Data Structure: Generalize list
1 Storage structure of generalize list
1.1 An example
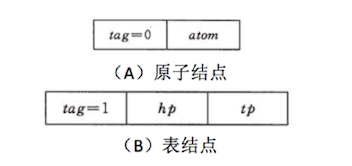
The generalize list can store item itself (we call atom) and sublist, so the basic node of generalize list have two types: Atomic node and List node:
typedef struct GLNode{
int tag; // Marking field
union{
char atom; // Value of atonic node
struct{
struct GLNode *hp,*tp
}ptr; // Sublist's pointer field
};
}*Glist;
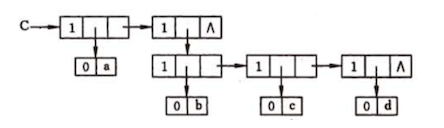
Here’s an example, generalize list {a,{b,c,d}} will be stored as the following:
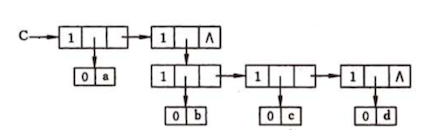
Glist creatGlist(Glist C){
// generalize list C
C=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->tag=1;
// 'a' is the atom of the list head
C->ptr.hp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->ptr.hp->tag=0;
C->ptr.hp->atom='a';
// '(b,c,d)' the sublist of list tail
C->ptr.tp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->ptr.tp->tag=1;
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->ptr.tp->ptr.tp=NULL;
// start to store the next element '(b,c,d)',the head is 'b' and the tail is '(c,d)'
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->tag=1;
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.hp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.hp->tag=0;
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.hp->atom='b';
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
// store '(c,d)', the head is 'c' and the tail is 'd'
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp->tag=1;
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp->ptr.hp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->tag=0;
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->atom='c';
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp->ptr.tp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
// store 'd'
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp->ptr.tp->tag=1;
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp->ptr.tp->ptr.hp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->tag=0;
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->atom='d';
C->ptr.tp->ptr.hp->ptr.tp->ptr.tp->ptr.tp=NULL;
return C;
}
1.2 Another type of storage structure

typedef struct GLNode{
int tag;
union{
int atom;
struct GLNode *hp;
};
struct GLNode * tp;
}*Glist;
For example, the generalize list {a,{b,c,d}} will be stored as following:
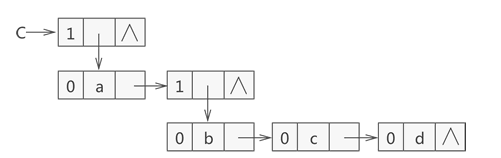
Glist creatGlist(Glist C){
C=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->tag=1;
C->hp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->tp=NULL;
// atom 'a' (list head)
C->hp->tag=0;
C->atom='a';
C->hp->tp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->hp->tp->tag=1;
C->hp->tp->hp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
C->hp->tp->tp=NULL;
// atom 'b'
C->hp->tp->hp->tag=0;
C->hp->tp->hp->atom='b';
C->hp->tp->hp->tp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
// atom 'c'
C->hp->tp->hp->tp->tag=0;
C->hp->tp->hp->tp->atom='c';
C->hp->tp->hp->tp->tp=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
// atom 'd'
C->hp->tp->hp->tp->tp->tag=0;
C->hp->tp->hp->tp->tp->atom='d';
C->hp->tp->hp->tp->tp->tp=NULL;
return C;
}
2 Length and Depth of generalize list
2.1 Length of generalize list
The length of generalize list is the number of elements it contains, meanwhile, we assign that the length of blank list {} is 0.

In two types of the storage method, we just need to count the elements that red part contains, here’s the code implementation of the first method:
int GlistLength(Glist C){
int Number=0;
Glist P=C;
while(P){
Number++;
P=P->ptr.tp;
}
return Number;
}
int main(){
Glist C = creatGlist(C);
printf("Length of the generalize list:%d",GlistLength(C));
return 0;
}
Output:

2.2 Depth of the generalize list
The depth of the generalize list equals the level of the list, for example, {1,{2,{3,4}}} means the depth is 3.
To calculate the depth of the generalize list, we can use the recursive algorithm:
- To traverse each node of the generalize list, if the list is atomic list (tag=0), return 0, else will return 1
- Let the variable ‘max’ compare with the return number and use the bigger one, when the traverse is over, max+1 will equal the depth.
Also, we just implement the first method:
int GlistDepth(Glist C){
if (!C) { // If blank, return 1
return 1;
}
if (C->tag==0) {
return 0;
}
int max=0;
for (Glist pp=C; pp; pp=pp->ptr.tp) {
int dep=GlistDepth(pp->ptr.hp);
if (dep>max) {
max=dep;
}
}
return max+1;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
Glist C=creatGlist(C);
printf("The depth of the generalize list:%d",GlistDepth(C));
return 0;
}
Output:

3 Copy the generalize list
The copy process if the generalize list is a process that circularly copy the list head and list tail.
For example:
void copyGlist(Glist C, Glist *T){
if (!C){
*T=NULL; // If blank, copy the blank list
}
else{
*T=(Glist)malloc(sizeof(Glist));
if (!*T){
printf("Failed to allocate");
exit(0);
}
(*T)->tag=C->tag;
if (C->tag==0) {
(*T)->atom=C->atom;
}else{
copyGlist(C->ptr.hp, &((*T)->ptr.hp));// Copy the list head
copyGlist(C->ptr.tp, &((*T)->ptr.tp));// Copy the list tail
}
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
Glist C=NULL;
C=creatGlist(C);
Glist T=NULL;
copyGlist(C,&T);
printf("%c",T->ptr.hp->atom);
return 0;
}