TensorFlow实战中AlexNet卷积神经网络的训练
01 出错
TypeError: as_default() missing 1 required positional argument: 'self'
经过百度、谷歌的双重查找,没找到就具体原因。后面去TensorFlow官方文档中发现,tf.Graph的用法如下:
g = tf.Graph()
with g.as_default():
# Define operations and tensors in `g`.
c = tf.constant(30.0)
assert c.graph is g因此,做了一点小改动。把语句:
with tf.Graph().as_default():改成:
g = tf.Graph()
with g.as_default():02 运行代码对比带LRN和不带
最后成功运行了第一个带有LRN的版本:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2018/11/20 10:42
# @Author : Chen Cjv
# @Site : http://www.cnblogs.com/cjvae/
# @File : AlexNet.py
# @Software: PyCharm
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2'
from datetime import datetime
import math
import time
import tensorflow as tf
batch_size = 32
num_batches = 100
# 展示每一个卷积层或池化层输出的tensor的尺寸,接收一个tensor输入
def print_activation(t):
print(t.op.name, '', t.get_shape().as_list())
def inference(images):
# 训练的模型参数
parameters = []
# 1th CL starting
with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope:
# 截断正态分布初始化卷积核参数
# 卷积核尺寸11 x 11 颜色3通道 卷积核64
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([11, 11, 3, 64],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
# 实现卷积操作,步长4x4(在图像上每4x4区域取样一次,每次取样卷积核大小为11x11)
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 4, 4, 1], padding='SAME')
# 卷积偏置为0
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
# 将卷积结果与偏置相加
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
# 对结果非线性处理
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
# 输出conv1的信息
print_activation(conv1)
# 添加参数
parameters += [kernel, biases]
# 1th CL ending
# add 1th LRN layer and max-pooling layer starting
# depth_radius设为4,lrn可以选择不用,效果待测试
lrn1 = tf.nn.lrn(conv1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9, beta=0.75, name='lrn1')
# 池化:尺寸3x3(将3x3的大小的像素块降为1x1 步长为2x2 VALID表示取样不超过边框)
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name='pool1')
print_activation(pool1)
# add 1th LRN layer and max-pooling layer ending
# designing second Convolutional Layer starting
with tf.name_scope('conv2') as scope:
# 不同第一卷积层,这层卷积核尺寸5x5,通道为上层输出通道数(即卷积核数)64
# 卷积核数量为192
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 64, 192],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
# 卷积步长为1,即扫描全部图像
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[192],
dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activation(conv2)
# designing 2th CL ending
# add 2th LRN layer and max-pooling layer starting
lrn2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9, beta=0.75, name='lrn2')
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool (lrn2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name='pool2')
print_activation(pool2)
# add 2th LRN layer and max-pooling layer ending
# designing 3th Convolutional Layer starting
with tf.name_scope('conv3') as scope:
# 卷积核尺寸3x3 通道数192 卷积核384
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 192, 384],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[384],
dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activation(conv3)
# designing 3th CL ending
# designing 4th CL starting
with tf.name_scope('conv4') as scope:
# 卷积核尺寸3x3 通道数384 卷积核降为256
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 384, 256],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv3, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256],
dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv4 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activation(conv4)
# designing fourth Convolutional Layer ending
# designing fifth Convolutional Layer starting
with tf.name_scope('conv4') as scope:
# 卷积核尺寸3x3 通道数256 卷积核256
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv4, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256],
dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv5 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activation(conv5)
# designing fifth Convolutional Layer ending
pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv5, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='VALID', name='pool5')
print_activation (pool5)
return pool5, parameters
# 评估每轮的计算时间
# session是训练句柄,target是训练算子,info_string是测试名称
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
# 只考虑预热轮数10轮之后的时间
num_steps_burn_in = 10
# 总时间
total_duration = 0.0
# 平方和
total_duration_squared = 0.0
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target)
duration = time.time() - start_time
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' %
(datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
# 计算平均耗时mn 标准差sd
mn = total_duration / num_batches
vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' %
(datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))
# 主函数
def run_benchmark():
g = tf.Graph ()
# 定义默认Graph
with g.as_default():
# 构造随机数据
image_size = 224
images = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(
[batch_size, image_size, image_size, 3],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1 ))
pool5, parameters = inference(images)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
# 统计运行时间
time_tensorflow_run(sess, pool5, "Forward")
objective = tf.nn.l2_loss(pool5)
grad = tf.gradients(objective, parameters)
time_tensorflow_run(sess, grad, "Forward-backward")
# 执行主函数
run_benchmark()下面是我的运行结果:
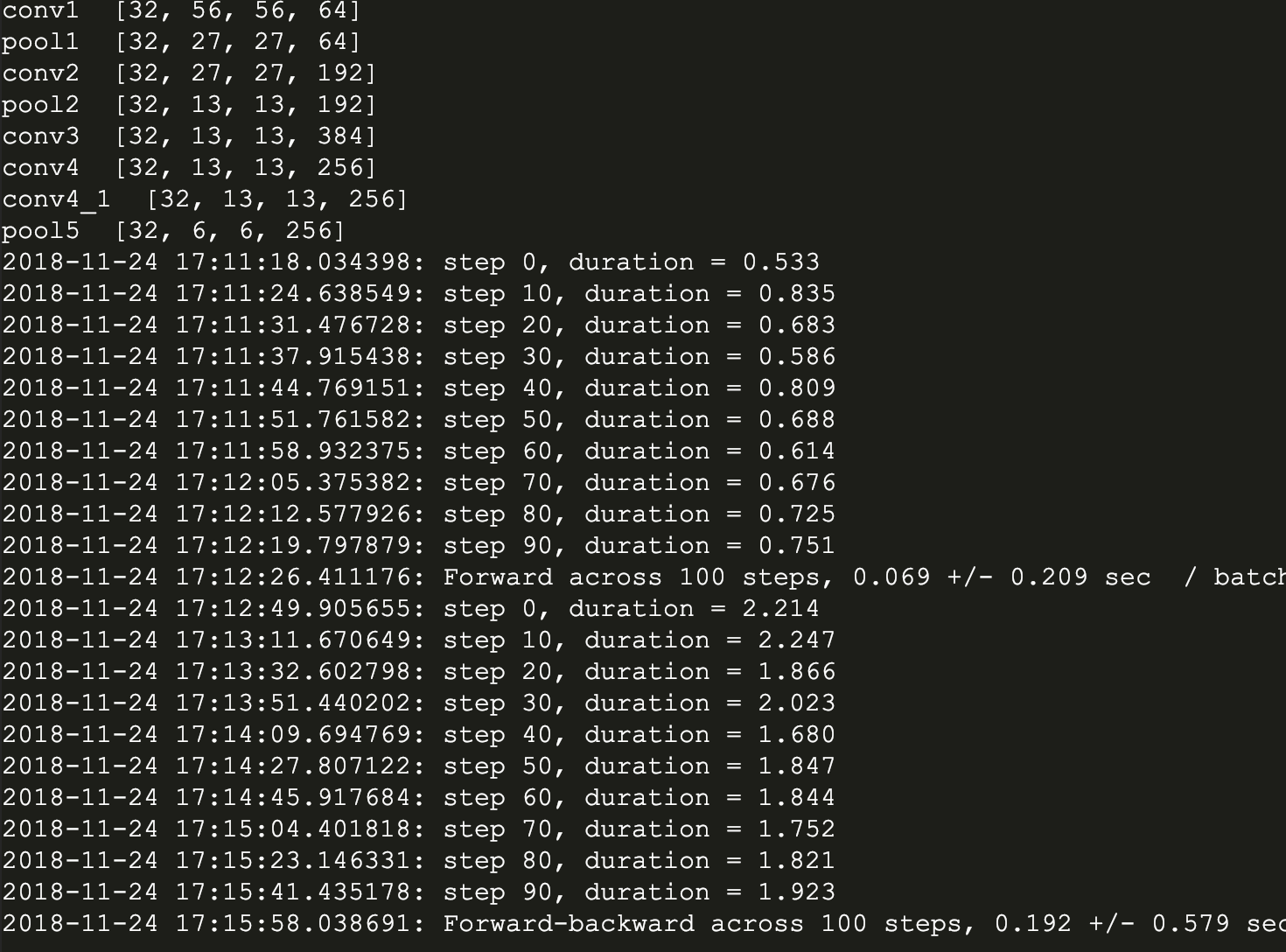
然后是不带LRN的版本:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2018/11/20 10:42
# @Author : Chen Cjv
# @Site : http://www.cnblogs.com/cjvae/
# @File : AlexNet.py
# @Software: PyCharm
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2'
from datetime import datetime
import math
import time
import tensorflow as tf
batch_size = 32
num_batches = 100
# 展示每一个卷积层或池化层输出的tensor的尺寸,接收一个tensor输入
def print_activation(t):
print(t.op.name, '', t.get_shape().as_list())
def inference(images):
# 训练的模型参数
parameters = []
# 1th CL starting
with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope:
# 截断正态分布初始化卷积核参数
# 卷积核尺寸11 x 11 颜色3通道 卷积核64
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([11, 11, 3, 64],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
# 实现卷积操作,步长4x4(在图像上每4x4区域取样一次,每次取样卷积核大小为11x11)
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 4, 4, 1], padding='SAME')
# 卷积偏置为0
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
# 将卷积结果与偏置相加
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
# 对结果非线性处理
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
# 输出conv1的信息
print_activation(conv1)
# 添加参数
parameters += [kernel, biases]
# 1th CL ending
# add 1th max-pooling layer starting
# 池化:尺寸3x3(将3x3的大小的像素块降为1x1 步长为2x2 VALID表示取样不超过边框)
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool (conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='VALID', name='pool1')
print_activation(pool1)
# add max-pooling layer ending
# designing second Convolutional Layer starting
with tf.name_scope('conv2') as scope:
# 不同第一卷积层,这层卷积核尺寸5x5,通道为上层输出通道数(即卷积核数)64
# 卷积核数量为192
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 64, 192],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
# 卷积步长为1,即扫描全部图像
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[192],
dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activation(conv2)
# designing 2th CL ending
# add 2th max-pooling layer starting
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool (conv2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='VALID', name='pool2')
print_activation(pool2)
# add 2th max-pooling layer ending
# designing 3th Convolutional Layer starting
with tf.name_scope('conv3') as scope:
# 卷积核尺寸3x3 通道数192 卷积核384
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 192, 384],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[384],
dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activation(conv3)
# designing 3th CL ending
# designing 4th CL starting
with tf.name_scope('conv4') as scope:
# 卷积核尺寸3x3 通道数384 卷积核降为256
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 384, 256],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv3, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256],
dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv4 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activation(conv4)
# designing fourth Convolutional Layer ending
# designing fifth Convolutional Layer starting
with tf.name_scope('conv4') as scope:
# 卷积核尺寸3x3 通道数256 卷积核256
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv4, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256],
dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv5 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activation(conv5)
# designing fifth Convolutional Layer ending
pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv5, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='VALID', name='pool5')
print_activation (pool5)
return pool5, parameters
# 评估每轮的计算时间
# session是训练句柄,target是训练算子,info_string是测试名称
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
# 只考虑预热轮数10轮之后的时间
num_steps_burn_in = 10
# 总时间
total_duration = 0.0
# 平方和
total_duration_squared = 0.0
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target)
duration = time.time() - start_time
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' %
(datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
# 计算平均耗时mn 标准差sd
mn = total_duration / num_batches
vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' %
(datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))
# 主函数
def run_benchmark():
g = tf.Graph ()
# 定义默认Graph
with g.as_default():
# 构造随机数据
image_size = 224
images = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(
[batch_size, image_size, image_size, 3],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1 ))
pool5, parameters = inference(images)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
# 统计运行时间
time_tensorflow_run(sess, pool5, "Forward")
objective = tf.nn.l2_loss(pool5)
grad = tf.gradients(objective, parameters)
time_tensorflow_run(sess, grad, "Forward-backward")
# 执行主函数
run_benchmark()运行结果:
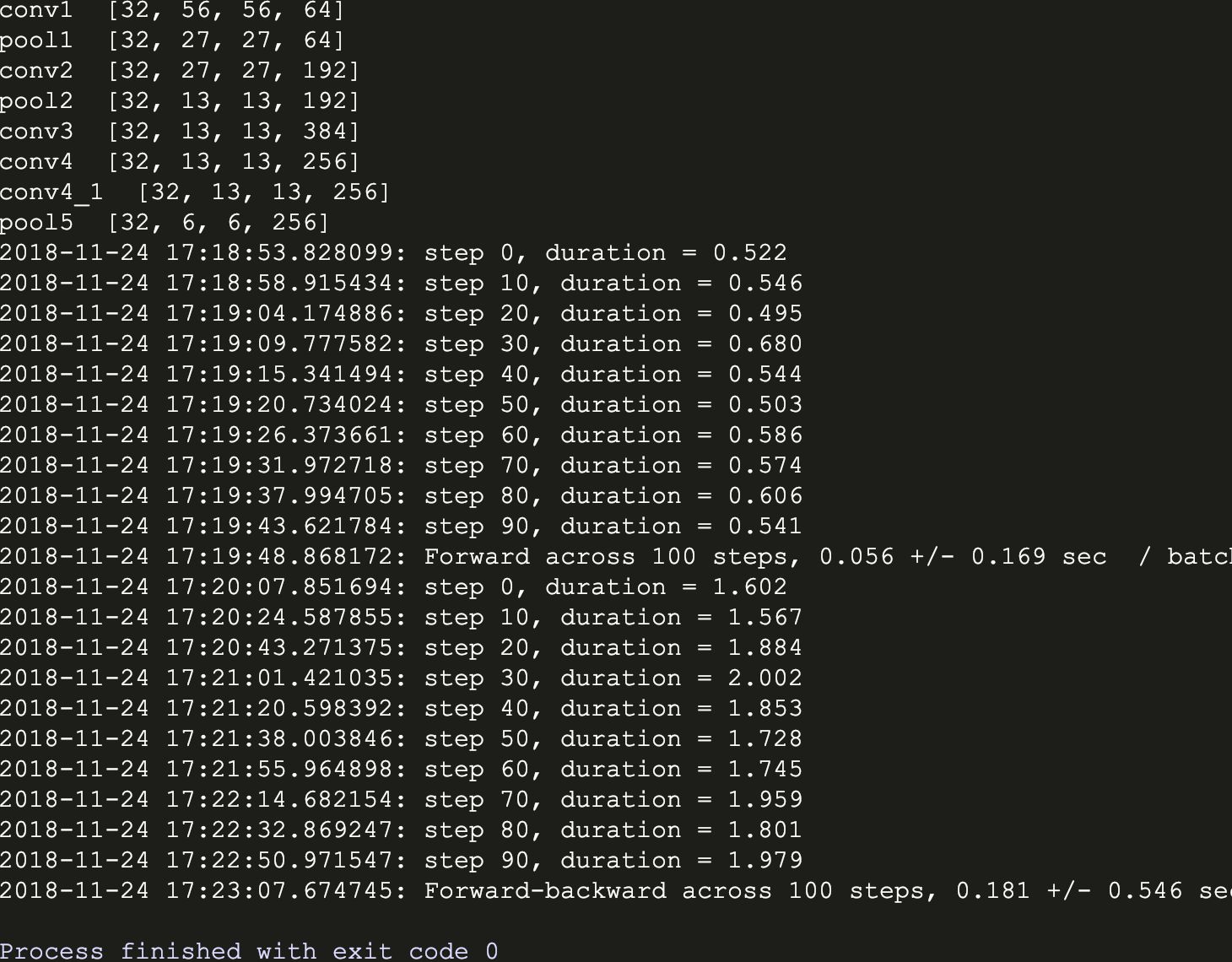
从两个版本可见,带有LRN层的AlexNet训练时间比较长,据说效果有待商榷。