版权声明: https://blog.csdn.net/shuiyixin/article/details/83246867
一、前言
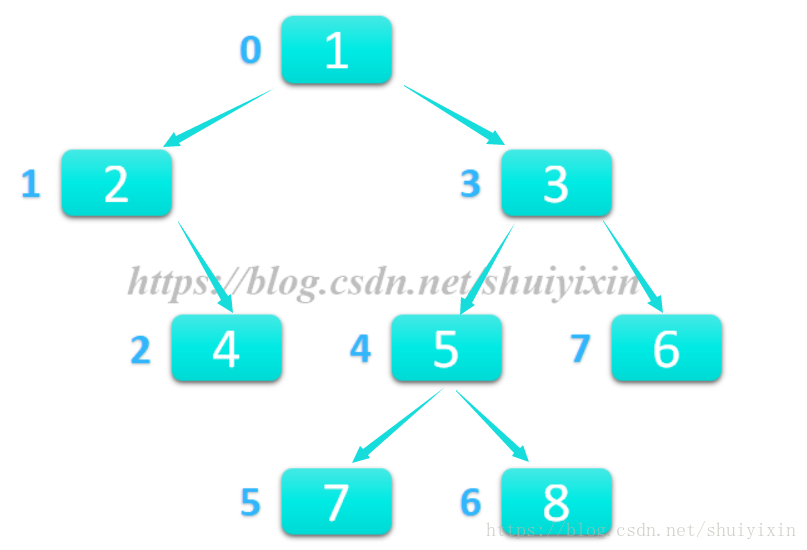
二叉树的遍历是比较多样化的遍历,有很多种遍历方式,先序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历,层次遍历等等。本次给大家讲的是层次遍历,为了方便,我将题目中的数据改为编号,从左往右,从上往下依次遍历。方便大家看到结果。
二、题目
将下图用二叉树存入,并通过层次遍历方式,自上而下,从左往右对该树进行遍历。其中圆角矩形内为结点数据,旁边数字为结点编号,编号为0的结点为根节点,箭头指向的结点为箭尾的孩子结点。要求遍历每个结点时能够查询当前结点的数据以及编号,如果结点是根节点或者叶子结点,请说明。
实现功能后,将层次遍历变换为:自下而上,从右往左对该树进行遍历。并将结果输出。
三、代码
#define MAXQUEUESIZE 10
#include<iostream>
#include<malloc.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct BiTNode {
int data,number;
struct BiTNode *lChild, *rChild,*parent;
}BiTNode,*BiTree;
typedef struct {
BiTree *qBase;
int front;
int rear;
}SqQueue;
typedef struct LNode{
BiTree data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkStack;
int InitQueue(SqQueue &SQ) {
SQ.qBase = (BiTree*)malloc(MAXQUEUESIZE * sizeof(SqQueue));
if (!SQ.qBase)
{
cout << "空间分配失败(Allocate space failure)" << endl;
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
SQ.front = SQ.rear = 0;
return 1;
}
int EnQueue(SqQueue &SQ, BiTree e) {
if ((SQ.rear+1)% MAXQUEUESIZE == SQ.front)
{
cout << "队列已满(The queue is full)" << endl;
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
SQ.qBase[SQ.rear] = e;
SQ.rear = (SQ.rear + 1) % MAXQUEUESIZE;
return 1;
}
int DeQueue(SqQueue &SQ, BiTree &e) {
if (SQ.rear == SQ.front)
{
cout << "队列已空(The queue is null)" << endl;
return 0;
}
e = SQ.qBase[SQ.front];
SQ.front = (SQ.front + 1) % MAXQUEUESIZE;
return 1;
}
int InitStack(LinkStack &S) {
S = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if (!S)
{
cout << "空间分配失败(Allocate space failure)" << endl;
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
S->next = NULL;
return 1;
}
int Push(LinkStack &S, BiTree e) {
LinkStack p = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if (!p)
{
cout << "结点分配失败(Allocate node failure)" << endl;
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
S->data = e;
p->next = S;
S = p;
return 1;
}
int Pop(LinkStack &S, BiTree &e) {
LinkStack p = S->next;
if (!p)
{
cout << "栈空(The stack is null)" << endl;
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
e = p->data;
S->next = p->next;
free(p);
return 1;
}
int number = 0;
int yon = 0;
int yesOrNo[] = { 1,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0 };
int numData[] = { 1,2,4,3,5,7,8,6 };
BiTree treeParent = NULL;
int OperationBiTree(BiTree &BT) {
BT = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
if (!BT)
{
cout << "空间分配失败" << endl;
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
BT->number = number;
number++;
BT->data = numData[BT->number];
BT->lChild = NULL;
BT->rChild = NULL;
BT->parent = treeParent;
return 1;
}
void PreOrderCreatBiTree(BiTree &BT) {
OperationBiTree(BT);
treeParent = BT;
if (yesOrNo[yon++])
PreOrderCreatBiTree(BT->lChild);
treeParent = BT;
if (yesOrNo[yon++])
PreOrderCreatBiTree(BT->rChild);
}
void VisitBiTree(BiTree BT) {
cout << "当前结点的编号为:" << BT->number << ", ";
cout << "数据为:" << BT->data << ",";
if (!BT->parent)
cout << "当前结点为根节点。";
if (!BT->lChild && !BT->rChild)
cout << "当前结点为叶子结点。";
cout << endl;
}
void LevelOrderBiTree(BiTree BT, LinkStack &S) {
SqQueue SQ;
InitQueue(SQ);
InitStack(S);
BiTree t = BT;
EnQueue(SQ, t);
while (SQ.rear != SQ.front)
{
DeQueue(SQ, t);
Push(S, t);
VisitBiTree(t);
if (t->lChild)
EnQueue(SQ, t->lChild);
if (t->rChild)
EnQueue(SQ, t->rChild);
}
}
void main() {
BiTree BT,t;
LinkStack S;
PreOrderCreatBiTree(BT);
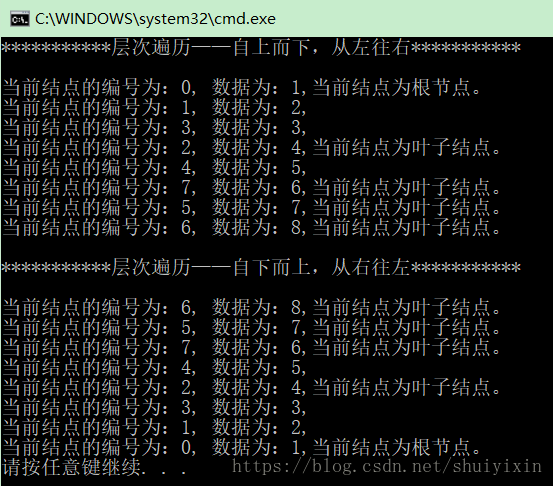
cout << "***********层次遍历——自上而下,从左往右***********\n\n";
LevelOrderBiTree(BT,S);
cout << "\n***********层次遍历——自下而上,从右往左***********\n\n";
while (S->next)
{
Pop(S, t);
VisitBiTree(t);
}
}