前端路由原理本质就是监听 URL 的变化,然后匹配路由规则,显示相应的页面,并且无须刷新。目前单页面使用的路由就只有两种实现方式
hash
history
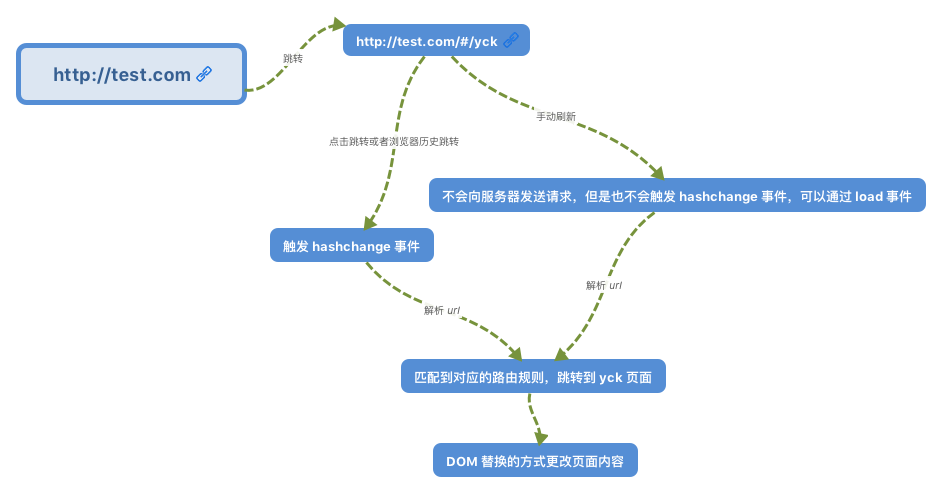
www.test.com/##/ 就是 Hash URL,当 ## 后面的哈希值发生变化时,不会向服务器请求数据,可以通过 hashchange 事件来监听到 URL 的变化,从而进行跳转页面。
vue-router hash实现源码(完整源码访问https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/blob/dev/src/history/hash.js#L22-L54):
** * 添加 url hash 变化的监听器 */ setupListeners () { const router = this.router /** * 每当 hash 变化时就解析路径 * 匹配路由 */ window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => { const current = this.current /** * transitionTo: * 匹配路由 * 并通过路由配置,把新的页面 render 到 ui-view 的节点 */ this.transitionTo(getHash(), route => { replaceHash(route.fullPath) }) }) }
检测到 hash 的变化后,就可以通过替换 DOM 的方式来实现页面的更换。
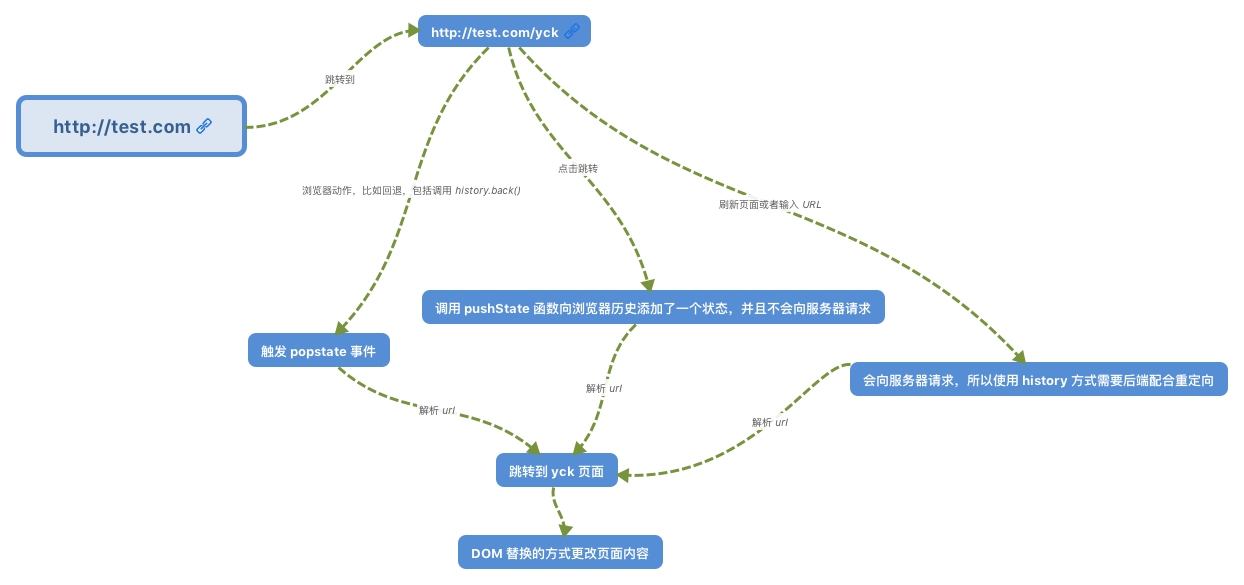
History 模式是 HTML5 新推出的功能,比之 Hash URL 更加美观
两个 API ,pushState和replaceState可以改变 url 地址且不会发送请求,还有onpopState事件。但因为没有 # 号,所以当用户刷新页面之类的操作时,浏览器还是会给服务器发送请求。为了避免出现这种情况,所以这个实现需要服务器的支持,需要把所有路由都重定向到根页面。具体可以访问官网:https://router.vuejs.org/zh/guide/essentials/history-mode.html
vue-router history实现源码(完整源码访问https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/blob/dev/src/history/html5.js)
export class HTML5History extends History { constructor (router, base) { super(router, base) /** * 原理还是跟 hash 实现一样 * 通过监听 popstate 事件 * 匹配路由,然后更新页面 DOM */ window.addEventListener('popstate', e => { const current = this.current // Avoiding first `popstate` event dispatched in some browsers but first // history route not updated since async guard at the same time. const location = getLocation(this.base) if (this.current === START && location === initLocation) { return } this.transitionTo(location, route => { if (supportsScroll) { handleScroll(router, route, current, true) } }) }) } go (n) { window.history.go(n) } push (location, onComplete, onAbort) { const { current: fromRoute } = this this.transitionTo(location, route => { // 使用 pushState 更新 url,不会导致浏览器发送请求,从而不会刷新页面 pushState(cleanPath(this.base + route.fullPath)) onComplete && onComplete(route) }, onAbort) } replace (location, onComplete, onAbort) { const { current: fromRoute } = this this.transitionTo(location, route => { // replaceState 跟 pushState 的区别在于,不会记录到历史栈 replaceState(cleanPath(this.base + route.fullPath)) onComplete && onComplete(route) }, onAbort) } }