station. The time it takes to move the candies is negligible.
Now, Alice wonders how much time is needed for the train to deliver all candies. Your task is to find, for each station, the minimum time the train would need to deliver all the candies were it to start from there.
Input
The first line contains two space-separated integers nn and mm (2≤n≤1002≤n≤100; 1≤m≤2001≤m≤200) — the number of stations and the number of candies, respectively.
The ii-th of the following mm lines contains two space-separated integers aiai and bibi (1≤ai,bi≤n1≤ai,bi≤n; ai≠biai≠bi) — the station that initially contains candy ii and the destination station of the candy, respectively.
Output
In the first and only line, print nn space-separated integers, the ii-th of which is the minimum time, in seconds, the train would need to deliver all the candies were it to start from station ii.
Examples
input
Copy
5 7
2 4
5 1
2 3
3 4
4 1
5 3
3 5
output
Copy
10 9 10 10 9
input
Copy
2 3
1 2
1 2
1 2
output
Copy
5 6
Note
Consider the second sample.
If the train started at station 11, the optimal strategy is as follows.
- Load the first candy onto the train.
- Proceed to station 22. This step takes 11 second.
- Deliver the first candy.
- Proceed to station 11. This step takes 11 second.
- Load the second candy onto the train.
- Proceed to station 22. This step takes 11 second.
- Deliver the second candy.
- Proceed to station 11. This step takes 11 second.
- Load the third candy onto the train.
- Proceed to station 22. This step takes 11 second.
- Deliver the third candy.
Hence, the train needs 55 seconds to complete the tasks.
If the train were to start at station 22, however, it would need to move to station 11 before it could load the first candy, which would take one additional second. Thus, the answer in this scenario is 5+1=65+1=6 seconds.
思路;
每个站不管前面的糖运送距离有多长,我们都需要花费n的时间,我们只有让最后一颗糖花费时间尽可能的小,才能保证总花费时间是最小的。所以贪心的策略就如开始说的那样,最远的最先取,最近的最后取。
因为每到一个站都可以运送一颗糖果,所以只要我现在在运送的糖果花费的时间是n,其他站的糖果如果花费的时间也是n,或者小于n,就可以顺便完成运送任务。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#define mset(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=9973;
const int N=505050;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
vector<int>q[110];
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
q[x].push_back(y);
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
int ans=0,mi;
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
int p=q[j].size();
if(p==0)
continue;
else
{
mi=inf;
for(auto &k:q[j])
{
mi=min(mi,((p-1)*n+(k-j+n)%n+(j-i+n)%n));
}
ans=max(mi,ans);
}
}
printf("%d ",ans);
}
return 0;
}还可以优化,输入是时候直接找到最短的
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#define mset(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=9973;
const int N=505050;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
int a[5050],b[5050];
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
mset(b,0x7f);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
a[x]++;
b[x]=min(b[x],(y-x+n)%n);
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
int ans=0;
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
if(a[j])
{
ans=max(ans,(a[j]-1)*n+(j-i+n)%n+b[j]);
}
}
printf("%d ",ans);
}
return 0;
}