直到20世纪90年代末,摩尔定律为商业硬件上的各类系统提供了足够的计算能力,才逐渐能够实现比较复杂的雷达算法。
Only in the late 1990s has Moore’s Law providedenough computing power to host radar algorithms for a wide range of systems oncommercial hardware.
重要的是,技术进步允许将新的、更复杂的算法应用于雷达信号处理,从而能够在检测、跟踪和成像能力方面进行重大改进。
Equally important, this same technologicalprogress has allowed the application of new, more complex algorithms to radarsignals, enabling major improvements in detection, tracking, and imagingcapability.
1.3. 脉冲雷达的组成要素
1.3. Elements of a Pulsed Radar
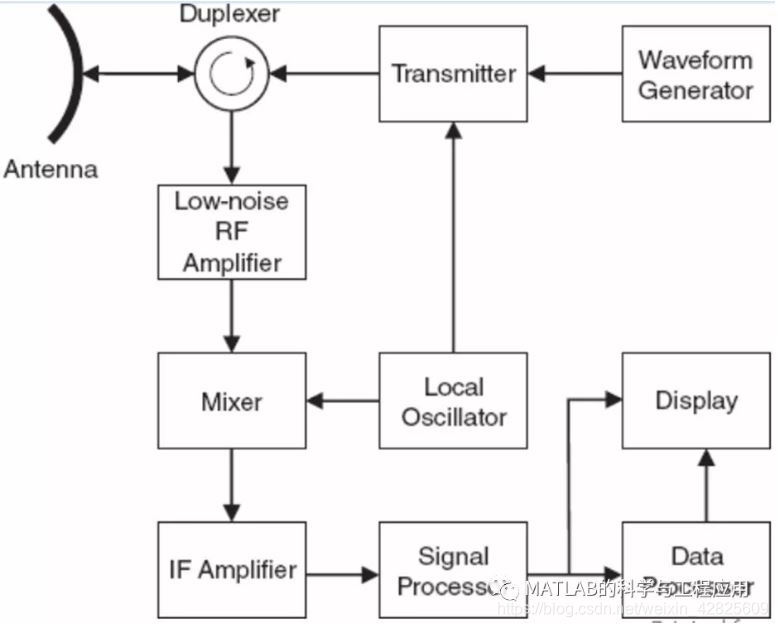
图1.2是一个简单的脉冲单基地雷达的可能的组成框图。
Figure 1.2 is one possible block diagram ofa simple pulsed monostatic radar.
Figure 1.2. 脉冲单基地雷达组成框图Block diagram of a pulsedmonostatic radar
波形发生器产生期望的脉冲波形。
The waveform generator output is thedesired pulse waveform.
发射机将该脉冲波形调制到所需的射频(RF),并将其放大到可用的功率电平。
The transmitter modulates this waveform tothe desired radio frequency (RF) and amplifies it to a useful power level.
发射机输出通过双工器(也称为环形器或T/R开关)连接到天线(用于发射/接收)。
The transmitter output is routed to theantenna through a duplexer, also called a circulator or T/R switch (fortransmit/receive).
从目标返回的回波再次由双工器送入到雷达接收机中。
The returning echoes are routed, again bythe duplexer, into the radar receiver.
接收机通常采用超外差设计,第一级一般采用低噪声RF放大器。
The receiver is usually a superheterodynedesign, and often the first stage is a lownoise RF amplifier.
然后通过将接收信号进行一级或多级相干解调,以不断降低中频(IF),并最终下变频到基带,基带信号中不包含任何载波频率。
This is followed by one or more stages ofmodulation of the received signal to successively lower intermediatefrequencies (IFs) and ultimately to baseband, where the signal is not modulatedonto any carrier frequency.
每次解调是用混频器和本地振荡器(LO)进行的。(译注:这里的用“modulation”不是很合适,接收机一般用“解调”进行表述,发射机用“调制”)
Each modulation is carried out with a mixerand a local oscillator (LO).
接下来,基带信号被发送到信号处理器,信号处理器执行诸如脉冲压缩、匹配滤波、多普勒滤波、积累和运动补偿等部分或全部功能。
The baseband signal is next sent to thesignal processor, which performs some or all of a variety of functions such aspulse compression, matched filtering, Doppler filtering, integration, andmotion compensation.
根据雷达的不同应用目的,信号处理器的输出表现为各种不同的形式。
The output of the signal processor takesvarious forms, depending on the radar purpose.
跟踪雷达输出具有测量距离和角度坐标的检测数据流,而成像雷达输出二维或三维图像。
A tracking radar would output a stream ofdetections with measured range and angle coordinates, while an imaging radarwould output a two- or three-dimensional image.
信号处理器的处理结果发送到雷达显示器和数据处理器。
The processor output is sent to the systemdisplay, the data processor, or both as appropriate.
图1.2中的原理框图并不是唯一不变的,实际应用中可能有很多种变化形式。
The configuration of Fig. 1.2 is notunique.
——本文译自Mark A. Richards所著的《Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing(Second edition)》
更多精彩文章请关注微信号: