Faster R-CNN 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.01497
一、创新点
- 目前object detection的成功主要在于region proposal方法以及region-based CNN网络方法。
- region proposal耗时成为object detection的瓶颈。
- 作者设计提出RPN网络,替代region proposal方法的同时,实现end-to-end网络。
- rpn网络利用特征图实现region proposal,使得时间降低到10ms/张。
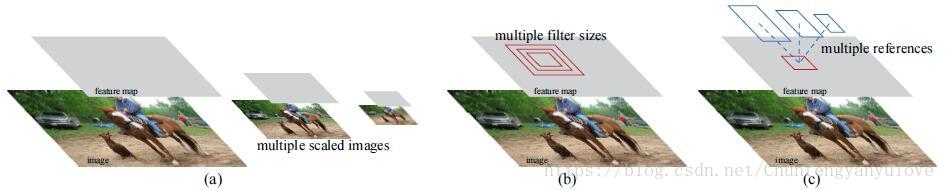
- rpn利用“anchor”实现多尺度,多方向的变换。(论文中同时介绍了其他的方法,比如图像金字塔,但是感觉还是anchor比较实用)
- 为了保证rpn与fast rcnn的一致,作者提出了一种交替训练的方法。
二、Faster R-CNN详解
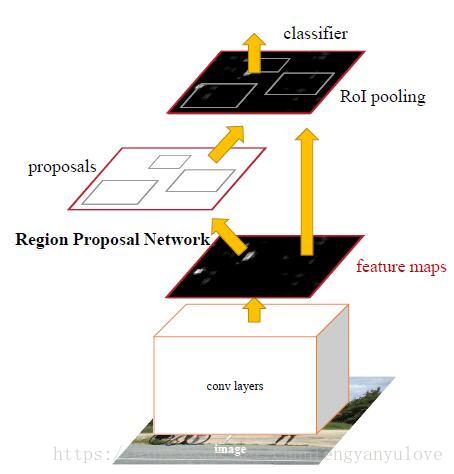
Faster RCNN整体结构采用Fast R-CNN,另外利用设计的RPN网络替代Selective Search方法实现region的生成,如下图所示:
2.1 RPN 网络
RPN网络的输入为任意尺寸的图像,输出为一系列的矩形框以及是否为object的得分。
RPN网络采用n*n(默认n取3)的滑动窗口,首先通过卷积进行降维(实验默认是ZF-256维,VGG-512维),然后分别连接两个全连接层reg以及cls,实现回归与分类。
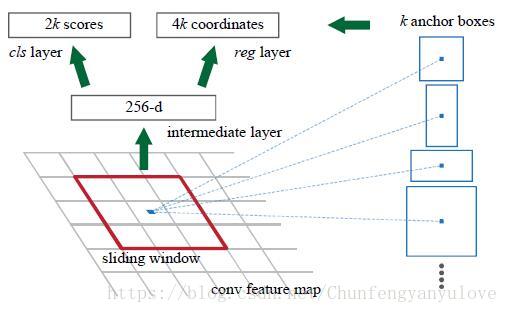
2.1.1 anchor
- 对于每个滑动窗口,rpn网络预测k个region proposal区域,这样reg网络便产生4k个输出代表着坐标,cls产生2k个输出,代表在是否为object
- k个不同大小的rp区域作者称之为anchor,faster r-cnn默认提取9个anchor,分别对应3个尺寸(作者默认为128,256,512),3个长宽比(作者默认为:1:1,1:2,2:1),如下是对应图像宽度缩放到600采用ZF网络时候对应的anchor的尺寸。
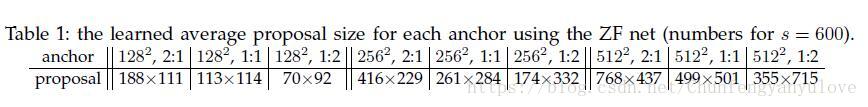
* 平移不变性。
* 相比较与multibox,采用本文方法的参数量大幅降低。
* multi-scale anchor,常用的多尺度方法如下,(a)为图像金字塔比较耗时,(b)为多尺度滤波器,本文选择方法(c)。
2.1.2 loss function
anchor 正负样本的分配:
* 与IOU重合度最大的标记被正样本
* 与IOU重合度大于70%的标记为正样本
* 与IOU重合度小于30%的标记为负样本。
loss function定于如下:
这里,
代表预测anchor为object的概率,如果anchor为正样本,
为1否则为0。
为bounding box的4个坐标, 代表,当anchor为正时计算reg坐标回归,否则不计算坐标回归。
为log 损失
为smooth L1损失
bounding box regression 的参数坐标定义为:
2.1.3 rpn的训练
RPN训练的时候,每个mini-batch便是一张图片。由于正负样本较多,训练时,每张图像随机采样256个anchor,正负样本的比例是1:1,如果正样本较少,用负样本补充。
2.2 Faster R-CNN的训练
对于Faster R-CNN的训练,本文作者采用了4步交替训练方法,以达到fast r-cnn与rpn网络的统一性。
1、利用ImageNet预训练模型进行训练RPN。
2、利用第一步的RPN,训练Fast R-CNN。
3、保持Fast R-CNN前面网络不变,训练RPN,使得Fast R-CNN与RPN共享卷积。
4、保持共享卷积不变,,训练Fast R-CNN后面的网络。
generate anchors
拿代码来说
import numpy as np
def generate_anchors(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2],
scales=2**np.arange(3, 6)):
"""
Generate anchor (reference) windows by enumerating aspect ratios X
scales wrt a reference (0, 0, 15, 15) window.
"""
# 这里选取16的原因在于,原始图像224x224,conv5卷积层输出feature maps大小为14x14,是16的缩放关系。对于
# feature maps上的每个点,在width方向最大偏移为14,同理在height上也是14.
# 在图像左上角生成一个anchors,剩下的anchors在此基础上做偏移即可得到。
# scales=[8, 16, 32],
#详细说明,基准坐标[0,0,15,15]利用ratios可以生成3个anchor分别为[0,0,16,16][-4,2,19,14][2.5,-3,13.5,19]
#然后再乘以变换比例得到9个anchor[128..,256..,512..]
base_anchor = np.array([1, 1, base_size, base_size]) - 1
ratio_anchors = _ratio_enum(base_anchor, ratios)
anchors = np.vstack([_scale_enum(ratio_anchors[i, :], scales)
for i in xrange(ratio_anchors.shape[0])])
return anchors
def _whctrs(anchor):
"""
Return width, height, x center, and y center for an anchor (window).
"""
w = anchor[2] - anchor[0] + 1
h = anchor[3] - anchor[1] + 1
x_ctr = anchor[0] + 0.5 * (w - 1)
y_ctr = anchor[1] + 0.5 * (h - 1)
return w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr
def _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr):
"""
Given a vector of widths (ws) and heights (hs) around a center
(x_ctr, y_ctr), output a set of anchors (windows).
"""
# 对于给定anchor中心坐标和长宽,生成三个anchors,分别时1:0.5, 1:1, 1:2
ws = ws[:, np.newaxis]
hs = hs[:, np.newaxis]
anchors = np.hstack((x_ctr - 0.5 * (ws - 1),
y_ctr - 0.5 * (hs - 1),
x_ctr + 0.5 * (ws - 1),
y_ctr + 0.5 * (hs - 1)))
return anchors
def _ratio_enum(anchor, ratios):
"""
Enumerate a set of anchors for each aspect ratio wrt an anchor.
"""
w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) #返回anchor的中心以及长宽
size = w * h
size_ratios = size / ratios #尺寸 [128,256,512]
ws = np.round(np.sqrt(size_ratios))
hs = np.round(ws * ratios)
anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) #得到[0,0,16,16] [-3.5,2,18.5,13][2.5,-3,12.5,18]
return anchors
def _scale_enum(anchor, scales):
"""
Enumerate a set of anchors for each scale wrt an anchor.
"""
# 对于每一个scale,生成三个anchors,总共可以生成9个anchors
w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor)
ws = w * scales
hs = h * scales
anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr)
return anchorsanchor_target
bottom值得注意的是rpn_cls_score,开始我以为会用到,在阅读代码之后,可以知道它的作用仅仅是为得到feature maps的width,height,用作anchors的生成。在获取anchors之后,
可以利用其计算与gt_boxes的overlap值,以此来获得目标还是背景的标签。(ps;这里贴代码时候需要四个空格才给算,也是醉了)上源码:
“`python
class AnchorTargetLayer(caffe.Layer):
def setup(self, bottom, top):
layer_params = yaml.load(self.param_str_)
anchor_scales = layer_params.get('scales', (8, 16, 32))
# generate 1:0.5, 1:1, 1:2 anchors,利用上述生成anchors方法。
self._anchors = generate_anchors(scales=np.array(anchor_scales))
self._num_anchors = self._anchors.shape[0]
self._feat_stride = layer_params['feat_stride']
if DEBUG:
print 'anchors:'
print self._anchors
print 'anchor shapes:'
print np.hstack((
self._anchors[:, 2::4] - self._anchors[:, 0::4],
self._anchors[:, 3::4] - self._anchors[:, 1::4],
))
self._counts = cfg.EPS
self._sums = np.zeros((1, 4))
self._squared_sums = np.zeros((1, 4))
self._fg_sum = 0
self._bg_sum = 0
self._count = 0
# allow boxes to sit over the edge by a small amount
self._allowed_border = layer_params.get('allowed_border', 0)
height, width = bottom[0].data.shape[-2:]
if DEBUG:
print 'AnchorTargetLayer: height', height, 'width', width
A = self._num_anchors
# labels
top[0].reshape(1, 1, A * height, width)
# bbox_targets
top[1].reshape(1, A * 4, height, width)
# bbox_inside_weights
top[2].reshape(1, A * 4, height, width)
# bbox_outside_weights
top[3].reshape(1, A * 4, height, width)
def forward(self, bottom, top):
# Algorithm:
#
# for each (H, W) location i
# generate 9 anchor boxes centered on cell i
# apply predicted bbox deltas at cell i to each of the 9 anchors
# filter out-of-image anchors
# measure GT overlap
assert bottom[0].data.shape[0] == 1, \
'Only single item batches are supported'
# map of shape (..., H, W)
# 利用rpn_cls_score来获得feature_maps的长宽
height, width = bottom[0].data.shape[-2:]
# GT boxes (x1, y1, x2, y2, label)
gt_boxes = bottom[1].data
# im_info
im_info = bottom[2].data[0, :]
if DEBUG:
print ''
print 'im_size: ({}, {})'.format(im_info[0], im_info[1])
print 'scale: {}'.format(im_info[2])
print 'height, width: ({}, {})'.format(height, width)
print 'rpn: gt_boxes.shape', gt_boxes.shape
print 'rpn: gt_boxes', gt_boxes
# 1. Generate proposals from bbox deltas and shifted anchors
# 利用获得每个anchor相对于图片左上角的anchor的移动步长。
shift_x = np.arange(0, width) * self._feat_stride
shift_y = np.arange(0, height) * self._feat_stride
shift_x, shift_y = np.meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y)
shifts = np.vstack((shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel(),
shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel())).transpose()
# add A anchors (1, A, 4) to
# cell K shifts (K, 1, 4) to get
# shift anchors (K, A, 4)
# reshape to (K*A, 4) shifted anchors
#简单说就是对9个anchor,每一个都加上一个位移,得到9*K个位移
A = self._num_anchors
K = shifts.shape[0]
# each anchor add with all shifts to get all anchors
all_anchors = (self._anchors.reshape((1, A, 4)) +
shifts.reshape((1, K, 4)).transpose((1, 0, 2)))
all_anchors = all_anchors.reshape((K * A, 4))
total_anchors = int(K * A)
# only keep anchors inside the image
# 丢弃所有超过边界的anchors,即使是一点点。
inds_inside = np.where(
(all_anchors[:, 0] >= -self._allowed_border) &
(all_anchors[:, 1] >= -self._allowed_border) &
(all_anchors[:, 2] < im_info[1] + self._allowed_border) & # width
(all_anchors[:, 3] < im_info[0] + self._allowed_border) # height
)[0]
if DEBUG:
print 'total_anchors', total_anchors
print 'inds_inside', len(inds_inside)
# keep only inside anchors
anchors = all_anchors[inds_inside, :]
if DEBUG:
print 'anchors.shape', anchors.shape
# label: 1 is positive, 0 is negative, -1 is dont care
labels = np.empty((len(inds_inside), ), dtype=np.float32)
labels.fill(-1)
# overlaps between the anchors and the gt boxes(x1, y1, x2, y2, cls)
# overlaps (ex, gt)
# 这里overlaps是计算所有anchor与ground-truth的重合度,它是一个len(anchors) x len(gt_boxes)的二维数组,每个元素是各个
# anchor和gt_boxes的overlap值,这个overlap值的计算是这样的:
# overlap = (重合部分面积) / (anchor面积 + gt_boxes面积 - 重合部分面积)
# argmax_overlaps是每个anchor对应最大overlap的gt_boxes的下标
# max_overlaps是每个anchor对应最大的overlap值相对应的
# gt_argmax_overlaps是每个gt_boxes对应最大overlap的anchor的下标
# gt_max_overlaps是每个gt_boxes对应最大的overlap值
# 计算anchors与gt_boxes的overlap
overlaps = bbox_overlaps(
np.ascontiguousarray(anchors, dtype=np.float),
np.ascontiguousarray(gt_boxes, dtype=np.float))
# 获取每行最大overlap
argmax_overlaps = overlaps.argmax(axis=1)
max_overlaps = overlaps[np.arange(len(inds_inside)), argmax_overlaps]
gt_argmax_overlaps = overlaps.argmax(axis=0)
# 获取每列最大的overlap, 目的是找到与roi重叠最大的区域,将其标记为1
gt_max_overlaps = overlaps[gt_argmax_overlaps,
np.arange(overlaps.shape[1])]
gt_argmax_overlaps = np.where(overlaps == gt_max_overlaps)[0]
if not cfg.TRAIN.RPN_CLOBBER_POSITIVES:
# assign bg labels first so that positive labels can clobber them
labels[max_overlaps < cfg.TRAIN.RPN_NEGATIVE_OVERLAP] = 0
# fg label: for each gt, anchor with highest overlap
# 无论如何,最大的overlap对应的是目标
labels[gt_argmax_overlaps] = 1
# fg label: above threshold IOU
labels[max_overlaps >= cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_OVERLAP] = 1
if cfg.TRAIN.RPN_CLOBBER_POSITIVES:
# assign bg labels last so that negative labels can clobber positives
labels[max_overlaps < cfg.TRAIN.RPN_NEGATIVE_OVERLAP] = 0
# subsample positive labels if we have too many
# 如果正标签过多,则进行下采样,提取部分正标签
num_fg = int(cfg.TRAIN.RPN_FG_FRACTION * cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE)
fg_inds = np.where(labels == 1)[0]
if len(fg_inds) > num_fg:
disable_inds = npr.choice( #随机选择标签为正的标记为-1
fg_inds, size=(len(fg_inds) - num_fg), replace=False)
labels[disable_inds] = -1
# subsample negative labels if we have too many
# 如果负标签过多,则进行下采样,提取部分负标签
num_bg = cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE - np.sum(labels == 1)
bg_inds = np.where(labels == 0)[0]
if len(bg_inds) > num_bg:
disable_inds = npr.choice(
bg_inds, size=(len(bg_inds) - num_bg), replace=False)
labels[disable_inds] = -1
#print "was %s inds, disabling %s, now %s inds" % (
#len(bg_inds), len(disable_inds), np.sum(labels == 0))
#这里将计算每一个anchor与重合度最高的ground_truth的偏移值
bbox_targets = np.zeros((len(inds_inside), 4), dtype=np.float32)
# transform anchors 's coordinate to [0, 1]
# 求bbox的回归目标
bbox_targets = _compute_targets(anchors, gt_boxes[argmax_overlaps, :])
# inside and outside means that anchors in geboxes or out of gtboxes.
bbox_inside_weights = np.zeros((len(inds_inside), 4), dtype=np.float32)
bbox_inside_weights[labels == 1, :] = np.array(cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BBOX_INSIDE_WEIGHTS)
bbox_outside_weights = np.zeros((len(inds_inside), 4), dtype=np.float32)
if cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT < 0:
# uniform weighting of examples (given non-uniform sampling)
num_examples = np.sum(labels >= 0)
positive_weights = np.ones((1, 4)) * 1.0 / num_examples
negative_weights = np.ones((1, 4)) * 1.0 / num_examples
else:
assert ((cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT > 0) &
(cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT < 1))
positive_weights = (cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT /
np.sum(labels == 1))
negative_weights = ((1.0 - cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT) /
np.sum(labels == 0))
bbox_outside_weights[labels == 1, :] = positive_weights
bbox_outside_weights[labels == 0, :] = negative_weights
if DEBUG:
self._sums += bbox_targets[labels == 1, :].sum(axis=0)
self._squared_sums += (bbox_targets[labels == 1, :] ** 2).sum(axis=0)
self._counts += np.sum(labels == 1)
means = self._sums / self._counts
stds = np.sqrt(self._squared_sums / self._counts - means ** 2)
print 'means:'
print means
print 'stdevs:'
print stds
# map up to original set of anchors
labels = _unmap(labels, total_anchors, inds_inside, fill=-1)
bbox_targets = _unmap(bbox_targets, total_anchors, inds_inside, fill=0)
bbox_inside_weights = _unmap(bbox_inside_weights, total_anchors, inds_inside, fill=0)
bbox_outside_weights = _unmap(bbox_outside_weights, total_anchors, inds_inside, fill=0)
if DEBUG:
print 'rpn: max max_overlap', np.max(max_overlaps)
print 'rpn: num_positive', np.sum(labels == 1)
print 'rpn: num_negative', np.sum(labels == 0)
self._fg_sum += np.sum(labels == 1)
self._bg_sum += np.sum(labels == 0)
self._count += 1
print 'rpn: num_positive avg', self._fg_sum / self._count
print 'rpn: num_negative avg', self._bg_sum / self._count
# labels for each anchors, so shape is (1, 1, A * height, width)
labels = labels.reshape((1, height, width, A)).transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
labels = labels.reshape((1, 1, A * height, width))
top[0].reshape(*labels.shape)
top[0].data[...] = labels
# bbox_targets
bbox_targets = bbox_targets \
.reshape((1, height, width, A * 4)).transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
top[1].reshape(*bbox_targets.shape)
top[1].data[...] = bbox_targets
# bbox_inside_weights
bbox_inside_weights = bbox_inside_weights \
.reshape((1, height, width, A * 4)).transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
assert bbox_inside_weights.shape[2] == height
assert bbox_inside_weights.shape[3] == width
top[2].reshape(*bbox_inside_weights.shape)
top[2].data[...] = bbox_inside_weights
# bbox_outside_weights
bbox_outside_weights = bbox_outside_weights \
.reshape((1, height, width, A * 4)).transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
assert bbox_outside_weights.shape[2] == height
assert bbox_outside_weights.shape[3] == width
top[3].reshape(*bbox_outside_weights.shape)
top[3].data[...] = bbox_outside_weights
def backward(self, top, propagate_down, bottom):
"""This layer does not propagate gradients."""
pass
def reshape(self, bottom, top):
pass
“`