学习目标
1、掌握类与对象的基础概念,理解类与对象的关系;
2、掌握对象与对象变量的关系;
3、掌握预定义类的基本使用方法,熟悉Math类、String类、math类、Scanner类、LocalDate类的常用API;
4、掌握用户自定义类的语法规则,包括实例域、静态域、构造器方法、更改器方法、访问器方法、静态方法、main方法、方法参数的定义要求;(重点、难点)
5、掌握对象的构造方法、定义方法及使用要求;(重点)
6、理解重载概念及用法;
7、掌握包的概念及用法;
8、了解文档注释技术;
一、 理论学习部分目的与要求
1、类与对象的基础概念
类:对具有相同属性和方法的一类事物的抽象。
对象:具体的某一事物,代表自身的一些属性和方法。
类(对象)之间的关系:类是一种抽象的概念集合,是最基础的组织单位,作为对象的模板、合约或蓝图。类是对象的类型,使用一个通用类可以定义同一类型的对象,类中定义对象的数据域是什么以及方法是做什么的。
关联(组合、聚合),继承,依赖、实现。
2、使用预定义类
(1)在java程序设计语言中,使用构造器构造新事例。构造器是一种特殊的方法,用来构造并初始化对象。
(2)更改器前缀为set;访问器前缀为get;
(3)构造器和类有相同的名字
3、用户自定义类
(1)Employee类
(2)隐式参数与显式参数
4、静态域与静态方法
(1)静态域: 如果将静态域定义为static ,那么每个类中只有一个这样的域,而每一个对象对于所有的实例域都有自己的一份拷贝本。
(2静态常量 :静态变量使用的比较少,但是静态常量却使用的比较多 。
(3)静态方法 : 静态方法是一种不能由对象操作的方法, 例如Math类中的求取一个数的次方的pow()方法就是一个静态方法。表达式是: Math.pow(x, a),在运算时,不使用任何Math对象,换句话说,没有隐式的参数。可以认为静态方法是没有this参数的方法(在一个非静态的方法中,this参数表示这个方法的隐式参数)
(4)main方法:我们学习java的时候,程序中大多会有一个main 方法,我们都称作程序的入口,main方法不对任何对象进行操作,事实上,在启动程序的时候,还没有任何一个对象,静态的main方法将执行并创建程序所需的对象。
5、方法参数
6、对象构造
7、包
Java允许把一个或多个类收集在一起成为一组,称作包,以便于组织任务,标准Java库分为许多包.java.langjava.utiljava,net等,包是分层次的所有的java包都在java和javax包层次内。
8、类路径
9、文档注释
10、类设计技巧
二、实验学习部分目的与要求
(1) 理解用户自定义类的定义;
(2) 掌握对象的声明;
(3) 学会使用构造函数初始化对象;
(4) 使用类属性与方法的使用掌握使用;
(5) 掌握package和import语句的用途。
实验内容和步骤
实验1 测试以下程序,掌握文件输入输出程序设计技术(文件输入输出,教材61-62)。
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class FileWriteReadTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ //写入文件演示 PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter("myfile.txt"); out.println("姓名 高数 Java 数据结构 平均成绩 总成绩"); out.println("张三 20 30 40 0 0"); out.println("李四 50 60 70 0 0"); out.close();//输出完毕,需要close //读入文件演示 Scanner in = new Scanner(new File("myfile.txt"));//为myfile.txt这个File创建一个扫描器in int number = 1;//行号 System.out.println(in.nextLine()); while(in.hasNextLine()){//判断扫描器是否还有下一行未读取,该循环把文件的每一行都读出 String line = in.nextLine();//读出myfile.txt的下一行 System.out.print("第"+(++number)+"行的内容: "); Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(line);//行内容建立扫描器 linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");//使用空格作为分隔符 String name = linescanner.next(); String math = linescanner.next(); String java = linescanner.next(); String ds = linescanner.next(); String avg = linescanner.next(); String total = linescanner.next(); System.out.println("name="+name+" math="+math+" java="+java+" ds="+ds+" avg"+avg+" total="+total); } in.close();//读入完毕,最后需要对其进行close。 } }
结果如下:

测试程序1:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-2(教材104页);
l 结合程序运行结果,掌握类的定义与类对象的用法,并在程序代码中添加类与对象知识应用的注释;
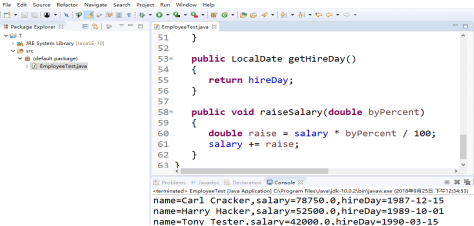
l 尝试在项目中编辑两个类文件(Employee.java、 EmployeeTest.java ),编译并运行程序。
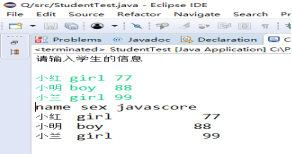
l 参考教材104页EmployeeTest.java,设计StudentTest.java,定义Student类,包含name(姓名)、sex(性别)、javascore(java成绩)三个字段,编写程序,从键盘输入学生人数,输入学生信息,并按以下表头输出学生信息表:
姓名 性别 java成绩
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; public class StudentTest { @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { Student[] staff = new Student[3]; System.out.println("请输入学生的信息"); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); for(int i=0;i<staff.length;i++) { staff[i]=new Student(in.next(),in.next(),in.nextInt()); } System.out.println("name"+" "+"sex"+" "+"javascore"); for (Student e : staff) System.out.println(e.getName() +" "+e.getSex()+" "+e.getJavaScore()); } } class Student { private String name; private String sex; private int javascore; public Student(String n, String s, int j) { name = n; sex = s; javascore =j; } public String getName() { return name; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public int getJavaScore() { return javascore; } }
结果如下:
测试程序2:
1、编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-3(教材116);
2、结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握静态域(netxtId)与静态方法(getNextId)的用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
3、理解Java单元(类)测试的技巧
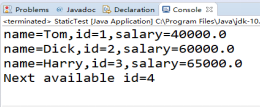
/** * This program demonstrates static methods. * @version 1.01 2004-02-19 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class StaticTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array with three Employee objects Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; staff[0] = new Employee("Tom", 40000); staff[1] = new Employee("Dick", 60000); staff[2] = new Employee("Harry", 65000); // print out information about all Employee objects for (Employee e : staff) { e.setId(); System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",id=" + e.getId() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary()); } int n = Employee.getNextId(); // calls static method System.out.println("Next available id=" + n); } } class Employee { private static int nextId = 1; private String name; private double salary; private int id; public Employee(String n, double s) { name = n; salary = s; id = 0; } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId() { id = nextId; // set id to next available id nextId++; } public static int getNextId() { return nextId; // returns static field } public static void main(String[] args) // unit test { Employee e = new Employee("Harry", 50000); System.out.println(e.getName() + " " + e.getSalary()); } }
结果如下:
测试程序3:
1、编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-4(教材121);
2、结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握掌握Java方法参数的用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
代码如下:
/** * This program demonstrates parameter passing in Java. * @version 1.00 2000-01-27 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ParamTest { public static void main(String[] args) { /* * Test 1: Methods can't modify numeric parameters */ System.out.println("Testing tripleValue:"); double percent = 10; System.out.println("Before: percent=" + percent); tripleValue(percent); System.out.println("After: percent=" + percent); /* * Test 2: Methods can change the state of object parameters */ System.out.println("\nTesting tripleSalary:"); Employee harry = new Employee("Harry", 50000); System.out.println("Before: salary=" + harry.getSalary()); tripleSalary(harry); System.out.println("After: salary=" + harry.getSalary()); /* * Test 3: Methods can't attach new objects to object parameters */ System.out.println("\nTesting swap:"); Employee a = new Employee("Alice", 70000); Employee b = new Employee("Bob", 60000); System.out.println("Before: a=" + a.getName()); System.out.println("Before: b=" + b.getName()); swap(a, b); System.out.println("After: a=" + a.getName()); System.out.println("After: b=" + b.getName()); } public static void tripleValue(double x) // doesn't work { x = 3 * x; System.out.println("End of method: x=" + x); } public static void tripleSalary(Employee x) // works { x.raiseSalary(200); System.out.println("End of method: salary=" + x.getSalary()); } public static void swap(Employee x, Employee y) { Employee temp = x; x = y; y = temp; System.out.println("End of method: x=" + x.getName()); System.out.println("End of method: y=" + y.getName()); } } class Employee // simplified Employee class { private String name; private double salary; public Employee(String n, double s) { name = n; salary = s; } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
结果如下:

测试程序4:
1、编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-5(教材129);
2、结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java用户自定义类的用法,掌握对象构造方法及对象使用方法,在相关代码后添加注释。
import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates object construction. * @version 1.01 2004-02-19 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ConstructorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array with three Employee objects Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; staff[0] = new Employee("Harry", 40000); staff[1] = new Employee(60000); staff[2] = new Employee(); // print out information about all Employee objects for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",id=" + e.getId() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary()); } } class Employee { private static int nextId; private int id; private String name = ""; // instance field initialization private double salary; // static initialization block static { Random generator = new Random(); // set nextId to a random number between 0 and 9999 nextId = generator.nextInt(10000); } // object initialization block { id = nextId; nextId++; } // three overloaded constructors public Employee(String n, double s) { name = n; salary = s; } public Employee(double s) { // calls the Employee(String, double) constructor this("Employee #" + nextId, s); } // the default constructor public Employee() { // name initialized to ""--see above // salary not explicitly set--initialized to 0 // id initialized in initialization block } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public int getId() { return id; } }
结果如下:

测试程序5:
1、编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-6、4-7(教材135);
2、结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java包的定义及用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
import com.horstmann.corejava.*; // the Employee class is defined in that package import static java.lang.System.*; /** * This program demonstrates the use of packages. * @version 1.11 2004-02-19 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PackageTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // because of the import statement, we don't have to use // com.horstmann.corejava.Employee here Employee harry = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); harry.raiseSalary(5); // because of the static import statement, we don't have to use System.out here out.println("name=" + harry.getName() + ",salary=" + harry.getSalary()); } }
结果如下:

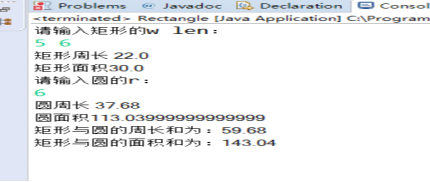
实验3:编写长方形类Rectangle与圆形类Circle,其中Rectangle类设置私有属性:width,length;Circle类设置私有属性radius。编写Rectangle类的带参构造函数Rectangle(int width,int length), Circle类的带参构造函数Circle(int radius),编写两个类的toString方法(Eclipse可自动生成)。上述2个类均定义以下方法:
求面积的方法public int getArea()
在main方法中完成以下任务:
(1) 输入1行长与宽,创建一个Rectangle对象;
(2) 输入1行半径,创建一个Circle对象;
将两个对象的周长加总输出,将两个对象的面积加总输出
import java.util.Scanner; public class Rectangle {// 创建一个Rectangle类 double width, length; static double A; double B; Rectangle(double x) { // 把两个变量初始化为相同传入值 width = x; length = x; } Rectangle(double w, double len) { // 分别对两个变量初始化不同的值 width = w; length= len; } public double BRectangle() { B= (width + length) * 2; return B;} public double ARectangle() { A= width * length; return A;} public static void main(String[] args) { // 声明对象和创建对象double @SuppressWarnings("resource") Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入矩形的w, len:"); int w = sc.nextInt(); int len = sc.nextInt(); double c,s;Rectangle Rectangle1 = new Rectangle(5, 6);Rectangle Rectangle2 = new Rectangle(8); c= Rectangle1.BRectangle(); s= Rectangle2.ARectangle(); System.out.println("周长是:"+ c); System.out.println("面积是:"+ s); System.out.println("矩形与圆的周长和为:"+c); } } class Perimeter{ public static double getPerimeter(double width, double height) { return 2*(width + height); } public static double getPerimeter(int r) { return 2*3.14*r; } }
实验总结:本周我们学习了一部分对象和类的知识,这次实验大多以解读代码和在已有代码上仿照编写程序为主,锻炼了我们的解读代码能力,感觉在理论知识的基础上,还得动手多练习,才有可能真正掌握书里说的内容,总得来说,还是得私底下多学java,多实践,多学习。