transfer_learning.py代码如下
#coding=utf8 import os import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import csv from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer from tensorflow_vgg import vgg16 from tensorflow_vgg import utils data_dir = 'flower_photos/' contents = os.listdir(data_dir) classes = [each for each in contents if os.path.isdir(data_dir + each)] # 首先设置计算batch的值,如果运算平台的内存越大,这个值可以设置得越高 batch_size = 10 # 用codes_list来存储特征值 codes_list = [] # 用labels来存储花的类别 labels = [] # batch数组用来临时存储图片数据 batch = [] codes = None with tf.Session() as sess: # 构建VGG16模型对象 vgg = vgg16.Vgg16() input_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 224, 224, 3]) with tf.name_scope("content_vgg"): # 载入VGG16模型 vgg.build(input_) # 对每个不同种类的花分别用VGG16计算特征值 for each in classes: print("Starting {} images".format(each)) class_path = data_dir + each files = os.listdir(class_path) for ii, file in enumerate(files, 1): # 载入图片并放入batch数组中 img = utils.load_image(os.path.join(class_path, file)) batch.append(img.reshape((1, 224, 224, 3))) labels.append(each) # 如果图片数量到了batch_size则开始具体的运算 if ii % batch_size == 0 or ii == len(files): images = np.concatenate(batch) feed_dict = {input_: images} # 计算特征值 codes_batch = sess.run(vgg.relu6, feed_dict=feed_dict) # 将结果放入到codes数组中 if codes is None: codes = codes_batch else: codes = np.concatenate((codes, codes_batch)) # 清空数组准备下一个batch的计算 batch = [] print('{} images processed'.format(ii)) with open('codes', 'w') as f: codes.tofile(f) with open('labels', 'w') as f: writer = csv.writer(f, delimiter='\n') writer.writerow(labels)
training.py代码如下
#coding=utf8 import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedShuffleSplit codes = [] labels = [] codes = np.fromfile("codes", dtype=np.int32) codes.shape = 3670, -1 print len(codes) with open('labels', 'r') as f: for line in f: line = line.strip() labels.append(line) print len(labels) lb = LabelBinarizer() lb.fit(labels) labels_vecs = lb.transform(labels) ss = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=1, test_size=0.2) train_idx, val_idx = next(ss.split(codes, labels)) half_val_len = int(len(val_idx)/2) val_idx, test_idx = val_idx[:half_val_len], val_idx[half_val_len:] train_x, train_y = codes[train_idx], labels_vecs[train_idx] val_x, val_y = codes[val_idx], labels_vecs[val_idx] test_x, test_y = codes[test_idx], labels_vecs[test_idx] print("Train shapes (x, y):", train_x.shape, train_y.shape) print("Validation shapes (x, y):", val_x.shape, val_y.shape) print("Test shapes (x, y):", test_x.shape, test_y.shape) # 输入数据的维度 inputs_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, codes.shape[1]]) # 标签数据的维度 labels_ = tf.placeholder(tf.int64, shape=[None, labels_vecs.shape[1]]) # 加入一个256维的全连接的层 fc = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(inputs_, 256) # 加入一个5维的全连接层 logits = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(fc, labels_vecs.shape[1], activation_fn=None) # 计算cross entropy值 cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels_, logits=logits) # 计算损失函数 cost = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy) # 采用用得最广泛的AdamOptimizer优化器 optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer().minimize(cost) # 得到最后的预测分布 predicted = tf.nn.softmax(logits) # 计算准确度 correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(predicted, 1), tf.argmax(labels_, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32)) def get_batches(x, y, n_batches=10): """ 这是一个生成器函数,按照n_batches的大小将数据划分了小块 """ batch_size = len(x)//n_batches for ii in range(0, n_batches*batch_size, batch_size): # 如果不是最后一个batch,那么这个batch中应该有batch_size个数据 if ii != (n_batches-1)*batch_size: X, Y = x[ii: ii+batch_size], y[ii: ii+batch_size] # 否则的话,那剩余的不够batch_size的数据都凑入到一个batch中 else: X, Y = x[ii:], y[ii:] # 生成器语法,返回X和Y yield X, Y # 运行多少轮次 epochs = 20 # 统计训练效果的频率 iteration = 0 # 保存模型的保存器 saver = tf.train.Saver() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for e in range(epochs): for x, y in get_batches(train_x, train_y): feed = {inputs_: x, labels_: y} # 训练模型 loss, _ = sess.run([cost, optimizer], feed_dict=feed) print("Epoch: {}/{}".format(e+1, epochs), "Iteration: {}".format(iteration), "Training loss: {:.5f}".format(loss)) iteration += 1 if iteration % 5 == 0: feed = {inputs_: val_x, labels_: val_y} val_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict=feed) # 输出用验证机验证训练进度 print("Epoch: {}/{}".format(e, epochs), "Iteration: {}".format(iteration), "Validation Acc: {:.4f}".format(val_acc)) # 保存模型 saver.save(sess, "checkpoints/flowers.ckpt") with tf.Session() as sess: saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint('checkpoints')) feed = {inputs_: test_x, labels_: test_y} test_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict=feed) print("Test accuracy: {:.4f}".format(test_acc))
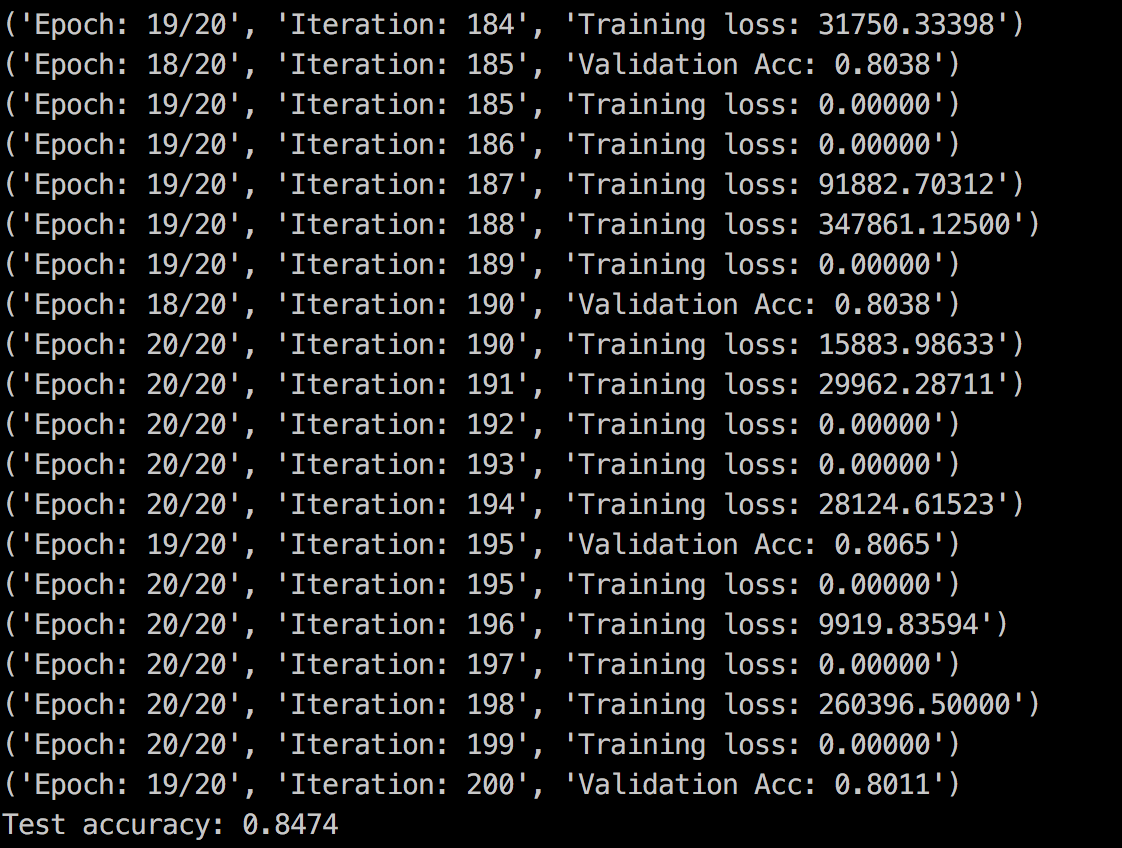
结果: